 Disturbances in the microcirculatory bed of periodontal tissues are the main link in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. A large number of studies that are regularly carried out over the past decade have revealed that there are two types of changes in the vessels: structural and functional.
Disturbances in the microcirculatory bed of periodontal tissues are the main link in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. A large number of studies that are regularly carried out over the past decade have revealed that there are two types of changes in the vessels: structural and functional.
It has been proven that the total number of functioning capillaries decreases, their permeability changes. Blood is also affected, namely its aggregation properties.
All changes occur at the same time. The degree of their manifestation will depend on the duration of the inflammatory phenomena. Therefore, the state of blood vessels and hemodynamics in the tissues of the periodontium is reflected in the results of the studies. Periodontal diseases affect all blood vessels. There are changes in the inner layer, which manifest themselves as a stratification of fibers of the elastic type. Such changes lead to an increase in the permeability of the endothelium. As a result, the gum acquires a swollen appearance.
In addition to the inner layer, the middle layer is also affected. The shell thickens and is sclerosed. Most of all, these changes are manifested with moderate to severe severity of periodontitis.
As a result of tissue proliferation and hyaline deposition, the oxidation-reduction balance in the tissues of the vessels is disturbed. All this leads to hypoxia of the periodontal tissues.

Contents
- Reoparodontography in dental practice
- What is being investigated
- Carrying out the research
- Applied equipment
- Interpretation of results
- Application of flowmetry
- How does it work?
- Conducting the
- study Used equipment
- Interpreting the results of the study
- Ultrasonic osteometry
- How does it work?
- Diagnostic steps
- Applied equipment
- Explanation of received information
- Kulazhenko sample
- Polarography
Reoparodontography in dental practice
Reoparodontography is a method for assessing the functional state of the vascular bed of periodontal tissues.
The result of the study is the rheogram. The specialist conducts its visual assessment based on numerical parameters:
- Rheographic imagery, or .This indicator characterizes the strength of pulse filling periodontal.
- Index of peripheral resistance, or IPS .It is used to assess the vascular tone.
- Index of wall elasticity, or IE .
- The index of the vascular tone, or PTS .This indicator is based on measuring the time intervals of the pulse curve, which will depend on the heart rate.

What is being investigated by
During the diagnostic activities, pulsation of blood flow is recorded.
The volume of transmitted blood depends on the state of the vessels, and their tone from the level of arterial pressure and local factors, which includes the masticatory load and the total number of inflammatory mediators.
As a result, both qualitative and quantitative evaluation of periodontal tissue filling with blood will be obtained. Changes in the tone of the capillaries of the microcirculatory bed are also revealed.
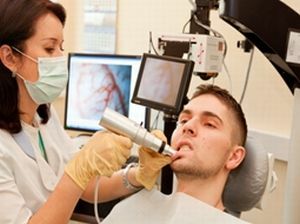
Conducting the
study For reoparodontography, a special electrode system is used. It is placed in the oral cavity in such a way that the zone, which is being investigated at the moment, is placed between the electrode pads.
Next on the computer screen will be displayed pulse curves. For optimal evaluation, their number should be 3-5.
Only one is decrypted.
Applied equipment
For the survey, the following is required:
- unit with Dial;
- computer with installed software;
- stainless steel electrode system, which is located in plastic plates.
Interpretation of
results Normally, the indices will have the following values: 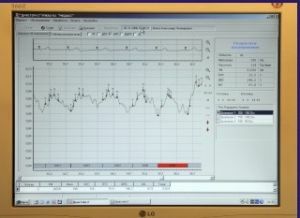
- peripheral resistance index, or IPS - 80-90%;
- index of elasticity, or IE - 70-80%;
- rheographic index, or RI - 0.36 Ohm.
Application of flowmetry
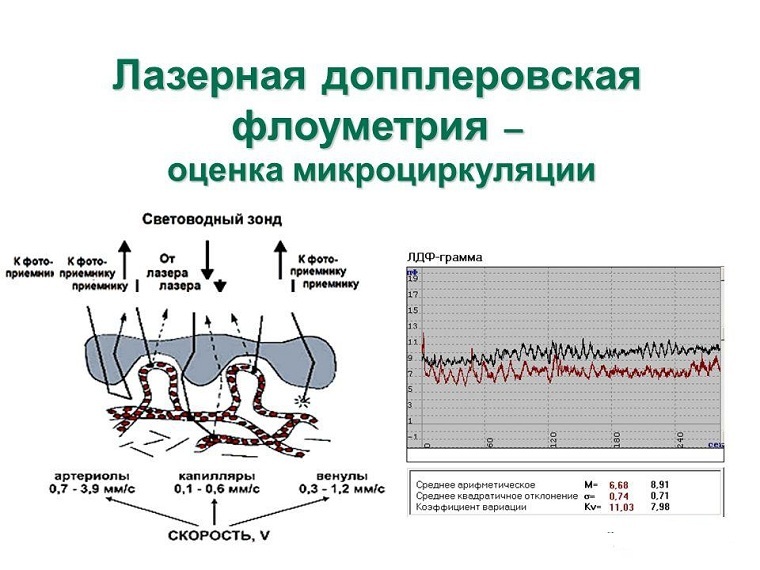
Laser Doppler flowmetry is a type of study of periodontal tissues, which is based on the Doppler effect.
With the help of such a survey, it is possible to reveal the condition of periodontal tissues and the degree of their changes due to inflammatory diseases.
How does it work?
The laser is reflected from red blood cells that move through the capillaries with blood flow. This leads to a change in the frequency of the transmitted signal. As a result, it is possible to estimate the intensity of the blood flow passing in a particular area.
The reflected signal is converted and allows to give a microcirculation characteristic at the site of the study by evaluating:
- the rate of movement of red cells;
- hematocrit capillaries;
- the number of active vessels that continue to function.
Carrying out the
study. Diagnostic stages:
- the patient is located in a semi-lying position, it will be optimal to place the area under study on the same level as the heart;
- the analyzer sensor is placed on the mucous membrane, which is immovably fixed;
- primarily determine the degree of filling of tissues with blood;
- further reveal abnormalities in blood circulation fluctuations in the time interval that was predetermined;
- , the degree of pressure drop is recorded at the end.
The obtained data should show the type and degree of disturbance in microcirculation of periodontal tissues, as well as changes in their regulation.
Used equipment
In our country the LAKK device is used in various modifications.
Interpretation of the results of the
study Laser flowmetry allows differentiating the degree of severity of the disease. In each stage, the indices will differ slightly:
- In the case of of moderate severity , the level of blood flow in the capillaries decreases by 17-20% below the norm. Changes in blood flow and vasomotor activity indicate a decrease in both total blood filling of tissues and its activity by 25-30%.The vascular tone also increases. This phenomenon is associated with increased resistance within them. The changes are about 25%.
- With , the severe periodontitis all the indicators differ even more. Blood flow activity is reduced by 40-50% compared to the norm. And the blood flow itself is reduced by almost 30%.Also, an increase in the tone of the vascular wall is almost 2 times. That speaks of an attempt to compensate for violations. Resistance inside the vessels is reduced by a factor of 2.
The data obtained suggest that the degree of abnormalities in hemodynamics is proportional to the severity of the underlying disease.
Ultrasonic osteometry
Ultrasonic osteometry, or echoostometry, is a method of estimating bone density by measuring the time that ultrasound passes through the area under investigation.
How does it work?
 This method is based on the ability of sound to change the speed of passage depending on the density of the medium. The tighter it is, the faster the sound penetrates through it.
This method is based on the ability of sound to change the speed of passage depending on the density of the medium. The tighter it is, the faster the sound penetrates through it.
Echoosteometry is highly sensitive to the degree of saturation of bone tissue with mineral components. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to obtain the most objective information about bone density.
As a result, the doctor is able to assess its strength at the required site of the jaw.
Diagnostic steps
The study assumes the following:
The- patient is located between the sensors;
- study area is fixed;
- further in one of the sensors an ultrasonic wave is triggered;
- the second sensor is perceiving, it converts the wave into an electrical signal, analyzed by the program;
- duration of the study - 2-3 minutes.
Applied equipment
The EOM-01C device is used for the study. The impulse, which is fed to the investigated region, is 1.2 MHz.
Decoding of the received information
The parameters on the upper and lower jaw differ somewhat:
- for the upper jaw the norm is the speed of 3100 m / s;
- on the lower jaw sound penetrates at a speed of 3320 m / s.
Kulazhenko sample
This is a fairly simple and informative study. It is based on the detection of the permeability of capillaries and their resistance to vacuum effects. 
During the examination, Kulazhenko's apparatus is used to treat periodontal disease. With its help, a hematoma is created on the gum, in terms of the time of its formation, the permeability of the vascular wall is assessed.
Normal indices in different areas:
- frontal group of teeth - 50-70 s;
- premolars - 70-90 s;
- lower molars - 80-100 s;
- upper molars - 80-90 s.
With periodontitis, the hematoma forms 7-10 times faster.
Polarography
This method of electrical analysis is used to determine the degree of oxygen filling of periodontal tissues.
It is based on recording the dependence of the current strength on its voltage when passing through biological media.
The main goal of polarography is to assess the degree of hypoxia in the periodontal tissues.
