 In dental practice, surgery for tooth extraction( extraction from the dental alveolus) is a common but difficult and traumatic manipulation. Tooth extraction is performed when its treatment is impossible, or the treatment tactics can not provide the proper effect.
In dental practice, surgery for tooth extraction( extraction from the dental alveolus) is a common but difficult and traumatic manipulation. Tooth extraction is performed when its treatment is impossible, or the treatment tactics can not provide the proper effect.
Surgical intervention is carried out for medical reasons: significant destruction of dental tissue( deep caries), inflammatory processes of the radical areas in the dental cavity, damage to the roots of the tooth and other dental diseases.
With a qualitatively performed operation, complete healing of the gum after tooth extraction occurs after 2-3 weeks. Edema and redness of the gums should go through one week on their own. The restoration of bone tissue takes more time - 2-3 months. However, sometimes after tooth extraction can occur complications - in the hole is formed pus, the gum inflames. It is important to correctly identify the cause of complications, to know the primary symptomatology, the basic rules of treatment and prevention of postoperative consequences.
Contents of
- Gnathing as a complication of extraction of
- What are the symptoms accompanying?
- What can and should be done?
- Prevention of postoperative complications
- What is dangerous?
Exposure as a complication of
extraction In specialized dental clinics, extraction operations are performed with strict adherence to surgical intervention technology, using sterile medical instruments according to GOST.
However, even with a qualitatively performed operation complications can occur. Most often this is due to the weakening of the patient's 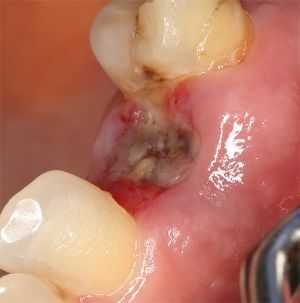 immunity. Even with exceptionally sterile instruments and observance of postoperative wound processing technology, if the defenses of the body are not able to withstand the bacterial environment of the oral cavity, inflammation of the socket and gingiva begins to fester.
immunity. Even with exceptionally sterile instruments and observance of postoperative wound processing technology, if the defenses of the body are not able to withstand the bacterial environment of the oral cavity, inflammation of the socket and gingiva begins to fester.
It should also be taken into account that tooth extraction is associated in most cases with purulent complications of caries( pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis).Aggressive bacteria( staphylococci, streptococci) expand the area of the lesion and can cause inflammation of the socket.
Another cause of inflammation and suppuration of the wound after surgery can be non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
After completion of the operation, a qualified dentist always gives advice on the care of the gums and teeth. It is in the patient's best interest to strictly follow these recommendations.
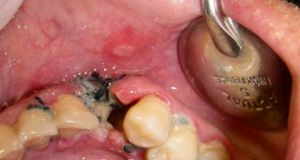
Violation of the technique of the operation, mechanical damage to the walls of the well can also provoke an inflammatory process at the site of the removed tooth. An open wound that is formed after tooth extraction, is exposed to the pathogenic environment of the oral cavity and, without proper treatment, becomes infected - purulent formations form in the hole. At the first symptoms of the alveolitis( inflammation of the dental hole), you should immediately contact your dentist for help.

Alveolitis( pictured right) after removal of the tooth provokes the release of purulent exudate in the hole
What are the symptoms accompanying?
In addition to the festering and inflammation of the gums, the complications resulting from the tooth extraction operation are manifested by the following symptoms:
- the onset and increase of the pain syndrome( severe pulling and pulsating pain in the gum area), while the pain does not pass by itself, lasts forfor several days;
- appearance of bad breath from the mouth, purulent exudate from the injured gingival part is exposed, there is soreness and puffiness of the hole, swelling of the face;
- redness of the hole, the appearance of cyanosis due to venous stasis;
- deterioration of state of health, general weakness, fatigue, lethargy, intense headache;
- increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above, chills, muscle pain;
- difficulty in swallowing and chewing food.
The development of the inflammatory process is signaled by such reactions of the body as a shooting pain in the region of the jaw that gradually spreads to the area of the temple and along the trigeminal nerve. If any of these symptoms occur, seek medical attention immediately.
What can and should be done?
The main principle of treatment of possible consequences after tooth extraction is timeliness. With the very first symptoms of 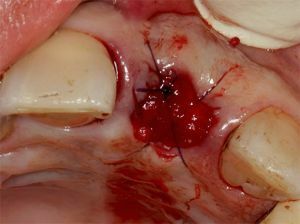 inflammation and suppuration, you should seek qualified dental care. The sooner the treatment begins, the better the chances of recovery. Otherwise, serious consequences may occur, the therapy will become difficult and financially costly.
inflammation and suppuration, you should seek qualified dental care. The sooner the treatment begins, the better the chances of recovery. Otherwise, serious consequences may occur, the therapy will become difficult and financially costly.
Conservative treatment tactics include the use of antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is important to carry out antiseptic procedures.
It is not recommended to clean the well of pus by itself, it should only be done by a dentist. After careful cleaning, the wells can be filled with the medicine.
Antibiotics for a long time in the inflammation zone can cope well with purulent secretions from the gums and wells. Drugs with a high penetrating ability include Sumamed, Azitral, Karitromycin( macrolide antibiotics), lincosamides, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones.
Antiseptic preparations are prescribed for mouth rinsing: 
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Furacilin;
- Cortisol;
- Hexoral;
- Stomatidin, etc.
To relieve inflammation, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are effective: Meloxicam, Voltaren, Nurofen, Ketonal, Ibuprofen, Nimesulid, etc.
Often in the treatment of alveolitis, Finlepsin is prescribed, which effectively relieves neurologic pain, normalizes the patient's mental state, improves mood.
At home, you can rinse the mouth with the use of a bark of oak, tea tree oil, sage broth, chamomile, calendula, and root of ara.
If the gingiva is suppurative, then pus can be removed surgically:
Prevention of postoperative complications
Prevention of suppuration and other consequences possible after extraction is based on the creation of conditions for the formation of a durable blood clot in the hole.
To prevent the development of inflammation and the formation of ulcers, it is necessary to perform a number of preventive measures:
- to carefully treat the wound, remove the bone debris, the fragments of the tooth;
- when removing a tooth due to a purulent complication of caries, you should remove granuloma and do not perform early mouth rinses to prevent the blood clot from washing away;
- in order to prevent the decay of a blood clot under the influence of infection due to chronic diseases to provide therapy with antibiotics with intramuscular injection, alternating them with injections around the wound.

This should be a wound after extraction of
. What is dangerous?
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment of pus and inflammation in the hole can lead to the development of serious pathologies. This is due to the growth of the zone of influence of the resulting infection. As a result, respiratory failure and pulmonary edema may occur.
In case, after the extraction of the tooth, the gum is suppurating, but nothing to do for treatment, the process can spread to other teeth and soft tissues, osteomyelitis develops.
Therefore, in order to avoid dire consequences after extraction, all dentist recommendations must be strictly observed. If there are first signs of inflammation in the hole, as evidenced by the formation of pus, do not engage in self-medication, you need to go to a dental clinic and conduct therapy under the supervision of a doctor.
