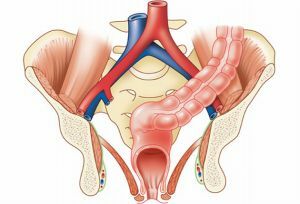
 Rectal prolapse is a very serious and unpleasant pathological condition, characterized by the exit of the rectum beyond the anus.
Rectal prolapse is a very serious and unpleasant pathological condition, characterized by the exit of the rectum beyond the anus.
The disease can affect both adults and children, it is quite difficult. But, despite the severe course of the disease, pathology does not threaten health, however, it causes a lot of inconvenience and trouble for the patient, especially if it concerns the child.
Contents
- Features of the pathology of
- Reasons for provoking the disease
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnosis and examination
- What kind of help will the child have?
- Preventive measures
Features of pathology
Rectal prolapse occurs in children much more often than in adults. For the most part, children from 1 to 4 years old suffer from this ailment, in boys pathology is diagnosed 3 times more often than in girls.
The essence of the disease lies in the fact that the walls of the distal part of the colon are displaced and fall through the anus. Many experts refer to this condition of hernia perineum.
In many cases, this symptom arises in connection with the anatomical features of the child's body. This is a weak physical development, the curvature of the sacrococcygeal department, the absence of sagittal flexures of the rectum, etc.
Very young children have not yet formed the necessary inclination of the pelvis, and the bowel has a rectilinear shape, it also significantly contributes to its prolapse.
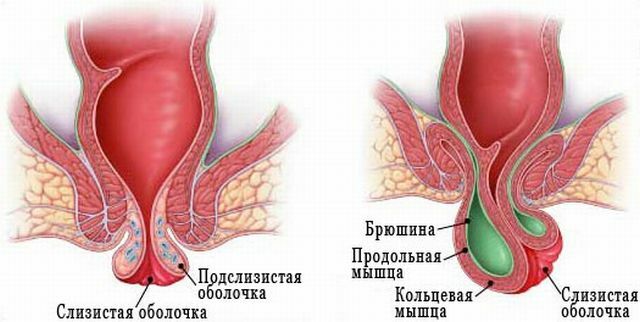
Children, as well as adults, have a partial and complete prolapse of the rectal mucosa. At partial - there is an abaissement only mucous membrane. But, if immediately, do not prevent this condition, then diagnose complete prolapse of the intestine.
When it is left unprotected for a long time, it can cause serious complications to the child. Typically, the fallout occurs immediately after emptying or excessive attempts, sometimes it can happen with a strong cry, crying.
Causes of disease
It is impossible to single out one underlying factor contributing to prolapse of the rectum, often several unfavorable circumstances can influence the appearance of the disease, the main ones are:
- Frequent constipation of is the main cause of rectal prolapse in a child. In a situation where he does not use the required amount of fluid and constantly presses, sitting on a pot, intra-abdominal pressure rises, muscles stretch. After a while they cease to hold the rectum, there is a fallout. Therefore, it is very important to limit the child's stay on the pot and control food.
- No less common cause of the disease are diarrhea .Often some intestinal infections, dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis, dyspepsia further exacerbate the situation.
- Rectal prolapse can also be caused by by a violation of the intestinal patency of the due to various diseases.
- Congenital bowel disease often provokes this pathology.
- In addition, the development of the disease in children hemorrhoids, various kinds of tumors, fistulas and polyps in the rectum affect the development of the disease.
- Constant screaming, crying or a prolonged severe cough increases intra-abdominal pressure, which can also lead to the prolapse of the rectum in the baby.
- In infants, this symptom develops against a background of frequent intestinal colic and with prolonged constipation of caused by malnutrition.
Features of the clinical picture
The most common complaints in the occurrence of the disease can be pain in the lower abdomen, a sensation of a foreign object in the anus, mucosal discharge. Violations of the stool, with time constipation can be replaced by diarrhea.
 For young children, the most characteristic manifestation of the disease is the protrusion of the rectum after defecation.
For young children, the most characteristic manifestation of the disease is the protrusion of the rectum after defecation.
Thus the dropped out site can reach the different sizes. Often this may be the only and main manifestation of prolapse.
In this case, rectification of the gut can occur without interference from the side. With a prolonged course of the disease, the child has constant pain, fecal incontinence, mucosal damage occurs.
In older children, gait may change, sleep is disturbed, food refusal occurs. There are various kinds of complications.
Diagnosis and inspection
As a rule, rectal prolapse in children is easy to diagnose. When you look at the visible part of the intestine, especially when straining.
If necessary, the specialist with palpation can investigate the state of the intestinal walls, their elasticity, muscle tone, etc.
Additional methods in this situation are sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, helping to establish the cause of the pathology.
Based on this survey, specialists establish an accurate diagnosis, which makes it possible to determine the correct treatment.
What kind of help will the child have?
Treatment of children diagnosed with prolapse of the rectum requires a special approach, using the least traumatic methods.
The main goal of therapy is to establish the cause of the disorder, and also to normalize the function of the rectum and prevent the further development of the disease.
Basically, the therapy of this condition in a child is carried out conservatively or using a sclerosing treatment technique, and is characterized by a fairly long course.
Often experts try to avoid surgical intervention and resort to its help only in extreme cases. 
The conservative method of treatment is aimed at restoring intestinal function, normalizing the stool and selecting a proper diet.
Therefore, doctors individually select food for each child, prescribe drugs that restore the rectal mucosa.
Besides this, an important task that costs considerable efforts from parents is to teach the child to defecate lying on its side. If you follow the above rules, after a few months the muscle structure is strengthened and this condition is eliminated.
The method of sclerosing therapy for the treatment of children is used with extreme caution, since it consists of painful injections that are injected into the cellulose surrounding the rectum.
This technique leads to scarring, and then to sclerosing tissues, which makes it possible to thoroughly fix the rectum. Depending on the child's condition, development of the disease and examination, the specialist decides how to properly help the child.
If the right time does not seek medical help and start the disease, the child can develop various kinds of complications.
Most often they appear as an inflammatory process in the rectum, and infringements and necrosis of the fallen part of the mucosa are also possible.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to observe some preventive measures: 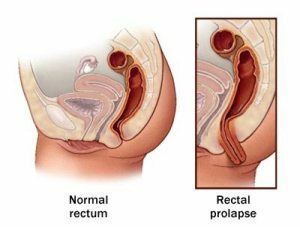
- normalize food and drinking regimen;
- to treat dysbacteriosis in a timely manner;
- do not allow prolonged constipation;
- to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor;
- to engage in special therapeutic exercise.
Rectal prolapse in children is quite an unpleasant disease, but if the treatment is started in time, the situation can be quickly corrected.
