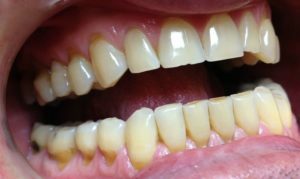
 Among the non-carious diseases of the teeth, the so-called wedge-shaped defect is widespread. It resembles cervical caries in appearance, but has a different origin. It is a wedge-shaped flaw on the outside of the tooth in the cervical region. The sharp part of the wedge is directed to the base of the tooth.
Among the non-carious diseases of the teeth, the so-called wedge-shaped defect is widespread. It resembles cervical caries in appearance, but has a different origin. It is a wedge-shaped flaw on the outside of the tooth in the cervical region. The sharp part of the wedge is directed to the base of the tooth.
This damage often affects those teeth, which have the greatest load - these are premolars and molars. The defect is less common on the front teeth, but can affect the fangs.
Tapered denudation is usually not accompanied by a change in the color of the enamel. If pigmentation is observed in the lesion, then this indicates the spread of erosion to the deep layers of the tooth. In severe lesions, there is an increased sensitivity.
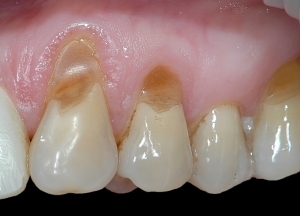
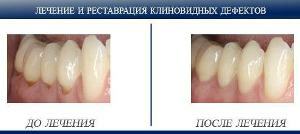
In the picture, a wedge-shaped defect in the teeth of the upper jaw
The wedge-shaped defect affects the teeth of both the upper and lower jaws, but the lower teeth suffer from this disease more often due to increased load.
The sphenoid lesion is characterized by slow growth rates and can develop imperceptibly for the patient for several years.
The erosion of the enamel has the correct form, which distinguishes it from the manifestations of a carious character. It is noted that over the past decade the number of patients with this disease has increased significantly, with the overwhelming majority of patients are women over 30 years old.
Contents of
- Reasons for a deviation
- Classification of defeat
- How to treat a pathology?
- The complexities of effective treatment
The causes of the deviation
 Dentists put forward several versions as to the causes provoking wedge-shaped erosion. The main factor is improper hygiene of the oral cavity, namely horizontal brushing of teeth with a rigid brush.
Dentists put forward several versions as to the causes provoking wedge-shaped erosion. The main factor is improper hygiene of the oral cavity, namely horizontal brushing of teeth with a rigid brush.
Horizontal movements during tooth cleaning are generally contraindicated, only the vertical and circular stroke of the brush is allowed.
Surface-active substances in the composition of hygiene products also contribute to the elution of enamel. The same action has different acids, including juices of citrus fruits and other berries and fruits.
The following are not so common, but there are reasons to be:
- According to another version, the cause of erosion of the enamel can be incorrect bite of , which is found in the overwhelming majority of the world's population. The load on the teeth spreads unevenly, which leads to the thinning of enamel in the most loaded areas.
-
 Frequent application of whitening formulations for teeth can also lead to erosion in the cervical area. It is noted that the risk of wedge-shaped cavity formation increases in the presence of GI diseases due to increased acidity in the mouth. The same happens in the presence of endocrine disorders and diseases of the nervous system.
Frequent application of whitening formulations for teeth can also lead to erosion in the cervical area. It is noted that the risk of wedge-shaped cavity formation increases in the presence of GI diseases due to increased acidity in the mouth. The same happens in the presence of endocrine disorders and diseases of the nervous system. - Natural calcium leaching with hormonal disorders is observed in women aged 35-40 years. The presence of concomitant diseases of the digestive system aggravates the situation and contributes to the faster destruction of enamel.
- Gum disease is also one of the reasons for the development of a wedge-shaped defect. With gingivitis, the enamel is significantly weakened and the cervical areas of the tooth are destroyed.
More details on the formation of a wedge-shaped defect:
Classification of lesions
There are four stages of enamel destruction:
-
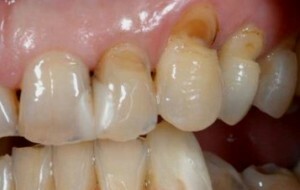
Deep affection
Initial - erosion of the enamel is invisible when viewed, although there is a loss of gloss and uniformity. In the area of initial loss, pain can be felt due to increased sensitivity to various stimuli.
- Average - is characterized by significant damage to the enamel, the level of hyperesthesia is increased.
- Progressive - defect depth may be of the order of 4 mm. Clearly visible wedge-shaped lesions with a sharp point.
- Stage of deep lesion - erosion reaches 5 mm or more. Degenerative processes affect the inside of the tooth. Together with the loss of enamel, pigmentation of the tooth can be observed due to the damage to the dentin.
How to treat a pathology?
Depending on the extent of the lesion, appropriate treatment is prescribed, which includes the elimination of irritating factors, proper oral hygiene, orthodontic measures.
 For deformations of small dimensions, sealing is not required. Wedge-shaped formations are filled with special dental compositions that eliminate hypersensitivity and prevent further destruction.
For deformations of small dimensions, sealing is not required. Wedge-shaped formations are filled with special dental compositions that eliminate hypersensitivity and prevent further destruction.
Usually, the method of fluoridation of enamel is used, which implies the use of formulations with a high content of fluoride or special applications. Remineralizing therapy is also prescribed to restore calcium deficiency in enamel.
High results allow to achieve paste with fluorine content. However, in order for the effect to have a prolonged effect, the pastes must be used for a long time.
Fluorine-containing oral hygiene products are recommended as prevention of erosion and loss of enamel.
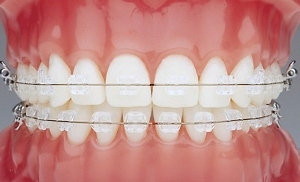 Fluoride on reception at the stomatologist means drawing of special highly concentrated compositions.
Fluoride on reception at the stomatologist means drawing of special highly concentrated compositions.
For home use, special varnishes and gels are usually prescribed, the use of which is of course character.
If the wedge-shaped defect is a consequence of an incorrect occlusion, the orthodontist can advise special braces, taking into account the age and physiological characteristics of the patient. For alignment of teeth, other methods can be recommended: partial grinding, straightening of the antagonist tooth by using crowns.
When the enamel is deeply affected, restoration of the tooth is necessary, which is carried out by means of a filling material. Composite compositions or glass ionomer cement are used to fill the loss. Since the lesion is not a consequence of carious spreading, a drill hole is not required. However, for a better fixation of the seal, special incisions are made on the enamel.
 Filling solves the problem of hypersensitivity and aesthetic appeal. It can also be recommended to install veneers, which are microprostheses and are selected taking into account the defect of the tooth. Veneers are installed with a significant loss of tissue, when the filling is ineffective or impossible.
Filling solves the problem of hypersensitivity and aesthetic appeal. It can also be recommended to install veneers, which are microprostheses and are selected taking into account the defect of the tooth. Veneers are installed with a significant loss of tissue, when the filling is ineffective or impossible.
In case of severe damage, prosthetics is recommended. Therapeutic treatment at the fourth stage of the lesion is similar to the treatment in the early stages.
Patient is assigned remineralization of the cervical region and fluorination of the affected area. When establishing prostheses, it is important to carry out complex therapy, otherwise the probability is high that the disease will progress, and under the prosthesis, voids are formed, into which the food particles will enter. This will lead to the formation of a carious cavity and tooth decay.
Complexities of effective treatment of
 When treated with the methods of tooth reconstruction, difficulties can arise due to improper diagnostics and a feature of damage. Sealing often does not have a lasting effect, as the fillings are destroyed or completely drop out for a short period of time.
When treated with the methods of tooth reconstruction, difficulties can arise due to improper diagnostics and a feature of damage. Sealing often does not have a lasting effect, as the fillings are destroyed or completely drop out for a short period of time.
This is due to the fact that the cervical zone experiences the most severe load, and during the chewing process the seal is squeezed out of the cavity. The incisions on the enamel contribute to a better penetration of the composition, but they do not completely solve the problem of loss of fillings.
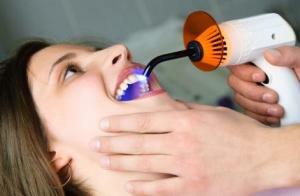 To liquidate wedge-shaped defects, liquid formulations with a high coefficient of elasticity are recommended. They are applied to the treated surface with a special syringe and are inspected by a lamp. This material, under load, responds to them by micro-compression, which saves the seal from extrusion.
To liquidate wedge-shaped defects, liquid formulations with a high coefficient of elasticity are recommended. They are applied to the treated surface with a special syringe and are inspected by a lamp. This material, under load, responds to them by micro-compression, which saves the seal from extrusion.
Another problem of treating the cervical area is its preparation for the main procedures. Close proximity to the gums significantly increases the risk of saliva entering the cavity, which is undesirable for filling and prosthetics.
In the process of restoration, bleeding of the gums may start, especially if it is a wedge-shaped defect in the background of periodontitis. Qualitative drying of the affected area will significantly increase the chance of successful treatment and effective restoration.
To keep the seals longer, you should follow simple rules:
-
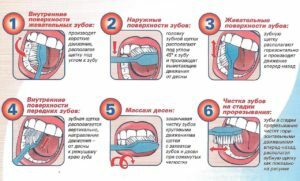 correctly clean the oral cavity using a brush;
correctly clean the oral cavity using a brush; - use an elixir for cleansing between meals;
- brush your teeth immediately after consuming acidic foods;
- fruit juices preferably drink through straw, without delaying the acidic environment in the oral cavity;
- refuse to use hard products, for example, crackers, nuts, etc.;
- exclude from the diet chewing sweets and carbonated drinks.
If this problem is solved, further damage to the teeth can be avoided. In any case, in the presence of at least one lesion, fluorine-containing pastes, protective varnishes and preparations containing calcium should be used for prophylaxis.
