=  Not everyone can boast of their real strong and healthy teeth. With the loss of one or more of them, dentures, implants and crowns made of various materials come to the rescue.
Not everyone can boast of their real strong and healthy teeth. With the loss of one or more of them, dentures, implants and crowns made of various materials come to the rescue.
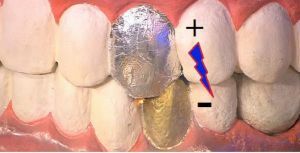
However, foreign objects in the mouth, especially of chemical origin, can cause a number of complications, one of which is galvanization - the occurrence of an electric current in the mouth in a person with installed dentures or metal crowns.
Contents of
- Where to find the root of the problem?
- Nature of the clinical picture of
- Diagnosis of
- Stages of therapy of
- Through how many passes?
- Complications and consequences
- Preventive measures
Where to find the root of the problem?
In recent years, in the dental practice, cases of galvanic disease have become more frequent, and this has been directly related to the individual intolerance of materials, on the basis of which crowns and prostheses are made.
To date, about ten chemical compounds are used to make crowns, implants, bridges and other types of prosthesis, among which there are both metals and non-metals.
The most common of these are: stainless steel, cobalt compounds, alloys from palladium, chromium, and 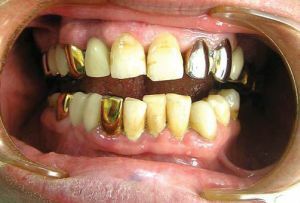 compounds, which include gold and even platinum. Material for alloying individual parts in this case can be: copper, silver, magnesium or manganese.
compounds, which include gold and even platinum. Material for alloying individual parts in this case can be: copper, silver, magnesium or manganese.
The cause of galvanism in this case may be the individual intolerance of a material. Before installing the prosthesis, the dentist often does not even think that the patient may have such a reaction to the material. One component may suit one patient perfectly, while another may have serious problems in the same situation.
Another reason for this disease may be the presence in the oral cavity of alloys from several metals, which leads to the appearance of galvanic current.
Nature of the clinical picture
The disease is characterized by a negative effect of galvanic electrical flows in the oral cavity, due to the emerging electrochemical processes between the metal parts of foreign structures in the mouth.
Negative changes can be felt a few months after the prosthesis or as a result of replacement or supplementation with new designs of metal, gold, chromium and cobalt.
Symptoms of developing galvanization in the oral cavity:
- is a characteristic metallic taste in the mouth;
- sour taste, which does not disappear after eating, nor after cleaning the prosthesis;
- itching of the gums, as well as pain sensations, manifested by burning;
- is a disorder and change in taste buds, so when eating sweet foods, they can be felt as bitter or acidic;
- dry mouth;
- frequent headaches, which causes the patient to become irritable and may feel a loss of strength and weakness throughout the body( symptoms similar to the initial stage of a cold disease).
 In medical practice, there are two forms of the disease, namely: typical and atypical.
In medical practice, there are two forms of the disease, namely: typical and atypical.
A typical form manifests itself in pronounced symptoms, so it is much easier to diagnose it. In this case, if you do not get rid of the cause of the disease, it will progress to months and even years.
Atypical form of galvanosis occurs in most cases asymptomatic and only in some cases there may appear single signs characterizing the disease.
Diagnosis of
Diagnosis is performed using a special measuring instrument. However, even in modern and specialized dental offices such a device is a rarity.
In the course of diagnosing with the aid of a special device, bioelectromagnetic activity is measured. In this case, the  site of the oral mucosa adjoining the prosthesis is measured. If the indicators differ from the norm by 30% or more, the diagnosis is confirmed.
site of the oral mucosa adjoining the prosthesis is measured. If the indicators differ from the norm by 30% or more, the diagnosis is confirmed.
In the absence of a special measuring device, a doctor can determine the diagnosis based on his medical experience, based on the symptoms that the patient displays.
A dentist can assign a spectral examination of a saliva to a patient. This analysis determines the content of trace elements in the saliva, which could get into it during the oxidation of the metal, if the result is positive, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Stages of therapy
Treatment of galvanism begins with the elimination of the causes that caused the disease, for this doctor dentist thoroughly studied the oral cavity and removed from it all the metal structures that caused the violation.
If their removal does not lead to an improvement, in this case the patient is advised to completely replace the prosthesis, mainly on homogeneous metals that are not capable of causing galvanization.
 If in the course of the development of the disease in the oral cavity there was an abscess, then it should be opened surgically and removed from it purulent formations.
If in the course of the development of the disease in the oral cavity there was an abscess, then it should be opened surgically and removed from it purulent formations.
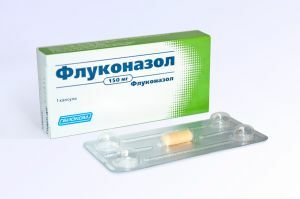
In the course of treatment, the patient may also be prescribed antifungal drugs such as Fluconazole and Terfenadine, but these medications have contraindications: individual intolerance to one of the components, as well as liver failure.
In addition, the appointment of immunostimulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, if necessary, antibiotics, as well as sedatives.
Through how many passes?
If galvanosis is diagnosed at an early stage, then immediately the appropriate treatment was prescribed, then the prognosis is positive.
In this case, you can get rid of the symptoms after a few days after the removal of the prosthesis, which provoked the ailment.
To heal completely, if during the development of the disorder there were no concomitant illnesses within a month, or even earlier. If there were complications, the process of recovery may take several months.
Complications and consequences
One of the permanent satellites of galvanism is the weakening of the immune system in the human body. As a result, other concomitant diseases that are not directly related to the oral cavity, namely acute respiratory disorders, bronchitis, and also herpes can develop.
In addition, if the atypical form of galvanose is not diagnosed in time, the consequences can be very serious and give an impetus to the development of oncology of the maxillofacial department.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of walking currents in the oral cavity, it is necessary to choose crowns and bridges from whole metals. If the  plant uses alloys, then you need to make sure that they are compatible with each other.
plant uses alloys, then you need to make sure that they are compatible with each other.
When installing crowns, bridges or other prosthetics, you must visit the dental office twice a year for examination and consultation with your doctor.
Regularly conduct hygiene of dentures. If you experience any discomfort or discomfort in your mouth, you should immediately contact your doctor or dentist.
If all of the above rules are followed, the risks of galvanization and other related diseases will be minimal.
