 On the status of the language, serious diseases can be detected in time, which have not yet appeared in the form of characteristic symptoms. It is this body, which is often neglected, reacts to the slightest changes inside the body and in the external environment.
On the status of the language, serious diseases can be detected in time, which have not yet appeared in the form of characteristic symptoms. It is this body, which is often neglected, reacts to the slightest changes inside the body and in the external environment.
It is important to learn how to read the signals you give, especially when tracking the condition in children.
Babies are not able to complain of discomfort and weakness, it is difficult for children to express the exact nature of the symptoms, so you should be guided by other signs. Language in this situation will be the best assistant.
Content of
- What should be the language of a healthy child
- At risk group - kids
- Why does the child have a hive older than the year
- What should I do?
How the tongue should be in a healthy child
The tongue of a healthy baby has a homogeneous light pink color. The body is flexible, soft and flexible. The papillae are velvety, do not stand out against the general background. Although the presence of a plaque is considered a deviation from the normal state, the following situations are permissible:
-
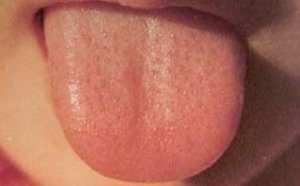
The language of a healthy child
is a slight white coating in the language of the child after sleep, which is easily eliminated after hygienic procedures and does not appear during the day;
- light milky color in infants after breastfeeding or baby food;
- the normal color of the language without visible deviations with a thin layer of subtle plaque also should not cause concern.
The huge influence on the presence of the plaque is exerted by external factors:
- The humidity and temperature of can affect the language status, but it will not signal the presence of diseases. For example, at elevated temperatures, the thickness of the plaque increases, and at low humidity, the tongue loses its velvety.
- In this connection, climate change, lack of vitamins and taking medications can change the appearance of the language, but this does not mean it's time to sound an alarm.
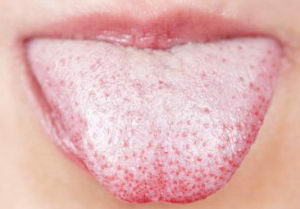 There may be many reasons for the appearance of white plaque in children. Often they are grouped into dangerous and safe. If the former are caused by diseases of different etiologies, the latter are associated with adaptive features and physical phenomena.
There may be many reasons for the appearance of white plaque in children. Often they are grouped into dangerous and safe. If the former are caused by diseases of different etiologies, the latter are associated with adaptive features and physical phenomena.
Also, the reasons may vary depending on the age of the child. In the period up to one year, the oral mucosa is not yet formed, so the sources of white plaque are the problems associated with its damage. In an older age, there are very different difficulties.
At risk group - babies
If a white coating appears on the tongue of a newborn baby, you should observe its condition and the events preceding the change in the state of the shell of the tongue.
If the behavior is not different from everyday, and the plaque passes after rinsing the mouth with boiled water, the reasons lie in the adherence of remnants of the mixture, breast milk or recent regurgitation.
Separately, it is worthwhile to consider the more serious problems reported by the white plaque in the language of the infant.
These are the following:
-
 Dysfunction of the digestive tract .This includes an impressive list of problems, for example, eating disorders, early feeding, dysbacteriosis, gastritis, acidity, constipation. The latter diseases, if not related to diet, are often peculiar to babies in connection with hereditary factors. In any case, you need to carefully monitor the baby's nutrition, as in the first year of life, the body adapts and strengthens all systems, including digestive organs. For babies there is a dysbacteriosis, which is manifested by pains in the abdomen, a dense film on the tongue, a bad weight gain and rashes on the body.
Dysfunction of the digestive tract .This includes an impressive list of problems, for example, eating disorders, early feeding, dysbacteriosis, gastritis, acidity, constipation. The latter diseases, if not related to diet, are often peculiar to babies in connection with hereditary factors. In any case, you need to carefully monitor the baby's nutrition, as in the first year of life, the body adapts and strengthens all systems, including digestive organs. For babies there is a dysbacteriosis, which is manifested by pains in the abdomen, a dense film on the tongue, a bad weight gain and rashes on the body. - Diseases of the oral mucosa .Children under one year are prone to stomatitis, since the microflora of the oral cavity is not yet formed. The most common variety is candidiasis or, in other words, thrush. It manifests itself in a dense, curdy bloom. The general well-being of the child worsens.
- Infectious and viral diseases .They include chicken pox, measles and many similar diseases.
-
 Nervous system disorders .Neuroses become the source of a thick white coating on the tongue. Another symptom of this cause is the imprint of teeth on the edges of the tongue.
Nervous system disorders .Neuroses become the source of a thick white coating on the tongue. Another symptom of this cause is the imprint of teeth on the edges of the tongue. - Anemia .In addition to the white plaque on the tongue, the baby has an increased dryness in the oral cavity.
- The lack of vitamins .For infants, this condition is dangerous, since the body programs the operation of all systems on the basis of the micronutrients obtained. With breast milk, a sufficient number of useful substances, but provided a balanced diet of the mother. At artificial feeding it is recommended to study structure, and also to follow advice or councils of the pediatrist on input of complementary foods.
- Immunodeficiency .
- Diabetes mellitus .
- The use of strong medications .
- Allergic reaction .
As a child, one can judge the presence of serious diseases, since they rarely manifest asymptomatically. The appearance of a plaque on the tongue, deterioration of sleep and nutrition are the main indicators of the presence of problems.

Children under one year are rarely prone to serious illnesses, and often the most dangerous of them can be thrush, which manifests itself in the form:
- curdled plaque in the tongue, the sky, the inside of the cheeks;
- poor sleep and lack of appetite;
- burning in the mouth;
- bad breath;
- presence of sores, but not always.
Why still a baby can have a white coating:
Why does the child have a plaque over the year
Children older than one year have already formed the oral mucosa, so with strong immunity they rarely have symptoms of thrush. But this does not exclude more serious problems associated with the above-described diseases.
 The color of the plaque and its consistency vary with the presence of respiratory tract diseases caused by bacteria or viruses. In case of influenza and acute respiratory disease white coating is accompanied by fever, but if it is localized not in tongue but on tonsils, then the cause is angina.
The color of the plaque and its consistency vary with the presence of respiratory tract diseases caused by bacteria or viruses. In case of influenza and acute respiratory disease white coating is accompanied by fever, but if it is localized not in tongue but on tonsils, then the cause is angina.
At the front of the tongue, the plaque is formed in bronchitis. Education acquires a foamy structure when the disease of the respiratory tract develops into a chronic form. In the presence of complications, white coating thickens and acquires a pronounced color, which later begins to darken. A viscous coating on the tip of the tongue speaks of bronchial asthma.

In the photo, the language with scarlet fever
Another common reason for changing the color of the tongue are infectious diseases. With scarlet fever, the whole tongue becomes white, red islets appear. The disease is most common in children 2-6 years old. Additional signs of the disease are:
- intoxication;
- rash over the body;
- redness of the throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- color of the tongue and tonsils in a yellowish white color.
Diphtheria affects not only the tongue, but also the pharynx, larynx, nose, eyes. Plaque with this infectious disease from white color flows into shades of gray.
Health indicator language
In case of gastrointestinal problems, it is necessary to pay attention to where the plaque is located and whether there are any other changes in the language. For example, with gastritis, plaque is formed in the center of the tongue. The organ shows cracks and grooves along the edges. The color of the plaque can go from white to brown. With enterocolitis, the plaque is located at the base of the tongue. The disease makes itself felt:
- bloating;
- colic;
- problems with stools;
- presence in feces of blood or mucus.
Psoriasis can manifest itself in the tongue. In this disease, the plaque is more like a plaque that rises high above the mucous surface of the organ. Color varies from white to gray.
Allergy can be manifested in different ways. Most often, the tongue acquires a pronounced red hue, on it light watery vesicles are formed.
Another dangerous condition with the appearance of white plaque is dehydration. There is weakness, sluggishness, dry mouth, light pink color of the tongue with a rough structure, an increase in papillae.
What should I do?
In the presence of white plaque, you need to contact a pediatrician who will assess the situation and, if necessary, refer to a specialist. It can be a dentist, an infectious disease specialist, a dermatologist or a gastroenterologist.
 Only after the carried out research the diagnosis will be diagnosed and the course of treatment is appointed. In connection with a wide range of possible diseases, diagnosis may take some time. Only complete elimination of the cause will remove the problem with the plaque on the tongue.
Only after the carried out research the diagnosis will be diagnosed and the course of treatment is appointed. In connection with a wide range of possible diseases, diagnosis may take some time. Only complete elimination of the cause will remove the problem with the plaque on the tongue.
In children up to a year the scurf in the tongue is scraped off with the help of a soda solution, which is wiped with a tongue. Since kids are prone to food allergies, lotion on honey water is recommended to do after reaching the age of one year. Hygienic treatment is carried out several times during the course of the day, especially after eating.
From one year to two years, viral and infectious diseases are a common cause, therefore  treatment is performed with special medications. A course of immunostimulating drugs may be prescribed.
treatment is performed with special medications. A course of immunostimulating drugs may be prescribed.
At a later age, a large range of diseases can manifest, which must be treated strictly according to the prescribed course. To combat plaque in the language, all the above methods, herbal solutions, as well as special scraping brushes are allowed.
White coating in infants is often not a dangerous signal, but at an older age, parents must take appropriate measures to identify the problem.
Focusing only on the condition of the tongue, it is possible to identify the incipient disease in a timely manner. From this, the process of its treatment will be much easier.
