 Desensitizers are a separate category of materials whose healing effect on tooth tissue is based on the sealing of the dentin tubules.
Desensitizers are a separate category of materials whose healing effect on tooth tissue is based on the sealing of the dentin tubules.
They are used to prevent the influence of external stimuli on the dentin. This reduces the sensitivity of the teeth, so that the patient ceases to feel discomfort and soreness.
Contents of
- What is tooth sensitivity?
- Mechanism of action of desensitizers
- Current classification of
- Unsatisfied without glutaraldehyde containing HEMA
- Unsupplemented containing HEMA and glutaraldehyde
- Desensitizers filled and containing HEMA
- Solutions containing surfactants and weak acid
- Drugs that act to form complex salts
- The mostWhat are tooth hypersensitivity?
Hypersensitivity of teeth is a consequence of exposure of dentin for one reason or another. As a result, the stimulus acts on the pulp, which leads to the appearance of pain.
The patient constantly feels discomfort, which is worse when eating, drinking tea or coffee. In particularly severe cases, pain occurs when breathing in cold air. This makes conversation and even breathing difficult.
Gradually, unpleasant feelings begin to bother constantly and greatly worsen the quality of life.
What could be the cause:
- removal of hard tooth deposits from the teeth;

- cleaning periodontal pockets for periodontal disease;
- teeth whitening;
- exposure of the neck or part of the root of the tooth;
- defects in the cervical region, for example, wedge-shaped;
- staging the seal.
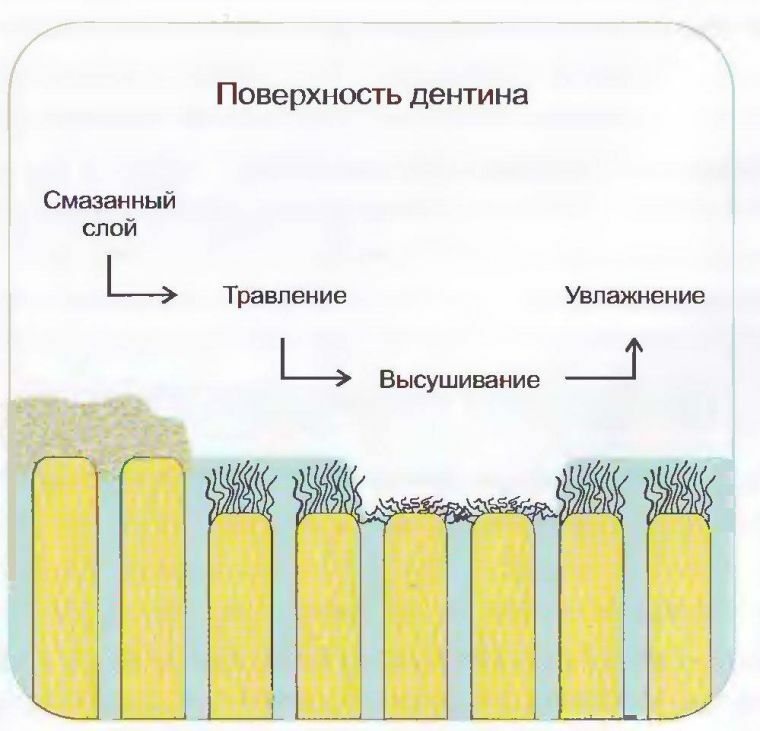
Mechanism of action of desensitizers
Desensitizers can act on the teeth in various ways:
- Mechanical blockade of the dentinal tubules by the agent itself. This method is affected by Desensitizer, which is available as a varnish. When applied, such compositions cover the surface of the bare tubules with a thin film. Thus the likelihood of developing pain is reduced.
- Precipitation of proteins and ions in nerve endings .Desensitizer coagulates proteins. This process breaks the passage of the nerve impulse, and the dentinal tubule itself closes.
- Nerve fiber depolarization .With this mechanism, the dentinal tubules are not closed. Due to the violation of the polarization process, the pulse does not pass, but the pain sensations do not develop. The advantage of this method is that there is no blockage of fluid movement along the tubules. As a result, the natural processes responsible for the exchange in the tooth tissues are not disturbed.
- Moistening of dentin before filling .The descentizer recreates the moisture of the dentin, which is lost when it is excessively dried. This improves adhesion of the adhesive, as it penetrates deeper into the tubule and provides the most durable bonding. Currently, most materials are based on a combination of mechanisms. Some drugs can only work on one of them, but the effectiveness will be noticeably lower.
Modern classification of
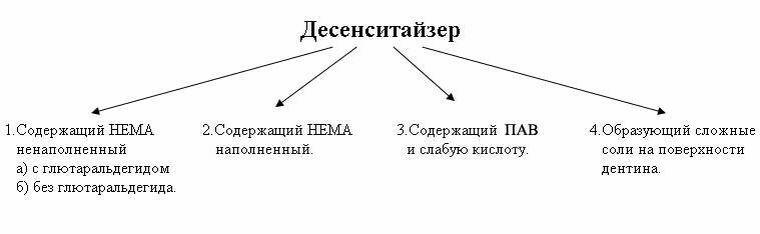
Among desensetizers, 4 main groups are distinguished:
- unfilled with HEMA content, glutaraldehyde can additionally be added;
- filled with HEMA content;
- with a content of weak acids and surface active substances;
- acting with the formation of complex salts on the surface of dentin.
Unfilled without glutaraldehyde containing HEMA
This is the most common group. The main component of these agents is hydroxyethyl methacrylate. It is a monomer that formed the basis of the first generations of adhesive systems. In this case, it acts as an agent that moistens dentin and reduces the collagen fiber degradation. As a result, the adhesive penetrates better into the dentin tubule.
In addition to the monomer in the composition contains water and fluorine. Instead of fluorides, an antiseptic may be added. Some desensitizers contain all 4 components. Fluoride is used as a way to prevent the development of secondary caries. As antiseptics can act 4% solution of Chlorhexidine. It has a bactericidal effect on microorganisms, which managed to penetrate deep into the dentinal tubules.
Indications for using this group of tools:
- restoration of composite material;
- installation of amalgam fillings;
- use of permanent prostheses on live teeth, if artificial crowns or patches are additionally present in the design;
- creation of adhesive prosthetic structures;
- fixing of veneers;
- increased sensitivity of teeth in the cervical region;
- professional hygiene related to the removal of solid deposits;
- whitening.
Method of use:
- is applied after etching the tooth before applying the adhesive;
- for application, microbrashes are used, the movements must be rubbing, without the formation of "puddles";
- give 20-30 seconds for drying;
- excess material is removed by the tow truck at high speed.
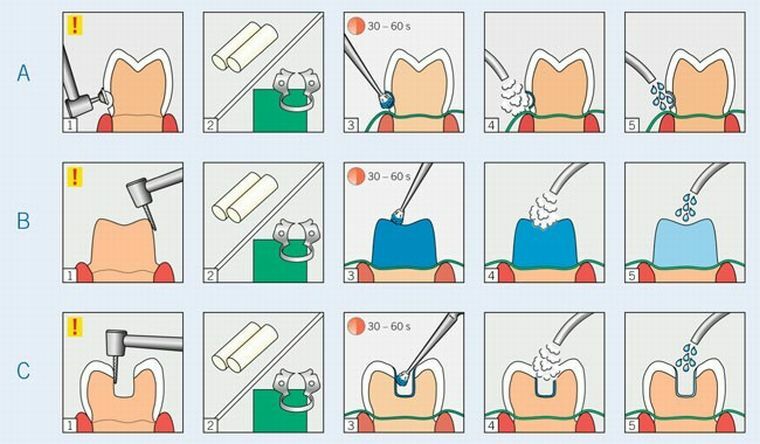
The material should not be washed off and lighted. At work it is necessary to use means of individual protection: gloves, a mask, glasses. It is recommended to apply the cofferdam on the tooth.
Key representatives of this group:
- HurriSeal;

- Shield Force Plus;
- Aqua-Prep F, additionally contains fluorine for anticaries action;
- Hemaseal & Cide Desensitizer, additionally contains 4% chlorhexidine solution;
- PrepEze Desensitizer, contains antiseptic and fluorine, 5% benzalkonium chloride solution acts as an antiseptic;
- MicroPrime Desensitizer, also contains fluoride and benzalkonium chloride.
Unsupplemented containing HEMA and glutaraldehyde
The main component of this group of agents is glutaraldehyde. The mechanism of its action is based on the coagulation of the proteins of the dentin tubules. HEMA promotes deeper penetration of the substance. Also, the growth and reproduction of microorganisms is suppressed.
Clinical use cases:- tooth hypersensitivity in the cervical region;
- sensitivity after installation of the artificial crown, this effect is especially pronounced when using zinc-phosphate cement for fixation.
Stages of use:
- cleaning of the tooth surface;
- surface is best dried with cotton balls, since it should remain slightly moistened;
- applying the desensitizer with a microbrush;
- exposure - 30 seconds;
- gently inflate the excess fluid with air from the puster until the surface brightness disappears;
- the mouth is washed with water. The exception will be the Desensitaizer of Gluma.
Glutaraldehyde is able to cause reactions of the body of a toxic nature. Therefore, it is recommended to use personal protective equipment during the use of the material.The third component in the composition is water.
Representatives:
- Gluma Desensitaizer;
- Quadrat FiniSense.
Desensitizers filled and containing HEMA
This group of substances contains special fillers up to 7 nm in size. The basis is compomer or ormoker. Also in the composition is added an antiseptic, for example, triclosan, and fluoride ions. These components reduce the rate of soft plaque formation on the teeth.
Clinical situations in which the use of such solutions is indicated:
- hyperesthesia in the area of bare teeth;
- protects the cervical area from excessive exposure to the toothbrush while brushing teeth.
Stages of use:
- tooth cleaning.
- surface etching;
- application of the first layer of the desensitizer with a micro-brush, then it is gently blown with a jet of air;
- application of the second layer by the same procedure;
- with a photopolymerization lamp.
Representatives of this group:
- Admira Protect. Contains fluoride and triclosan in its composition. The basis is ormoker.
- Seal & Protect. Desensitizer based on the compomer. Fluorides and triclosan are also added to it.

Solutions containing surfactants and mild acid
This group exhibits the following effects:
- , surfactants wet the dentin prior to application of the adhesive;
- antiseptic action; benzalkonium chloride acts as an antiseptic;
- anticaries action due to the content of fluoride ions;
- weak acid helps to clean the dentin surface.

The only drug that is on the market: Tubulicid Red and Tubulicid Blue.
Use when:
- cleans surfaces before fixing artificial crowns;
- hypersensitivity in the cervical region.
Instruction for use:
- application of the product using a micro-brush;
- exposure 20-30 seconds;
- application of adhesive.
Drugs that act to form complex salts
The action of this group of drugs is based on the formation of an indelible film. It consists of macrocrystals deposited on the surface of dentin. This blocks the movement of fluid along the tubules.
These desensitizers do not contain substances that can have a toxic effect. Therefore, the possibility of irritation of the gum tissue is practically reduced to zero.
When recommended use:
- treatment of live teeth, which will be fixed fixation of artificial crowns and supports of non-removable prostheses;
- hypersensitivity of cervical areas;
- removal of hard dental deposits;
- whitening.
Instructions for use:
- tooth cleaning;
- application of the preparation with a microbrush;
- air drying.
Representatives of this group:
- Pain Free;
- D / Sense 2;
- Zarosen;
- BisBlock;
- Super Seal.
Most popular drugs
The effectiveness of this or that desensitizer depends on the initial clinical situation. Of course, they reduce sensitivity. But it is impossible to say how much the drug will help in this or that situation. In some cases, its reuse is required.
Now the most widely used:
- Gluma Desensitizer;
- Aqua-Prep F;
- Admira Protect;
- Shield Force Plus;
- BisBlock.
A large number of options on the market indicate that there is no single tool. The doctor makes a choice based on the clinical data and indications for the use of each of the groups represented.
- removal of hard tooth deposits from the teeth;
