 In modern dentistry more and more additional methods of research are used. Radiography and computed tomography are a prerequisite for a correct diagnosis. Unfortunately, they can not always give a complete picture of the disease.
In modern dentistry more and more additional methods of research are used. Radiography and computed tomography are a prerequisite for a correct diagnosis. Unfortunately, they can not always give a complete picture of the disease.
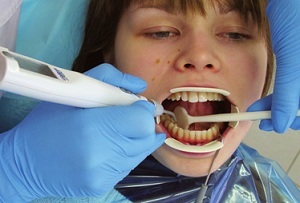
In Soviet times, when such studies were unavailable, no less informative methods were used. One of these is electro-odontometry( EOM).
Electrodontiagnosis( EDI) is a research method by which it is possible to assess the viability of a tooth pulp in case of traumatic injury, neoplasm, inflammation or any other disease of the teeth and jaws. As a result, the physician can choose the most rational method of treatment and evaluate the results of the therapy.
Contents
- How does it work?
- Indications for EDI
- Restrictions on the use of this technique
- Diagnostic procedure
- Used equipment
- Difficulties during the research
- Decoding of indicators
- Cost of the study
How does it work?
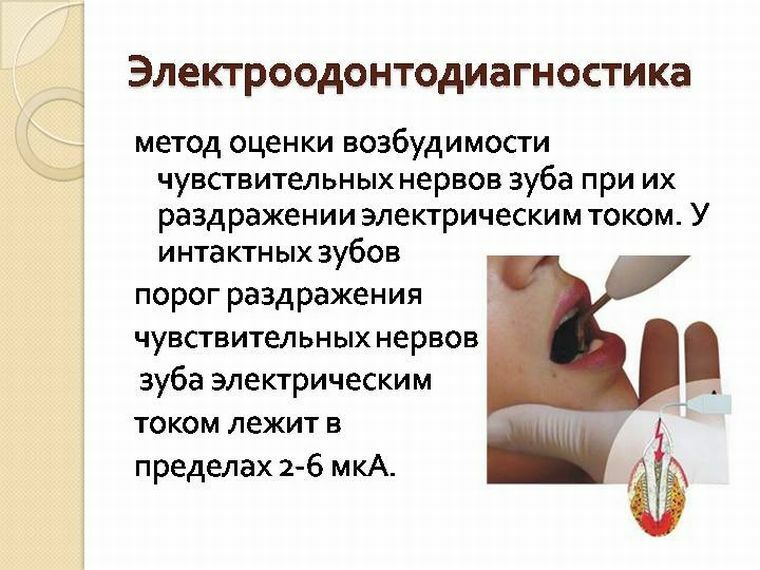
The method of electrodontodiagnostics is based on the ability of living tissues to be excited by the stimulus. The same tissue, depending on its functional state at the time of examination, has a different excitability. Conclusions about the degree of excitability are made on the basis of the strength of the stimulus, sufficient to obtain a response from the tissues. For this purpose, the minimum intensity of stimulation is revealed.
In the case of a decrease in excitability, the answer arises only when the intensity of the acting stimulus increases. When you raise the other way around, you need less influence to stimulate the tissues.
Electrodes for carrying out EDI
Electric current refers to one of the most effective and accessible pathogens. The time of its action can be changed, and the irritation can be repeated several times without harm to the tissue.
The electrical conductivity in the tissues of the tooth is affected by the amount of water. The larger the number, the higher the number of ions capable of responding to current. The pulp of the tooth contains a larger volume of liquid than in the enamel, therefore, during the study, special sensitive points were identified that correspond to the minimum distance to the pulp chamber.
The aim of the study is to determine if a tooth can be cured.
Indications for EDI
Electroodontometry in modern dentistry is used in the following cases:
- differential diagnosis of depth of carious lesion;
- differential diagnosis of pulpal lesions( pulpitis diagnosis);
- diagnosis of periodontitis;
- revealing a cyst on the roots of the tooth;
- traumatic injury to the jaws and teeth;
- Inflammation of the maxillary sinus;
- osteomyelitis;
- actinomycosis;
- tumors of the jaws of various etiologies;
- neuritis and neuralgia;
- radiation injury;
- treatment with orthodontic devices.
Restrictions on the use of this technique
Contraindications to the use of electrodontometry are divided into absolute and relative.
The study will be completely ruled out when: the
- patient has a pacemaker;
- there are psychiatric disorders;
- it is impossible to effectively dry the surface to be tested;
- electric current is not transferred for one reason or another;
- patient is less than 5 years old.
Cases where there is a chance of receiving a false result, that is, relative contraindications:
- nervousness of the patient during admission;
- presence of a crown on the tooth;
- availability of metal orthopedic structures in the oral cavity;
- presence of amalgam fillings;
- root crack;
- perforation of root canal or tooth cavity;
- malfunction in the equipment used for the study;
- violation of the methodology.
Methods of diagnostic
The study involved both a doctor and a nurse.
- First, the patient is explained what sensations may occur during the diagnosis. In the examined tooth,
 may appear tingling, tremors, trembling or a feeling of stirring. The patient is warned that he should immediately report all the new sensations. The most commonly used sound is "a".
may appear tingling, tremors, trembling or a feeling of stirring. The patient is warned that he should immediately report all the new sensations. The most commonly used sound is "a". - The patient is then given one of the electrodes that is wrapped in wet gauze.
- On the second electrode, the doctor winds the turunda out of cotton wool, which is also moistened.
- An important step is the drying of the surface of the tooth. For this purpose it is better to use balls from cotton wool. The research area is also isolated with the help of cotton and gauze rollers.
- After drying, the electrode with turunda is placed on special points. In the frontal group of teeth, this place is the middle of the cutting edge. Small molars are best to
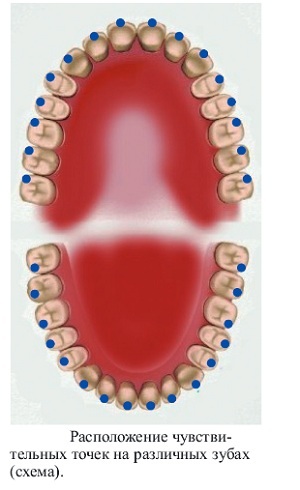 at the apex of the buccal hillock. In large molars, a special point is located in the middle of the medial-buccal hillock. In the carious cavity, the study is carried out along its bottom. To determine the excitability of the pulp, the electrode is placed at the mouth of each root canal.
at the apex of the buccal hillock. In large molars, a special point is located in the middle of the medial-buccal hillock. In the carious cavity, the study is carried out along its bottom. To determine the excitability of the pulp, the electrode is placed at the mouth of each root canal. - Soft tissues of the oral cavity should be drawn.
- During the preparation of the patient, the nurse leads the equipment into working order.
- After completing all the preparations, the nurse rotates the potentiometer clockwise by 1-1.5 mm, gradually increasing the supply voltage.
- If the patient reports the appearance of uncharacteristic sensations, the result is recorded and the current is reduced.
- This manipulation is repeated several times to reveal the exact values.
Used equipment
EDI is performed with the following devices:
- OD-2M;
- EOM-3;
- IVN-1;
- OSM-50;
- Puppetest 2000;
- EOM-1.
Difficulties during the
During electrodiometry, it is important to remember that the tooth can react differently to the current. Be sure to take into account the age of the patient and the presence of systemic diseases. Also, the sensitivity of the tooth tissues alter the pathologies of the jawbones and peri-jawbone soft tissues.
In addition, external interference can also exert influence. Apparatus UHF and UHF negatively affect the devices for electrodontometry and lead to the appearance of false results.
The most important thing is to fully comply with the research methodology. It must exactly correspond to the instructions to the device. Only in this case reliable results can be obtained.
Decoding of indicators
Indicators of EDI, which are used by dentists in evaluating diagnostic results:
- The normal values range from 2-6 μA.
- In children during the period of the change of teeth, the reaction may be completely absent. In the process of teething the indicators are constantly changing. At the initial stages of excitability can reach up to 150-200 μA.Then it rises to 30-60 μA.Normal values appear only after the complete formation of the root.
- With initial and average caries of , EDI values correspond to normal values, and with deep ,
 decreases to 18-20 μA.Such values indicate initial changes in the tooth pulp.
decreases to 18-20 μA.Such values indicate initial changes in the tooth pulp. - Values of 20-5 μA indicate reversible changes in the pulp, or focal pulpitis .With the development of necrosis in the coronal pulp, the indices are 50-60 μA.Values greater than 60 μA indicate the spread of the process to the root canals.
- With , the periodontitis excitability will be 100-200 μA, such EOD values indicate complete loss of pulp. Only receptors located in the periodontium react.
- With the periodontitis values will be 35-40 μA.The obtained data indicate the presence of inflammatory changes in the bone tissue around the tooth. There is its resorption, the root of the tooth is bare. As a result, the pulp chamber begins to decrease in size to avoid an increased reaction to external stimuli.
- With , periodontal disease values can vary from normal to low. The results are possible up to 30-40 μA.The mechanism of changes in excitability is the same as in periodontitis.
- With , neuralgia values will correspond to the norm.
- With , the does not degrade electrically. Perhaps its complete absence.
- With tooth injuries , the indices will correspond to the degree of damage to the pulp.
- If there are lesions in the tissues of the jaws , there will be a gradual decrease in the indices in the affected area.
Cost of research
The price of this type of diagnosis varies from 150 to 400 rubles per tooth.
Electroodontodiagnostics is an accessible and informative method for studying tooth tissues. But you can not use it yourself. Because of the complexity and a large number of contraindications, electrodontometry can only act as an additional examination.
In conjunction with other methods of research, the physician will receive full information about the changes that have arisen in the dental tissues and put the right diagnosis.
