 Sometimes anal fissure seems to be a minor disease, so not all people recognize it.
Sometimes anal fissure seems to be a minor disease, so not all people recognize it.
But the timely access to a specialist and the use of appropriate treatment will help to quickly normalize the condition.
Basically this disease is characterized by constipation, it can appear in women, men, children.
Usually, a crack is localized on the back wall of the anal opening, the mucosa of which is more susceptible to the phenomenon.
An anal sharp crack( recently appeared) is represented by a hole with smooth edges, along the edges and on the bottom of which gradual granulation appears( red-colored cloth with a granular surface).
A sharp crack in the anus occurs suddenly when the mucosa breaks. The main reasons for its appearance include dense feces.
Contents
- What is the difference between an acute and a chronic crack?
- What causes trouble?
- Clinical picture
- Diagnostic methods
- Main goals and methods of treatment
- Possible complications
- Preventive measures
What is the difference between acute and chronic fracture?
In general, the acute form of the disease does not last long, it is characterized by standard pain in the rectal area.
With timely detection and proper treatment, an acute crack is eliminated. In the absence of suitable therapy, there is a complication of mucosal lesions and the transition of the acute form to a chronic one.
In general, the chronic fissure of the anus is characterized by complications with the formation of a "watchdog", sealing the edges of the wound.
What causes trouble?
There are several reasons for the appearance of an acute anal fissure, which are divided into the following categories: 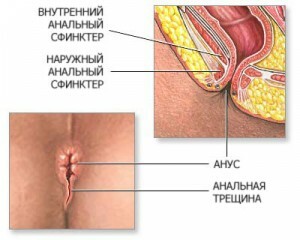
- Neuro-reflector .Neuro-reflex factor of appearance of anal fissures is characterized by inflammation of nerves located in the anus.
- Infectious .The infectious factor is characterized by the appearance of inflammation and infections that appear in the glands and mucosa. With chronic inflammation, less scar tissue forms on which cracks can appear.
- Mechanical. It is the mechanical factors that directly affect the mucosa, damaging it. This action is different feces, which contain solid components( seeds, bone fragments, fruits and vegetables), which, when moving, damage the intestinal walls and form cracks. It also damages the mucous thick feces that form with constipation.
The main causes of the appearance of a defect are:
- stool disorder( diarrhea or constipation);
- heavy physical work, loads;
- anal intercourse;
- childbirth;
- use of invasive methods of research( ultrasound, endoscopy);
- wrong enema setting.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of the appearance of an acute anal fissure are similar to the chronic form. Their main difference is the duration.
The main signs of the disease include:
- spasms in the anal sphincter;
- pain and itching in the anus and rectum;
- appearance of blood from the anus( when passing dense masses).
Itching in the anal area can be enhanced by running, jumping, walking or prolonged sitting.
Acute cracks in the anus are common in children, their main cause being constipation. Cracks are characterized by pain. But they quickly pass.
There is also a violation in pregnant women, who in early stages are similar to hemorrhoids. The main treatment is aimed at softening the stool and eliminating constipation.
At occurrence of any sign of disease, the patient should address to the expert for consultation and in due time to eliminate this phenomenon.
Diagnostic methods
 The doctor reveals an anal fissure when examining the anus by diluting the buttocks. Sometimes finger examination can be performed, which reveals a spasm of the sphincter.
The doctor reveals an anal fissure when examining the anus by diluting the buttocks. Sometimes finger examination can be performed, which reveals a spasm of the sphincter.
With expressed spasms and pains, instrumental examination( sigmoidoscopy, anoscopy) is not carried out. Exceptions are indications for purulent complications, tumors, paraproctitis, severe bleeding.
Diagnostics allows distinguishing a crack from a fistula, infections and other diseases.
Main goals and methods of treatment
The primary goal of treating an acute anal fissure is to eliminate pain and spasms of the sphincter. It also requires healing of injuries and normalization of the stool.
Now there is a wide variety of therapeutic methods, which are divided into the following types:
- conservative;
- non-surgical active;
- combined methods.
The choice of method depends on the condition of the body, the duration of the disease, the presence of complications. But it is necessary to comply with hygiene and diet.
In acute anal fissures, conservative treatment is usually prescribed, including changes in the diet, use of 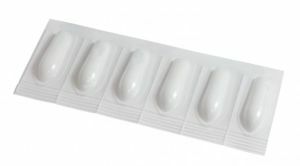 suppositories, ointments, stools, sessile trays with potassium permanganate, enemas.
suppositories, ointments, stools, sessile trays with potassium permanganate, enemas.
Non-surgical active methods are also used. Surgical treatment is used only to eliminate chronic anal fissures.
The diet should include a sufficient amount of plant fiber. This contributes to the softening of stool.
The menu excludes refined foods, spicy, salted and fried foods. Be sure to add to the diet of salads, cereals, fruits, prunes, dried apricots, figs, boiled beets with butter. The patient should drink plenty of fluids per day.
Hygienic measures for the prevention and treatment of injuries include:
- use of enemas;
- washing with cold water after emptying and draining the anal passage with a soft cloth.
The course of treatment with enemas is 14 days. The course is aimed at the appearance of regular urges to emptying, softening and fragmentation of primary dense feces.
An oily or water enema with the addition of astringent, hemostatic, disinfectant and anti-inflammatory components can be used.
Conservative therapy has the following methods:
- physiotherapy( UHF, darsonvalization, diathermy);
- conducting thermal procedures;
- relieve pain with antispasmodics;
- moxibustion with silver nitrate, carbolic acid or iodine;
- ointments, lotions or compresses.
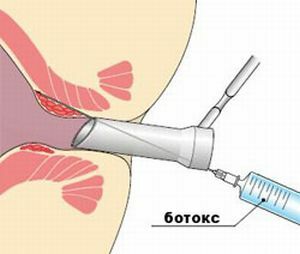
Active non-surgical methods include:
- sphincter ring sprain;
- pain relief with anesthesia( oil, novocaine).
Also prescribed maintenance therapy with medications that relax the sphincter, contributing to the healing of the wound and the removal of pain.
Botox injections are a good effect.
Possible complications of
It should be understood that the development of the disorder is associated with a risk of the following complications: 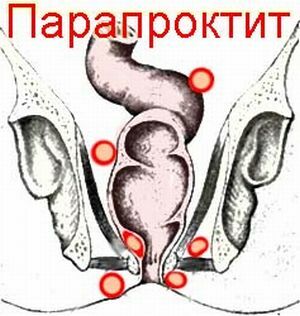
- with acute paraproctitis, the disease manifests itself when an infection enters the damaged fatty tissue located in the anal passage region;
- marked pain, which develop with severe spasm of the sphincter;
- colitis, with this damage the inner shell of the large intestine, and inflammation;
- with strong blood secretions;
- by prostatitis( inflammation of the prostate);
- with fistula in the anus.
Preventive measures
To preventive maintenance carry an active way of life, a correct delivery, in due time therapy of the diseases connected with disturbances of a chair.
To avoid stagnation in the pelvic area, physical exercise, walking, constant walking are recommended.
Timely detected and cured anal fissure is eliminated completely in 60-90 percent of cases. During self-treatment, postponement or incorrect therapy, acute forms of the disorder become chronic, which may require surgical intervention.
