Content
- Corpus luteum formation
- Why is it yellow
- Pathology of the corpus luteum
- Lack of work of the corpus luteum
- Corpus luteum cyst
- The mechanism of occurrence of the cyst of the corpus luteum
- Classification and stages of development of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
- Causes of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
- Medicines to regulate the menstrual cycle
- Emergency contraceptive drugs
- Inflammatory diseases
- Surgical interventions and chronic diseases
- Psychological and physical disorders
- Hormonal disbalance
- Weight loss
- Symptoms of the cyst of the corpus luteum
- Can a corpus luteum cyst hurt: signs of growth
- Diagnostics of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
- Treatment of corpus luteum cysts
- Drug therapy
- Physiotherapy treatment
- Laparoscopy
- Is it possible to cure a cyst of the corpus luteum without surgery
- Why is this disease dangerous?
- Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
- Menstruation with a cyst of the corpus luteum
- Delay on cyst
- Questions and answers about corpus luteum cyst
- Risk group
- Prevention and prognosis for cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
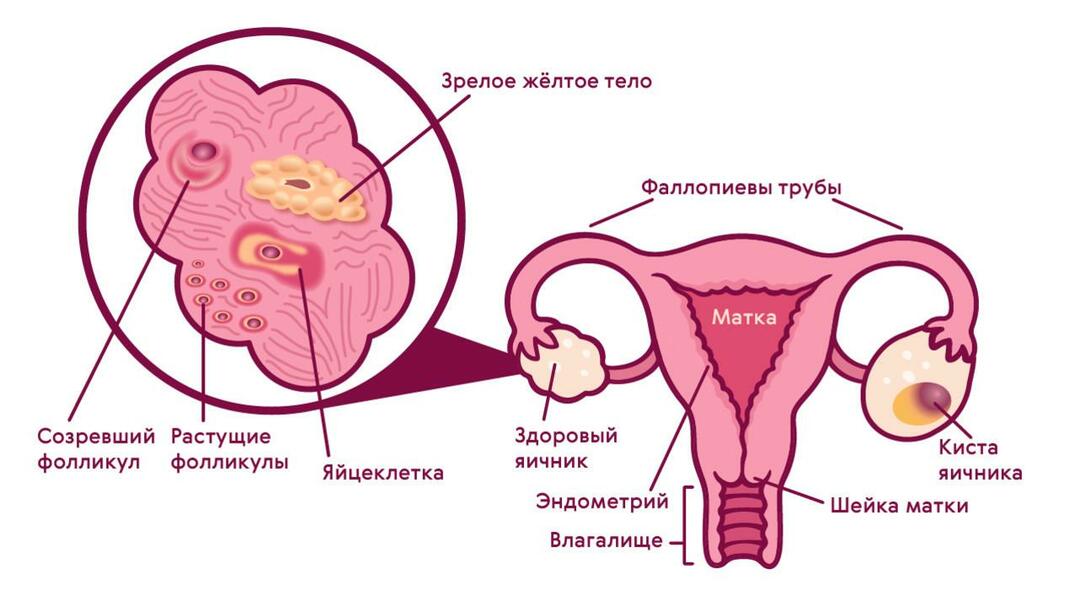
Corpus luteum formation
The corpus luteum, it is also the luteal body, is an endocrine gland that occurs immediately after each ovulation in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. The main function of this gland is to prepare the body for conception and bearing a child in the first 4 months, until the placenta is fully formed.
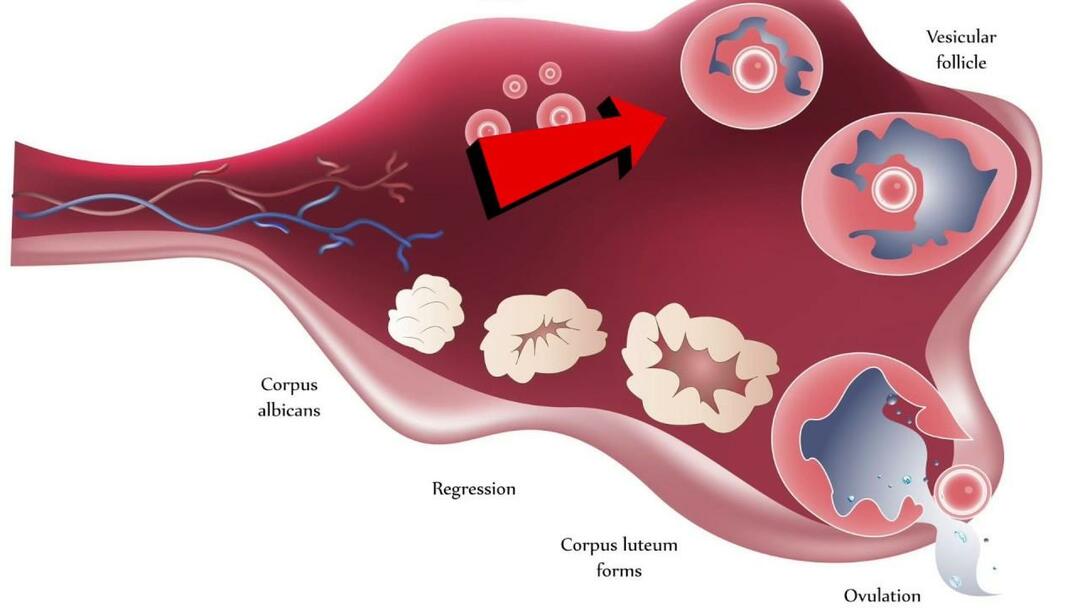
The corpus luteum is formed after the release of the egg from the follicle after ovulation. The process of maturation of the corpus luteum takes place in several stages:
- Polyiferation, characterized by active cell division, the formation of lutein, the accumulation of yellow pigment, the acquisition of characteristic shapes and sizes.
- Vascularization, in which the gland enlarges and acquires its own circulatory system.
- It flourishes when the gland reaches its maximum size.
- Regression occurs in the absence of fertilization and is accompanied by atrophy and disappearance of the corpus luteum.
If, for some reason, regression does not occur, the corpus luteum begins to accumulate serous fluid and blood, a dense capsule forms - a cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary.
Why is it yellow
In the process of formation of the corpus luteum, granulosa cells located inside the follicle and theca-luteocytes that cover the folds of the walls of the former follicle are involved. Due to the accumulation of lutein substance, these structures have a yellowish tint, therefore, the formation that appears in the ovary after ovulation is called the corpus luteum.
During its development, this gland first increases in size, its cells swell and gain a lot of yellow pigment. Then, for 12-14 days, she will produce the hormone progesterone, which supports conception and implantation. During this period, the corpus luteum looks like a large dark spot with heterogeneous contents on ultrasound of the small pelvis.
Pathology of the corpus luteum
In women of fertile age, pathologies of the corpus luteum are found.
Lack of work of the corpus luteum
Insufficiency of the corpus luteum, which is responsible for the production of progesterone, can provoke an inability to conceive, fetal freezing in the early stages of pregnancy, or miscarriages. It is possible to diagnose this pathology only by the results of a comprehensive examination, consisting of ultrasound, construction charts of basal body temperature for 2-3 menstrual cycles, tests for the amount of progesterone in blood. You will also need an endometrial biopsy.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed progesterone-containing hormonal drugs, for example, duphaston or urozhestan. Also effective is a course of natural progesterone injections, which can continue even with a confirmed pregnancy up to 12-13 weeks to prevent breakdowns. Also, if the formation of the corpus luteum in the ovary is insufficient, drugs such as dostinex or bromocriptine, etc. may be recommended.
Corpus luteum cyst
The corpus luteum cyst is a functional formation that forms at the site of the corpus luteum during the menstrual cycle. A cyst of this origin is often diagnosed in clinical practice. It can occur in patients of reproductive age.
The mechanism of occurrence of the cyst of the corpus luteum
The cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary is a tumor-like cavity formation filled with serous or hemorrhagic fluid. The cyst is formed from the corpus luteum - a temporary endocrine gland of the female body, which develops in the second (luteal) phase of the menstrual cycle at the site of the ovulating follicle. If fertilization has not occurred, the corpus luteum undergoes a reverse development and gradually resolves and disappears.
Normally, its dimensions should not exceed 23-25 mm.
However, in some cases, this mechanism is disrupted, and the corpus luteum does not dissolve. This leads to impaired blood circulation inside the ovary and the accumulation of serous or hemorrhagic fluid, concentrated in the place of the corpus luteum. As a result, a capsular cavity is formed in the ovary - a corpus luteum cyst. Like another type of functional cyst (follicular), it tends to dissolve on its own over several menstrual cycles.
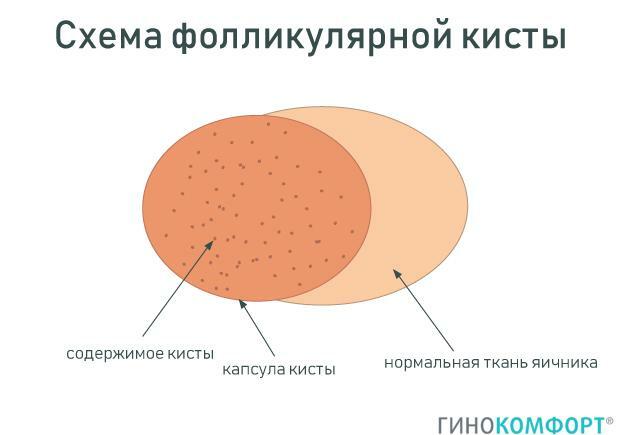
Such a cyst belongs to benign formations. If its size is small (up to 4 cm), it is considered harmless, but it still needs supervision. If the dimensions are from 4 to 8 cm, there is a risk of rupture of the cyst cavity of the corpus luteum with hemorrhage or hemorrhage into the cyst capsule. In such cases, it is usually recommended to take hormones to accelerate resorption, or to remove it surgically so that it does not burst.
Normally, the maturation of the dominant follicle should occur alternately in the right and left ovary.
But, despite this, in many women, the right ovary works more actively than the left. This just explains why the cyst of the corpus luteum of the right ovary is observed somewhat more often than a similar pathology of the left organ.
Classification and stages of development of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
Depending on the internal structure, there are 2 types of cystic neoplasms:
- Single sheet. They represent one cavity, the surface of which is formed from epithelial glandular cells.
- Multi-cavity. Consists of several interconnected cavities. Such a tumor develops relatively rarely, but in the absence of treatment, it causes serious complications: inflammation, suppuration, capsule rupture.
Taking into account the place of localization, the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary is:
- left-sided;
- right-sided.
Due to the anatomical features of the location of the ovaries, a tumor of the corpus luteum is more often formed on the right.
The disease proceeds in 3 stages, each of which is characterized by a peculiar clinical picture:
- Early. At this stage, the tumor is insignificant, so it does not bring significant concern to the woman. Diagnosis of pathology often occurs during a routine preventive examination by a gynecologist. If the cyst is stable, treatment is not yet prescribed, because in most cases it disappears on its own.
- Progressive. At this stage of development, a woman begins to be bothered by pathological symptoms, which should be a reason to immediately visit a gynecologist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. In most cases, at this stage, conservative treatment is prescribed, which is carried out by sweat with the careful supervision of a specialist.
- Launched. The cyst has become large, squeezes the nearby organs, causing disruption of their functioning. In the last stages, surgical treatment is carried out, because conservative methods are powerless here.
Causes of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
There is still no exact opinion in clinical gynecology about the question of what factors contribute to the development of a corpus luteum cyst. The main reasons that modern medicine distinguishes:
- Hormonal disorders: deviations in one direction or another of the hormones produced inside the female body, can lead to the formation of an ovarian cyst;
- Medicines aimed at instant contraception during intercourse. The intake of such drugs is based on the consumption of hormones, the concentration of which increases sharply after absorption into the blood by the body;
- Medicines to regulate the menstrual cycle. This category is also a potent risk factor for corpus luteum cysts. Recommended medications to control and stimulate ovulation during the menstrual cycle, as well as medications prescribed for infertility, can provoke a violation of the internal blood circulation of the ovarian tissue and cause favorable conditions for the formation of a corpus luteum cyst ovary;
- Psychological and physical disorders. The risk of developing an ovarian cyst increases in the presence of such reasons as constant stress; depression; difficult working conditions associated with danger; working conditions under which the body receives chronic poisoning with toxic substances; inaccuracies in diet, unbalanced nutrition, one type of diet for a long time;
- Surgical interventions and chronic diseases of the body. Unwanted pregnancies that continually lead to abortion increase the risk of corpus luteum ovarian cysts. Diseases such as oophoritis and salpingo-oophoritis can lead to the development of education.
Medicines to regulate the menstrual cycle
This category is also a potent risk factor for corpus luteum cysts. Recommended medications to control and stimulate ovulation during the menstrual cycle, as well as medications prescribed for infertility, can provoke a violation of the internal blood circulation of the ovarian tissue and cause favorable conditions for the formation of a corpus luteum cyst ovary.
Emergency contraceptive drugs
Medicines aimed at instant contraception during intercourse. The intake of such drugs is based on the consumption of hormones, the concentration of which increases sharply after being absorbed into the blood by the body.
Inflammatory diseases
A decrease in the body's defenses caused by hypothermia, exhaustion, unbalanced nutrition when infected with STDs, leads to the growth of pathogenic flora and inflammation of the ovary - oophoritis. The inflammatory process becomes the cause of a violation of the blood supply to the organ, creating conditions for the development of a cyst.
Surgical interventions and chronic diseases
Surgical interventions and chronic diseases of the body. Unwanted pregnancies that continually lead to abortion increase the risk of corpus luteum ovarian cysts. Diseases such as oophoritis and salpingo-oophoritis can lead to the development of education.
Psychological and physical disorders
The risk of developing an ovarian cyst increases in the presence of such reasons as constant stress; depression; difficult working conditions associated with danger; working conditions under which the body receives chronic poisoning with toxic substances; inaccuracies in diet, unbalanced diet, one type of diet for a long time
Hormonal disbalance
Deviations in one direction or another of the hormones produced inside the female body can lead to the formation of an ovarian cyst. Failure can be caused by endocrine diseases, dysfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, menopause. It is also worth considering hormonal stresses, which are caused by artificial termination of pregnancy, taking emergency contraception, stimulating ovulation, etc.
Weight loss
Rapid weight loss caused by fasting and adherence to strict diets can lead to weight loss. A sharp decrease in the percentage of subcutaneous fat often becomes the cause of hormonal imbalance and, therefore, the possible development of the disease.
Symptoms of the cyst of the corpus luteum
Pathology can be asymptomatic or with a mild clinical picture. Occasionally, it can provoke:
- Increased duration of menstrual bleeding;
- Bloating;
- An increase in temperature to subfebrile values;
- Delayed menstruation;
- General intoxication;
- Stool disorder;
- Increased urge to urinate;
- Abdominal pain during physical activity.
If the symptomatic picture develops on an accrual basis, this may indicate the occurrence of complications: torsion of the cyst legs or ovarian apoplexy.

Can a corpus luteum cyst hurt: signs of growth
A growing ovarian cyst in women can be complicated by rupture, suppuration, torsion of the cyst leg. The provoking factor can be sexual intercourse or physical stress. In this case, the following symptoms occur:
- intense, sudden pain in the lower abdomen;
- an increase in body temperature up to 38-39C;
- nausea or vomiting that does not bring relief;
- soreness when probing the abdominal muscles, their tension;
- tension of the anterior abdominal wall;
- constipation, flatulence with difficulty passing gas;
- sweating, pallor;
- heart palpitations (tachycardia);
- increased pain with a sharp abduction of the hand after pressing on the abdomen (Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom is positive).
In addition to the risk of malignancy, the danger of the disease is that ovarian cysts can grow and burst, become inflamed, bursting, squeezing adjacent organs, such as the intestines or bladder, and twist. Moreover, torsion of the cyst leg can occur both in isolation and together with the ovary and fallopian tube. With these complications, there is a need for emergency surgery, which is always worse than planned and prepared in advance.
Diagnostics of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
If a pathology such as a cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary is suspected, ultrasound can provide a lot of diagnostically valuable information.
That is, the size, structure, type of formation, structure and size of the ovaries, the degree of development in the last vessels, etc.
On ultrasound, this formation looks different.
The cyst is completely homogeneous or with a mesh structure.
Many displaceable partitions can be found in the cavity, dense inclusions (blood clots) near the walls or throughout the volume.
If the cyst is completely filled with blood, then it is very similar to a tumor on ultrasound.
A distinctive feature of the cysts under consideration is a rather high sound conductivity (i.e., almost complete, without reflection, passage through the formation of ultrasonic waves).
A more accurate differentiation of cysts with tumors is provided by ultrasound with color Doppler mapping (CDC).
Such a study is carried out in the first phase of the cycle.
If necessary, resort to the methods of magnetic resonance and computed tomography, laparoscopic examination.
When using methods with contrasting (the introduction of contrasts - substances that are clearly visible with this instrumental examination), the absence of accumulation of contrast by education is characteristic.
This serves as a characteristic diagnostic sign of a cyst.
Diagnostics also involves testing for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, pregnancy hormone), tumor markers (what the doctor specifically determines, often the ovarian tumor marker CA 125 is examined to differentiate with cancer).
The most common complication is hemorrhage of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary, in which significant bleeding can occur.
This condition is manifested by the symptoms of an "acute abdomen".
Treatment of corpus luteum cysts
With a small size of education and the absence of complaints, dynamic observation is shown for several cycles. This is due to the possible regression of the cyst. For the period of monitoring the cyst or conservative treatment, physical and sexual rest is prescribed. Conservative therapy has a good effect.
Drug therapy
Medications are prescribed for large neoplasms, usually therapy includes:
- Preparations containing progesterone ("Duphaston", "Utrozhestan" and others) - the action is aimed at blocking growth luteal cyst, suppression of ovulation and menstruation, which leads to the reverse development of the tumor, up to its disappearance.
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) - contain estrogens and progestins, which reduce the secretion of gonadotropins by the pituitary gland hormones, thereby inhibiting the maturation of follicles and suppress ovulation, which prevents the formation of new cystic formations. Also, drugs in this group relieve symptoms and promote cyst regression.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Diclofenac) - have analgesic antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
In each case, a specific drug is prescribed individually.
Physiotherapy treatment
Recurrent and symptomatic formations in the female genital gland can be cured by resorting to methods of conservative therapy.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal contraceptives are selected for a woman. Good results can be achieved:
- Balneotherapy (vaginal irrigation, therapeutic baths);
- Laser therapy. In the course of treatment, forced low-intensity radiation of the light range is used. It dilates blood vessels, has an immuno- and tropho-stimulating effect, and helps relieve inflammation. Also, laser therapy increases the body's susceptibility to drugs;
- Peloid therapy (mud therapy). It implies the use of crushed clay, silt or other sediments from the bottom of the sea, salt lake, fresh water reservoir. The mud heated to a temperature of 39–40 ° C is characterized by a high heat capacity. They have a pronounced thermal effect (increase the temperature of tissues locally), have a positive chemical effect;
- CMT therapy. During treatment, a modulated high frequency current is used. It creates separate "bursts" of pulses, separated by short pauses. The procedure relieves pain, dilates blood vessels;
- Medicinal electrophoresis. It involves the introduction of drugs through the skin and mucous membranes using an electric current. As a result of treatment, the maximum concentration of the main active substance is observed precisely in the focus of inflammation;
- Phonophoresis. Medicines are administered using ultrasound;
- Magnetotherapy. The body is physically affected by a pulsed or constant magnetic field. The treatment provides expansion of blood vessels, activation of microcirculatory blood flow, enhancement of metabolic processes, and removal of puffiness. As a result, the pain subsides, the severity of the inflammatory process in the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary is minimized.
If conservative treatment lasting 4-6 weeks does not provide resorption of the cystic formation, the question arises of surgical removal of the cyst.
Laparoscopy
It is considered normal when the cyst disappears after 2-3 menstrual cycles. If this does not happen, laparoscopy is performed, during which the cavity is exfoliated and its walls are sutured.
Laparoscopic cystectomy has a clear advantage over laparotomy, as it allows you to preserve the organ, prevents the development of adhesions. The cyst cavity is exfoliated, and its walls are sutured. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. There are practically no traces of surgery on the body. Surgical manipulations are performed through punctures with a diameter of 5-10 mm.
After a few hours, the patient can move independently, and after 3 days she can leave the hospital. The general recovery period after cystectomy is 2-3 months.
In cases complicated by bleeding, tissue necrosis, tissue resection or removal of the ovary is performed using laparotomy.
Is it possible to cure a cyst of the corpus luteum without surgery
In uncomplicated forms, it is possible to treat the cyst without surgery - monophasic and 2-phase oral contraceptives are used. Vitamins A, E, B1, B6, K, ascorbic acid are prescribed. In some cases (with the exception of dermoids and endometrioid formations, cysts of significant size) can effectively treat ovarian cysts with folk remedies, including at home conditions.

In particular, in some specific cases, experts in reviews talk about the positive role of acupuncture, homeopathic remedies, setting leeches in specified zones and other methods of treating gynecological diseases.
Why is this disease dangerous?
In rare cases, this anomaly can provoke:
- Development of infectious inflammation;
- Ovarian torsion;
- Cyst rupture.
Recall that the pathological process begins when the corpus luteum does not dissolve during subsequent menstruation, but, on the contrary, grows. The main danger of a corpus luteum cyst is possible damage (apoplexy). The risk is that a rupture and hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity may occur - such situations require immediate hospitalization and surgical treatment. Symptoms of a ruptured cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary: acute, piercing pain in the lower abdomen. May be accompanied by increased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting.
There is a group of patients in whom functional cysts occur frequently. What advice can you give them? In such cases, contraceptives are also usually prescribed. When taking contraceptives, the function of the ovaries is suppressed and they rest. As a result, the risk of cyst formation is reduced.
Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
If a cyst on the corpus luteum is found during pregnancy, progesterone-containing drugs are prescribed. In addition, a reduction in physical activity is recommended. As the gestational age increases, the cyst will usually disappear on its own. If a cyst on the corpus luteum occurs in a non-pregnant woman, it will disappear after the next menstrual period or over several cycles. She does not pose a significant danger to women's health and the development of the fetus in the womb, but it is better to keep her under control.
Menstruation with a cyst of the corpus luteum
If the cyst is small, then the nature, frequency and volume of menstrual flow are usually not disturbed. However, with an increase in growth, spotting on the eve of menstruation, delays, more abundant or scanty menstruation are possible.
Delay on cyst
Delayed menstruation with a corpus luteum cyst is associated with the predominant influence of the hormone progesterone. Progesterone helps to prolong the secretion phase (2nd phase of the menstrual cycle), preventing the onset of menstruation. The duration of the delay in menstruation against the background of a cyst of the corpus luteum, as a rule, does not exceed 14 days. Delayed menstruation is often painful (dysmenorrhea), profuse, clotted, often longer than usual (menorrhagia, in some cases turning into uterine bleeding (menometrorrhagia).
Questions and answers about corpus luteum cyst
Question: Is it possible to treat corpus luteum cysts simultaneously according to gynecological and therapeutic programs? What will be the results?
Answer: We consider a woman / girl as a whole and we treat not a disease, but a suffering (sick) person!
We provide a combination of gynecological and therapeutic treatment programs. And in fact, we always adjust the corpus luteum cyst treatment program taking into account the accompanying diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, neuroendocrine and respiratory systems.
The procedures are combined in such a way that each subsequent one potentiates (enhances) the effect of the previous ones.
Respectfully yours, Chief Physician of the Spa Clinic for Women's Health, Cand. honey. sciences O.Yu. Ermolaev.
Question: I am pregnant. The term is 10 weeks. I was recognized as a cyst of the corpus luteum of the right ovary, 5.2 cm in diameter. How dangerous is it? Do you need an operation?
Answer: A corpus luteum cyst often occurs during pregnancy. The biological role of the corpus luteum and corpus luteum cysts during pregnancy is the production of the hormone progesterone, which is responsible for the maintenance and development of pregnancy.
If the corpus luteum cyst is removed, the pregnancy will be terminated.
The cyst of the corpus luteum during pregnancy, as a rule, independently resolves (disappears) by 18-20 weeks, when the functions of the corpus luteum are taken over by the placenta (a child's place in the uterus).
Question: Can a corpus luteum cyst cause a delay of more than 8 days? In this case, the pregnancy test is negative.
Answer: A corpus luteum cyst can cause a delay in menstruation for more than 8 days.
Q: Can a corpus luteum cyst give a positive pregnancy test result?
Answer: With a corpus luteum cyst due to pregnancy, the pregnancy test will be positive.
Question: I am 12 weeks pregnant. When I got up for registration, they found a cyst of the corpus luteum on the left ovary. I am very worried about my child. Will it affect him?
Answer: The cyst of the corpus luteum is not dangerous to the fetus.
Question: On what day of the cycle does a corpus luteum cyst form?
Answer: A corpus luteum cyst forms after ovulation from 16 to 28 days from the onset of menstruation.
Question: There are still 8-9 days before menstruation. Ultrasound revealed a corpus luteum cyst 4 cm in diameter, pregnancy is not detected. What is the likelihood of getting pregnant?
Answer: It is possible to determine the presence of pregnancy before the expected date of menstruation on the basis of blood test data for the content of hCG.
Question: Can there be an increase in the uterus with a corpus luteum cyst?
Answer: The corpus luteum cyst produces progesterone. Progesterone increases the blood supply to the uterus, thus increasing the size of the uterus by 3-5 mm.
Ultrasound examination after 3 days of delayed menstruation allows you to determine uterine pregnancy and identify other causes of uterine enlargement: ectopic (tubal, ovarian) pregnancy, postpartum uterine hypertrophy due to bearing multiple pregnancies or a large fetus, internal endometriosis, uterine chorionepithelioma, cystic drift, myoma uterus.
Risk group
The risk group for the development of a yellow cyst includes women:
- preparing for IVF;
- taking emergency contraceptive medications;
- having abortions;
- working in hazardous conditions;
- observing mono-diets;
- under stress conditions for a long time.
Prevention and prognosis for cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
The prevention of the formation of functional ovarian cysts is facilitated by the timely and complete treatment of inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system, as well as the correction of the disturbed hormonal balance. Observation of a gynecologist-endocrinologist and ultrasound control when detecting a cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary allows you to take the necessary measures in time and prevent complications. The cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary does not pose a threat to the developing pregnancy. With spontaneous regression or planned removal of the cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary, the prognosis is favorable.
Sources of
- https://www.z7ya.ru/uslugi/ginekologiya/kista-zheltogo-tela/
- https://www.raduga-clinic.ru/articles/zheltoe-telo-uzi/
- https://www.probirka.org/biblio/polezno/9233-obrazovanie-zheltogo-tela-v-yaichnikach
- https://ginokomfort.ru/spravochnik/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika-u-zhenshchin/
- https://www.mosmedportal.ru/illness/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika/
- https://mrt-v-spb.ru/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika/
- https://women-health-center.moscow/ginekologija/zhenskie_bolezni/kista_jaichnika/
- https://kvd-moskva.ru/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika/
- https://medcentr-Endomedlab.ru/zabolevanija/kista-zhyoltogo-tela.html
- https://ProBolezny.ru/kista-zheltogo-tela/
- https://illness.DocDoc.ru/kista_zheltogo_tela_jaichnika
- https://www.medzhencentre.ru/zhenskie-bolezni/lechenie-kisty-zheltogo-tela/
- https://www.kurortklinika.ru/kista-zheltogo-tela/
- https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/corpus-luteum-cyst
