 Candidiasis of the oral cavity is a mucosal lesion with a characteristic white coating caused by a fungal infection of the genus Candida albicans.
Candidiasis of the oral cavity is a mucosal lesion with a characteristic white coating caused by a fungal infection of the genus Candida albicans.
The cause of the disease is a general decrease in immunity, which promotes the reproduction of fungal infection. Candidiasis causes itching and burning in the mouth, as well as other unpleasant symptoms, modern antifungal agents are used to treat it.
Contents
- Medication for fungal infection
- Medications for adult patients
- Means for topical treatment
- Systemic therapy
- Treatment of children and infants
- Local exposure to fungus
- Systemic therapy
- Remedies for the treatment of throat and tonsil candidiasis
- Editorial selection
- A few tips
Medication for combating fungus
Antimycotic drugs - drugs that have direct antifungal action, directedto prevent further growth( fungistatic effect) or complete elimination of the pathogen( fungicidal effect).Antimycotics are prescribed both for the prevention of the disease, and for the treatment of all forms of candidiasis.
Modern antimycotics are divided into: 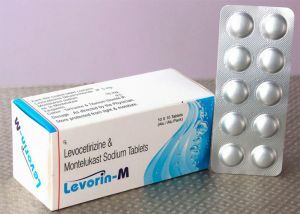
- polyene antibiotics , causing destruction of the fungal cell by insertion into its membrane and metabolic disorders( most effective in candidiasis Natamycin, Amphotericin B, Levorin, Nystatin);
- imidazoles , blocking certain enzymes necessary for the functioning of the fungal cell. These include miconazole, imidazole and clotrimazole;
- bis-quaternary ammonium compounds ( Decamine) also have an antifungal effect, are applied both topically to the lesion site and in systemic therapy;
- echinocandins ( Kaspomfungin, Mikafungin) inhibit the synthesis of polysaccharides of fungi used to construct the cell wall.
Antiseptics is used as a rinse to prevent the spread of infection and to sanitize existing foci of inflammation. These solutions include solutions of Chlorhexidine and Stomatidin. Lubrication of mucous membranes with Lugol, Fucortsin and Resorcinol is also performed.
As prevention of the disease, vitamin therapy is used to stimulate immunity, taking into account the deficiency of group A, C, E, B1, B2, B6.

What you need to know about antifungal agents: pharmacological features, classification, nuances of application:
Treatment for adult patients
The goal of therapy is to simultaneously act on infection from several application points. This is a local suppression of the infection, the essence of which is the application of antimycotics and other drugs directly to the foci of the affected oral mucosa, and the systemic treatment of candidiasis by taking antibiotics.
Means for topical exposure
Treatment of candidiasis begins with the use of drugs, the action of which is aimed at sanitation of the oral cavity. Typically, aniline dyes can be used for this:
- Solution methylene blue .Used to apply to the fungal areas of mucous cotton swab moistened with
 solution. The properties of the dye are directed to the damage of the membrane of fungal cells. There is no drug interaction with other drugs. However, with extensive application, the blue can cause burn mucous, and the risk of overdose, which manifests itself in allergic reactions, increases.
solution. The properties of the dye are directed to the damage of the membrane of fungal cells. There is no drug interaction with other drugs. However, with extensive application, the blue can cause burn mucous, and the risk of overdose, which manifests itself in allergic reactions, increases. - Preparations based on iodine ( Lugol Solution or Iodicilin).Drugs can be used in the form of a solution for applications or a spray to irrigate the necessary areas.
- Nystatin ointment. Especially effective in fungal galling and candidiasis, manifested by cheilitis( damage to the lips in the form of cracks).The effect decreases with simultaneous use with Clotrimazole. The ointment is applied in a thin layer on the required site of the mucosa two times a day, for one week.
- Rinse with 2% solution of boric acid or sodium tetraborate .Used for mucosal disinfection, as well as better separation of fungal deposits, reducing inflammation and improving tissue regeneration. Rinsing is performed every 3 hours, after meals and at bedtime for up to two weeks.
Systemic therapy
For systemic treatment of candidiasis in adult patients, the following drugs are used:
- Levorin .It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, it is available in tablet form. It has low toxicity and does not accumulate in the body. It is prescribed by reception 3 times a day for 12 days. It can cause a cough and in rare cases a fever. It is used for the purpose of systemic suppression of a fungal infection in the body. Contraindicated in hepatic insufficiency and ulcerative gastrointestinal lesions.
- Fluconazole .Presented as a solution of 0.2%.It is an antifungal agent with specific inhibition of the synthesis of fungal compounds. It is administered orally in the form of capsules and syrup, but also intravenously once a day for up to 2 weeks, but it is possible to use the drug and up to 30 days. Of the side effects possible diarrhea, flatulence and an allergic rash.
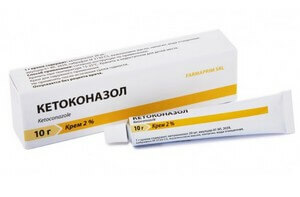
- Ketoconazole .Oppresses the synthesis of phospholipids of fungi of the genus Candida. It is used once a day during meals with a course of 2 weeks to 2 months. Possible diarrhea, headache and allergic pruritus, as well as a decrease in libido. Produced in the form of tablets. Can be used and as a prophylaxis of candidiasis with a decrease in immunity.
- Nystatin .For systemic use it is used as tablets up to 4 times a day for two weeks. Does not cause side effects. Perhaps its combination with nystatin ointment. The drug is a polyene antibiotic, the action of which is directed to fungi of the genus Candida.
Treatment of children and infants
Candidiasis therapy in children is more complex in terms of selecting drugs, there is only a limited list of permitted drugs, among which for local use are derived oxyquinoline-8 and-4, quaternary ammonium compounds and herbal preparations.
Local effects on the fungus
The permitted products are:
- Chinozole .It is a synthetic antibacterial drug with a wide spectrum of action. It is used for
 disinfection of the oral cavity from a fungal infection. Used as a solution and ointment 5%.
disinfection of the oral cavity from a fungal infection. Used as a solution and ointment 5%. - Etonium .Used as an ointment 0.5%, applied topically to the affected areas. The drug is a tool with bactericidal action, and also has a local anesthetic effect, which allows to reduce the clinical manifestations of candida fungus in a child. Reduces the degree of inflammation of the oral mucosa. Use in the form of applications lasting 15 minutes 3 times a day for one week.
- Sanguirythrine .It has an antifungal effect. Applied applique on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Use 1% aqueous solution 3 times a day for one week. Contraindicated in epilepsy and bronchial asthma.
Systemic therapy
For systemic exposure, the following are used:
- Amphotericin .Practically non-toxic, which allows it to be used in any childhood. Has a high activity in respect of yeast-like fungi. Primarily used for intravenous administration. In this case, the drug is administered dropwise for 4-6 hours at intervals of one day. Contraindicated in the failure of the liver and kidneys, it is also possible individual intolerance. May cause nausea, vomiting, headache and decreased pressure.
- Miconazole .Has a fungicidal effect. Candidiasis is prescribed tablets, less often a remedy in the form of a gel or solution in ampoules for intravenous administration. It is prescribed in the calculation of 20 mg per kg 4 times a day for one week. Possible allergic reactions and thrombophlebitis with multiple injections of the drug.
- Natamycin .Antifungal agent causing destruction of the cell wall of the fungus. It is a powder. Assigned inside of 100 mg 2 times a day. Possible nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
- Nystatin .It can also be used in children with a dosage of 100- 125 thousand units.4 times a day in tablet form.
Treatment for candidiasis of throat and tonsils
Affected areas of the throat and tonsils should be treated with a moistened cotton swab antiseptic. For this apply:
- Copper sulfate solution .Acts as a disinfectant astringent. Use a solution with a concentration of 0.25%.Treatment of mucosal sites occurs three times a day until the disappearance of clinical manifestations of fungal infection.
- Borax in glycerin 20% .Apply to the foci of the affected mucous throat and tonsils for the eradication of fungal infection.
- Lugol .Has the same properties as other solutions.
- Resorcinol .Apply 0.5% solution for application to the mucosa of the throat. In rare cases, allergic reactions are possible.
- Fucorcine solution .May cause temporary local burning and pain. It is applied from 2 to 4 times a day.
- Solution of silver nitrate solution .Has a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect. For application on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity 2% liquid is used.
Local treatment should be accompanied by systemic therapy, which includes the following medications:
- Mikostatin .A modern antifungal drug. Assigned inside the tableted form 3-4 times a day for 500 thousand
 units.in two weeks. Of the side effects possible dyspeptic disorders, chills, individual hypersensitivity.
units.in two weeks. Of the side effects possible dyspeptic disorders, chills, individual hypersensitivity. - The levorin for washing the tonsils with a solution is less commonly used as inhalations for 10 minutes twice a day until the pain symptomatology disappears completely.
- Diflucan .It is active against Candida fungi. Quickly absorbed from the digestive tract and has its effect on pathogens. Assigned within 0.2-0.4 grams per day for 6 weeks. As a rule, it does not cause side effects, but it is not prescribed during pregnancy and during lactation.
Also in the candidiasis of the larynx, the physiotherapeutic measures are effective with alternating procedures every two days.
Editor's choice
Among all the variety of medicines it is difficult to choose the best anti-Candida drugs from the point of view of efficiency and safety, but we tried to do it. Our top-5:
- Fluconazole .The drug has a systemic inhibitory effect on the synthesis of biological compounds of the fungal membrane, due to which its destruction occurs. Has a wide spectrum of action and a low degree of toxicity.
- Levorin .It does not have accumulative properties in the body, which reduces the risk of side effects. It is popular with doctors and patients.
- Amphotericin B In .Oppresses all kinds of fungi. It is widely used in pediatrics and has almost no side effects.
- Nystatin .The drug can be used in large quantities without the risk of adverse reactions. Interacts with all antifungal medicines.
- Ketoconazole .Appointed for both external and internal use. Its dosing allows you to apply the drug once a day.
Some tips after
Any antifungal drugs should be prescribed by your doctor and only after examination and diagnosis. Thus, with the appointment of an agent, the specialist will take into account co-morbidities, individual susceptibility and severity of candidiasis.
 When taking medication, you must follow the recommended dosage to avoid side effects. Treatment should be comprehensive and consist of several types of therapy( local and systemic).
When taking medication, you must follow the recommended dosage to avoid side effects. Treatment should be comprehensive and consist of several types of therapy( local and systemic).
It must be remembered that treatment should be taken through the course, and its interruption can lead to relapse of the disease. When there are side effects of any complexity, you need to contact your doctor to correct the therapy and eliminate the symptoms.
Candidiasis requires special attention, modern treatment and accurate diagnosis. At the moment there are many groups of drugs that are individually selected depending on the severity of the disease, concomitant pathologies or existing contraindications.
This type of fungal infection, if observed, disappears forever, without repeated manifestations and complications.
