The quality of the material, as well as the skill of the specialist, to which the patient comes to be treated, is an important factor when making impressions or molds of the dentition.
The quality of the material, as well as the skill of the specialist, to which the patient comes to be treated, is an important factor when making impressions or molds of the dentition.
Impressive are the modeling materials used most often in the manufacture of dentures, the scope of their application is orthopedic dentistry. The impression, as well as the impression, is the negative image of the patient's jaw in convex form;in other words, the mapping of the teeth and any other parts of the jaw required for the manufacture of the prosthesis, in the opposite form.
The most popular sphere of application of such manufacturers is dental prosthetics. Experts in casts are orthopedic doctors, as well as orthodontists.
The terms "impression" and "cast" are commonly used as synonyms. But someone believes that they are designated products made of different materials. Usually, when creating a prosthesis dentists work with two large groups of materials: these can be thermoplastic mixtures, then the imprint can be called an impression, or impression mass, in which case it is called a mold. To date, some experts consider the concept of a mold obsolete and use only the term "impression".
This division can be considered conditional, because usually every specialist in his practice gets used to his term.
content
- Classification prints
- Impression trays
- requirements impression materials
- process of removing the imprint
- Types and prints characteristic
- Gypsum
- Tsinkoksidevgenolovye paste
- thermoplastic mass
- Agar
- alginate
- elastomeric impression materials
- Polyester weight
- thiokol mass
- output
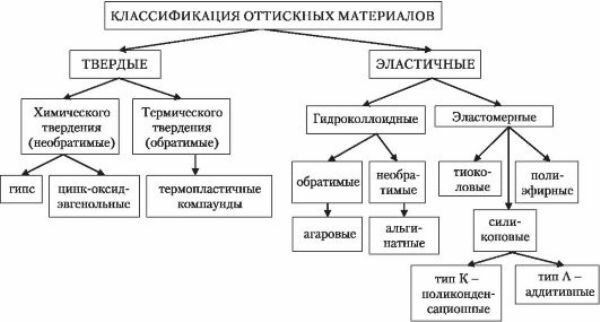
Classification prints
In orthopedic dentistry, impression materials can be classified into several categories:
- By appointment: functional( display of the oral cavity in various states) and anatomical( display of all tissues of the oral cavity at rest).
- On the jaw part of : complete and partial.
- By the material impression : alginate, silicone, polyester and others.
- On the stages of removal of : one-stage, two-stage.
- For the phases of the applied material : single-phase, two-phase.
- Based on the pressure on the mucosa : compression and decompression.
The organs and tissues in contact with the denture are called the prosthetic bed.
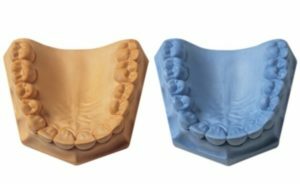
As a result, after receiving the impression, the doctor creates a model - a fragment of the jaw that is attached to the prosthetic bed. There are three types of models:
- Working .They make dentures and devices.
- Auxiliary .They are opposite to the prosthesis and are used to replace the shortcomings of the dentition of one of the jaws.
- Diagnostic, or control .With their help, the diagnosis is clarified or a prosthesis is planned.
Impression spoons
When preparing the impression, the doctor uses a special tool - an impression spoon, it can be standard and individual.
The standard ones are made of plastic or stainless steel, the choice is very large, because the shapes and sizes of the spoons depend on the individual characteristics of the patient, and therefore a large stock of the usual dimensions of this tool is required.
But there are cases when even among the standard spoons does not turn out to be necessary for the patient( for example, if the patient has lost his teeth completely).Then the doctor resorts to making an individual spoon. To do this, they use basic plastic or polystyrene, which is covered with a gypsum model of the jaw in a thermovacuum apparatus.

The size and shape of such a dental instrument depends on many factors:
- the shape of the jaw;
- length and width of the dentition;
- characteristics of the defect;
- height of the remaining teeth.
The spoon should not reach to the teeth about 3-5 mm. You also need to know that when removing the lower impression, you need to clean especially many soft tissues of the oral cavity, so you need to select a spoon very carefully.
Requirements for impression materials
Earlier materials for dental prostheses and other orthopedic procedures were not as perfect as they are today, but with the development of dentistry the list can be represented already in 7 groups, each of which contains not less than 3 known in medicine formulations. At the same time, they all must meet certain quality standards.
Here are the requirements for the impression materials in production:
- the ability to accurately convey the texture of soft tissues and do not collapse when removed;
- storage of the form during storage;

- free disinfection;
- free detachment from the finished model;
- no damage to the oral cavity due to burns;
- good curing speed;
- no dissolution in saliva;
- easy involvement into the oral cavity and excretion from it;
- acceptance of a state of greater plasticity afterwards;
- no bad smell, unpleasant taste, harmless to the patient;
- no swelling in the water;
- the possibility of sterilization and reuse.
- availability and low price.
The process of removing the impression
To begin with, the doctor examines the oral cavity, if necessary, the treatment or removal of individual teeth. After the patient chooses the design that he will be wearing, a further process of preparation for the removal of the impression takes place.
The doctor then enters an anesthetic solution and prepares the bone organs of the oral cavity to remove the imprint. After that, he dries the patient's mouth with cotton swabs. The doctor must then knead the material to make the impression.
The impression can be taken in different ways. Here's how one of them passes:
- A spoon is spread on the spoon, after that - a thick paste, then a cast of teeth is immediately removed. All this is done before the preparation of the elements, so that there will be room for a correcting composition.
- Then, after the preparation of the teeth, an expansion occurs in the recesses of the gingival support elements. This is where it is necessary to insert retraction threads impregnated with the composition of the vasoconstrictor.
- To stop blood from gums and fix retraction threads, a wadded cylinder is placed in the prepared element.
- At the end, the patient closes his mouth to ensure that the recesses between the teeth and gums cease to bleed.
- With this impression the doctor removes the paste layer and fills it with a new composition.
- Next cast in the second time sent to the mouth and now dries up completely.
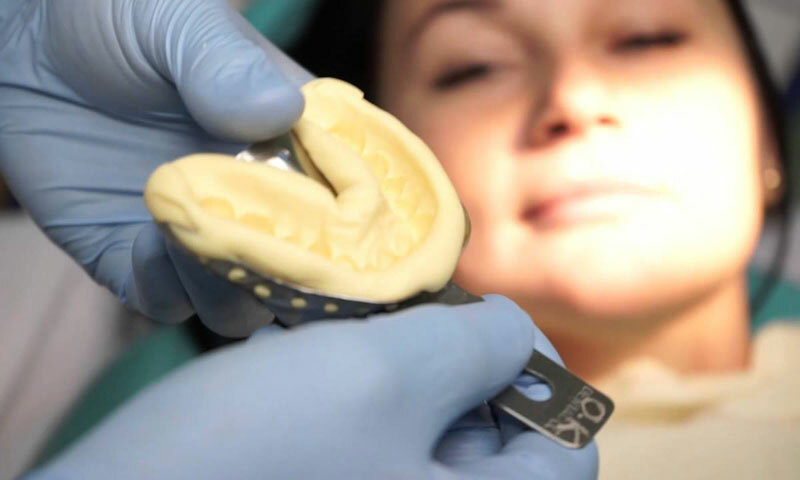
There is also another way of making an impression, which is carried out in 3 stages:
- First .The doctor pours in the cavity of the dental spoon first the basic composition, and then correcting.
- Second .After that, he applies a corrective paste in the prepared oral cavity of the patient.
- Third .Then the dental spoon is inserted into the oral cavity, the patient's jaws close, and then the doctor gently removes the spoon from his mouth and receives a ready-made impression.
In the second case, silicone masses are used, and therefore slight deformation and shrinkage occur during manufacture. Because of this, there is a need for a fairly rapid use of the obtained fingerprint.
Types and characteristics of the prints
Existing impression or impression materials in orthopedic dentistry can be divided into two large groups:
- solid;
- are elastic.
Solids can harden with chemical hardening( irreversible) and thermal hardening( reversible).
Gypsum
Irreversible raw material is gypsum - it is produced by burning natural gypsum. Sifted raw materials are mixed with water before making a cast, and the gypsum hardens quickly, which allows you to create clear impressions.
Disadvantages of gypsum:
- low quality - poor grinding - does not allow the mixture to harden quickly;
- is likely to break, as the gypsum is fragile enough;
- not all substances can be used when detaching the model and impression, for example, fat containing;
- it is very important to store gypsum in a dry room, since after its moistening it is difficult to create artificial limbs, etc.;
- in gypsum powder with prolonged storage begins to form lumps.

Advantages of gypsum:
- low price;
- no unpleasant odor and taste;
- no adverse effect on peri-toothed tissues and mucous membranes of the mouth;
- stickiness;
- get a clear picture.
Zincoxide-eugenol paste
Another irreversible material is zincoxide-eugenol paste, in which zinc eugenolate is mixed with water, and after this reaction the mixture becomes plastic. They are used by dentists in adentia( full or partial), i.e.absence of teeth.
Preference can be given to this mixture due to the fact that it is easily separated from the model, has high sharpness and quickly sticks.
But at the same time the process of correct mixing is very important, because the pastes can break when removed due to their fragility.
Thermoplastic masses
Reversible solids include thermoplastic masses: rosin, stearin, gutta-percha, wax, Weinstein mass, Kerr mass, stent, paraffin.
Such materials have a distinctive feature - when heated they become plastic. The mass is filled mainly with chalk, pumice, talc and other powders.
 Softening of such substances should occur at a temperature of no more than 60 ° C, otherwise there may be a burn of the oral cavity.
Softening of such substances should occur at a temperature of no more than 60 ° C, otherwise there may be a burn of the oral cavity.
Correctly heated mass for impression making is well adjusted during processing, but the most optimal is the temperature of the human body. Another obligatory property is homogeneity, a similar mass should not solidify in separate areas. Also, a good thermoplastic mass will not become sticky even at high temperatures and will remain safe for the patient's health.
The next group of impressions is elastic. They are divided into 2 groups:
- hydrocolloid;
- elastomeric.
Hydrocolloid substances are divided into 2 groups: reversible and irreversible.
Agar
Agar materials( agar, potassium sulfate, borax, alkyl benzoate, water) are irreversible, alginate( sodium salt of alginic acid) is irreversible.
Agar is a galactose sulphate, that is, a substance that forms a colloid during mixing with water, then when heated, the suspension becomes viscous and fluid. Then there is packaging in tubes( tube).
Agar has several advantages: 
- high fluidity;
- the correct display of all areas of the mouth, including soft ones;
- easy and quick separation from the finished model.
However, agar has a drawback - it is too plastic, and therefore the specialist does not always manage to easily separate the impression and the spoon, which can lead to rupture of the print.
Alginate
Alginate, or sodium salt of alginic acid, is a powder that is mixed with water. To obtain the right mixture it is important to clearly observe the proportion of powder and water.
The alginate has several disadvantages:
- a large amount of water will lead to a short hardening;
- rapid dissolution can lead to very rapid solidification of the mass;
- if the mass is poorly kneaded, then it will begin to crumble;
- it is very important to clearly observe the proportions when kneading, so it's better to use prepackaged bags with powder to get an impression.
If during mixing everything was done correctly, the impression is easy and quick, it is easily separated from the model and keeps the received form long enough.
Elastomeric impression materials
Elastomeric impression materials in dentistry are divided into silicone, polyester and thiocarbon.
There are two types of silicone impression copings in dentistry: polycondensation( K) and additive( L).
 The basis of these materials is the base paste, which reacts with the catalyst, and after 3-4 minutes the hardening takes place. An additional layer is applied from above to obtain all contours, depressions and protrusions.
The basis of these materials is the base paste, which reacts with the catalyst, and after 3-4 minutes the hardening takes place. An additional layer is applied from above to obtain all contours, depressions and protrusions.
This raw material is very good in application for the production of an initial impression, an individual spoon or a tread compound.
Like other substances, it has several advantages:
- high fidelity;
- reasonable price;
- very fast adhesion - adhesion of two dissimilar bodies;
- no smell and no taste.
But there are also disadvantages:
- requires 2 hours for the model;The
- model may decrease in volume;
- mixture has the property of absorbing moisture and in this case becomes substandard;
- product can change its shape at pressure.
Polyester weights
Polyester weights are pastes with medium consistency. The base of the paste is polyesters with a low molecular weight.
Further, the mass is filled with silica, elasticity is imparted to it by glycol etherphthalate. Next comes the packaging in tubes( or tubes).
The advantages of polyester weights can be called: 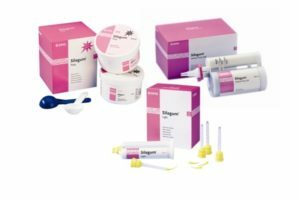
- versatility - a wide field of application in orthopedics;
- high accuracy of the resulting impression;
- secondary use in the manufacture of the model;
- fast curing;
- sufficient strength of products;
- long service life - the density persists for more than a month;
- availability of the possibility to sterilize the impression.
But in this case there are also disadvantages: the high price of the substance and the complexity of the excavation from the oral cavity of the patient.
Thiokoll masses
Thiokol masses have another name - polysulphide, because thiokol has another name - polysulphide rubber. In dentistry, it is also referred to as a tiodent.

Prepare such a mass by connecting the base - paste - and the catalyst.
Hardening occurs with water or oleic acid, in the first case, hardening occurs faster, in the second - slower. In the mouth, hardening begins in 2 minutes.
The purpose of this mixture is the production of inlays, prostheses with no adhesions, teeth with pins, solid bridge prostheses.
This mixture has many advantages:
- high level of accuracy and reproduction of small parts;
- rapid congealing;
- high level of elasticity;
- no shrinkage;
- long enough storage life without changing the quality;
- possibility of reuse in the production of the model.
But at the same time it must be said that the mixture does not smell very nice, and also begins to gradually lose its properties after the warranty period.
Conclusion
Due to the large selection of impression materials, specialists can choose any composition suitable for creating an impression or impression in a variety of cases. It can be noted that as yet no one has invented a universal composition for the creation of dental prints, which has a very high accuracy, suitable for doctors in any case and without any shortcomings.
If possible, specialists try to use cheaper substances( for example, gypsum).But sometimes, for medical reasons, when making dentures or dental treatment, you have to face certain difficulties, and therefore, when removing the impression, you will have to use more expensive materials.
It is also known that now they are starting to use a new method - scanning the dentition and producing tooth models from 3D-scan images. Perhaps in the future this will lead to the partial disappearance of impressions using impression materials in dentistry.