Content
- How the female body works and why nature fails
- Typical pathogenesis of the anovulatory cycle
- Causes of the anovulatory cycle
- How to identify anovulatory cycle
- Diagnostics of the anovulatory cycle
- Basal temperature during anovulation
- Treatment methods
- Hormone therapy
- Laparoscopy
- Folk remedies
- Forecast and prevention of a one-phase cycle
- Is pregnancy possible with anovulation cycles
- Ovulatory and anovulatory cycles: what's the difference?
- Possible complications
- Should I see a doctor?
- Forecast. Prophylaxis
- Where to get qualified help
- Opinion of doctors
- Patient questions
The short word "anovulation" in a detailed translation would mean "the absence of the normal process of maturation of the egg and its migration through the fallopian tube into the uterus for potential fertilization." Indeed, such a menstrual cycle is called anovulatory, in which there is no bleeding is preceded by the maturation of the hormonally active corpus luteum, i.e. conception is impossible in any phase of the cycle. However, the actual menstruation in such cases is most often irregular or absent altogether.

If the anovulatory cycle is single or extremely rare, and the reasons for this are quite specific and understandable, this phenomenon is not considered by modern gynecology as pathological. However, if a woman of reproductive age is anovulatory most or all menstrual cycles, this is definitely a pathology that requires consultation, examination and medical interference.
How the female body works and why nature fails
Normally, the menstrual cycle is divided into three phases:
- Follicular, which occurs after the end of menstrual bleeding. During it, the cerebral appendage - the pituitary gland - secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), "Spurring" the development of follicles, one or two of which will burst in the middle of the cycle and release ripe eggs. In parallel, the ovaries increase the production of female estrogen hormones, especially estradiol.
- Ovulatory - closer to the end of the maturation of the egg, the production of another hormone, luteinizing (LH), begins. Ovulation occurs under its influence. The follicle bursts and the egg is released into the fallopian tube to meet with the sperm.
- The corpus luteum phase, during which the fertilized cell descends into the uterus and is implanted. The bursting follicle turns into a corpus luteum, secreting progesterone and sex hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy.
With anovulatory cycle, this system gets lost. Most often, the violation is associated with a change in the concentration of female hormones, which may be too much or too little. Due to hormonal imbalance, there is a significant thickening of the inner uterine layer - the endometrium.
Having reached a certain limit, the mucous membrane begins to exfoliate, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the vessels and menstrual bleeding. Its strength and duration can be different and change from month to month. The constant thickening of the mucous membrane leads to the formation of polyps - mushroom growths, which further complicate fertilization.
In some periods of life, for example, at puberty (adolescence) and when entering menopause, this situation is considered the norm and does not require treatment. Periodic anovulatory cycles in a healthy woman are not dangerous either. Medical assistance is required in the absence of ovulation, which prevents pregnancy and negatively affects the state of health.
Typical pathogenesis of the anovulatory cycle
In the ovaries during the anovulatory cycle, periods of development and degradation of the follicle vary in duration and characteristics. The anovulatory cycle is characterized by oversaturation of the action of estrogens, which must fall under the influence of the progestogenic hormone progesterone, which does not occur with the anovulatory cycle. In very rare situations, the anovulatory cycle is comparable to hypoestrogenism.
The development of the level of estrogenic influence affects the endometrium of various types.
Follicle atresia becomes the cause of hormonal disruption, and this already becomes the cause of the development of the anovulatory cycle and the cause of such menstrual bleeding. During each anovulatory cycle, the endometrium begins to malfunction, and the anovulatory cycle will therefore be accompanied by hemorrhages, extravasations, and necrosis. The uppermost layers of the endometrium are quite unstable and often disintegrate, which causes bleeding, but with in the absence of self-rejection of the endometrium, the development of bleeding is accompanied by diapedesis erythrocytes. At times, hyperestrogenism does not decrease and the excretion of estrogen in the urine remains fairly stable throughout the current anovulatory cycle.
With the maturation of menstrual function in puberty, the cause of the anovulatory cycle may be the lack of the required the ratio of luteinizing and luteotropic hormones, the synthesizing reactions of which become the most active by 16 years.
Inversely, the gynecology of the female body develops in menopause:
- cyclic secretion is disrupted;
- there is an increase in gonadotropic influence.
Such unsystematic alternations of full menstrual and anovulatory cycles with wilting reproductive function are accompanied by changes in the nature of menstruation and the duration of the cycle.
Causes of the anovulatory cycle
In average healthy women, anovulatory cycles are practically not observed during reproductive age. In rare cases, anovulatory cycles alternate with menstrual cycles, but are not characterized by consistency. In such women, the anovulatory cycle can be triggered once with a sharp change in climate or a change in geographic zone.
The most common reasons for the development of anovulatory cycle of physiological origin include age-related changes in the female body, such as:
- puberty;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- menopause.
In nature, the anovulatory cycle and pregnancy, as well as the postpartum recovery of the female body, are closely related. As soon as the woman in labor recovers the menstrual cycle, in 50% of women who are breastfeeding, this cycle remains single-phase anovulatory.
The reasons for the development of a pathological anovulatory cycle include:
- ovarian dysfunction;
- hypothalamic-pituitary regulation of the menstrual cycle.
Ovarian dysfunction has a direct effect on the development of the anovulatory cycle. First, the anovulatory cycle is greatly influenced by inflammatory processes in the ovaries or appendages. Secondly, improper internal secretion of the ovaries can also lead to menstrual irregularities. Thirdly, the impaired performance of the thyroid gland becomes the first cause of the occurrence of single-phase anovulatory cycles.
With erroneous processes of hypothalamic-pituitary regulation, the following is observed:
- insufficient production of the amount of FSH, due to which the full maturation of the follicle is impossible, thereby the follicle loses its ability to ovulate;
- LH deficiency;
- hormonal instability;
- excess prolactin productivity.
Very often, the development of anovulatory cycles is influenced by congenital malformations of the reproductive system, delayed sexual development, and genetic pathologies.
How to identify anovulatory cycle
Its main distinguishing feature is the absence of ovulation and the secretory phase that occurs after it. That is, the follicle does not mature, therefore the egg does not come out of it. Almost the entire cycle is occupied by the proliferation phase. Despite this, with anovulation, menstruation is cyclical and even regular. Sometimes in terms of blood loss and regularity, they are no different from menstruation with a normal menstrual cycle. In this case, anovulation can be suspected by the absence of signs of ovulation:
- lower abdominal pain;
- swelling of the breast, as well as an increase in its sensitivity;
- change in basal temperature.
Normally, these symptoms should appear on the 12-15th day of the MC, but, therefore, they are absent during anovulation. But the following violations appear: the cycle may become too short, less than 21 days, or vice versa, very long, more than 35 days.
If a woman is diagnosed with excess estrogen, uterine bleeding is more profuse and prolonged. Blood loss exceeds the physiological norm. The volume of blood loss is more than 80 ml against the background of regular MC, with an interval of 21-35 days. Due to heavy periods, the woman's well-being worsens, anemia occurs.
If the level of estrogen is low, then on the contrary, menstruation is scanty, lasting 3-4 days. During a gynecological examination, the doctor can detect a narrowing of the vagina and a shrinking of the uterus.
A mandatory symptom of the anovulatory cycle, which is present in all women of childbearing age, is hormonal infertility.
Diagnostics of the anovulatory cycle
Approach 1.
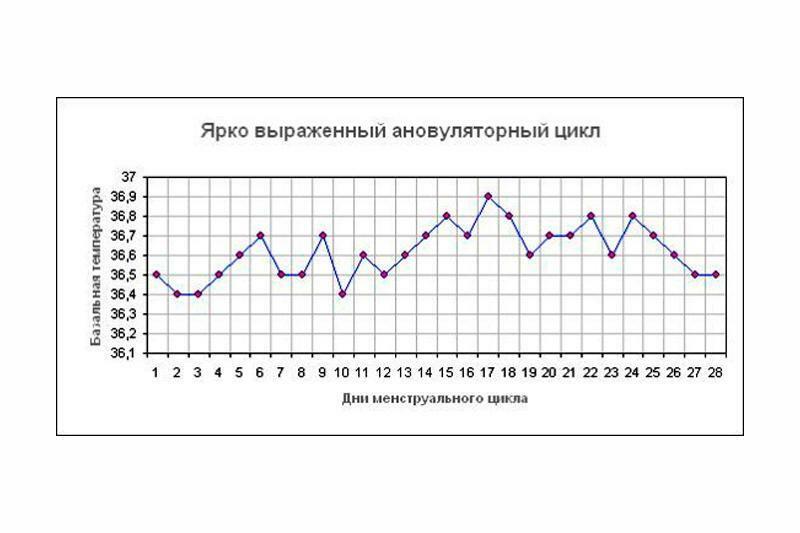
The simplest and most common method for diagnosing anovulatory cycle is to determine the basal temperature. A full menstrual cycle is accompanied by an increase in basal temperature during the activation of the progesterone phase. During the anovulatory cycle, a single phase temperature remains.
Approach 2.
An active estrogenic effect in the anovulatory cycle is detected on the basis of functional tests (symptom of the "pupil" during a one-phase cycle, a positive phenomenon of the fern), colpocytological data.
Approach 3.
The main signs of the anovulation cycle include the absence of a dominant follicle, which can easily be found out using dynamic ultrasound radiation when examining the ovaries.
Approach 4.
One of the decisive approaches to diagnosing the anovulatory cycle is gynecological curettage of the uterine cavity before the so-called menstruation. After that, a histological examination of the scraping is mandatory. Confirmation of the absence in the analysis of secretory changes in the endometrium indicates a violation of the menstrual cycle and the active development of the anovulatory cycle.
Approach 5.
Elucidation of the etiological causes of the development of the anovulatory cycle is carried out by studying the state of the thyroid gland, the hypothalamic-pituitary hormonal system, and the adrenal cortex. All sorts of inflammatory processes in a woman's genitals are necessarily diagnosed.
But since the menstrual and anovulatory processes can alternate irregularly, only six-month dynamic control over the state of follicle development can make the diagnosis accurate.
Basal temperature during anovulation
The method of measuring temperature helps to understand at home if ovulation is occurring. Normally, the temperature graph during the cycle consists of two phases - in the first phase of the cycle, the body temperature is lower than in the second. A few days before ovulation, the low temperature of the first half of the cycle drops even more, and from the day of ovulation under the influence of progesterone begins to grow by about 0.2 degrees per day, so that by the end of the cycle again decline. The temperature difference per cycle is about one degree.
To build a graph of basal temperature, you need to measure the temperature and record the values every morning from day 1 of the cycle, without getting out of bed. The temperature can be measured by holding the thermometer in the mouth, vagina or rectum for at least 5 minutes. The measurement is always carried out in the same place. Then, based on the data, you need to build a diagram, connecting all the values.
With anovulation, the basal temperature is monotonic: there are no pronounced rises or falls, since there is no a corpus luteum is formed, which produces progesterone, respectively, the temperature does not rise by 2 phase of the cycle.
Treatment methods
If the absence of ovulation is caused by a metabolic disorder, you need to normalize the diet. If the reason is different, resort to hormonal drugs, laparoscopy.
Hormone therapy
The main treatment for ovulatory dysfunction is hormone therapy. With polycystic ovary, the patient is prescribed FSH, chorionic gonadotropin, pergonal, estrogen-progestational agents. Another option is to give the body a break, to take monophasic contraceptives for 2-3 months - COCs.
In the treatment of anovulation with endocrine infertility, Dufaston is used - a broad-spectrum drug. In its pharmacological properties, it is close to progesterone, stimulates the activity of the corpus luteum, while it has no side effects in the form of impaired blood clotting and metabolism. Prevents endometrial hyperplasia, and in combination with Ovarium Compositum contributes to the general regulation of the reproductive system.
Sequential therapy with hormones and physiotherapy is effective in 70% of cases.
Laparoscopy
Ovarian pathologies requiring surgical intervention are treated by laparoscopy. If, during the diagnosis, cysts or fibroids are found in the abdominal cavity, they are removed immediately. At the same time, ovarian biopsy is performed for histological examination to exclude tumor processes. The surgeon can "help" the egg to leave the ovarian capsule by cutting the thickening.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies cannot be carried out without consulting a doctor. Herbal tincture concentrates may contain toxins harmful to the body.
Forecast and prevention of a one-phase cycle
With timely started treatment and well-chosen tactics of therapeutic effects, pregnancy after anovulatory cycle occurs in 45% of cases. If it is not possible to conceive naturally, the woman is advised to use assisted reproductive technologies. The most common is the method of in vitro fertilization. In the absence of mature healthy eggs, a donor egg is used for artificial conception.
Failure to identify and treat anovulation cycles in a timely manner can lead to anemia, dysfunctional menstrual bleeding, infertility, and ovarian dysfunction.
Compliance with the following recommendations will help to avoid the development of the listed complications and the appearance of anovulatory cycles:
- A balanced, nutritious and healthy diet with the inclusion of foods that contain a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins;
- Timely and competent therapy of inflammatory, infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- Exclusion of excessive psycho-emotional, physical stress;
- Maintaining an active lifestyle (giving up addictions, moderate physical activity);
- Regular examination by a gynecologist (once every six months).
With the systematic appearance of single-phase cycles, menstrual dysfunction and problems with conception, you should consult a doctor. After conducting a series of studies, the doctor will determine the cause of the pathological condition and develop an effective treatment that will help restore the menstrual cycle and ovulation.
Attention! This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances is scientific material or medical advice and cannot serve as a substitute for face-to-face consultation with a professional a doctor. For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment prescription, please contact qualified doctors!
Is pregnancy possible with anovulation cycles
Many women ask, "If I don't ovulate, will I ever become a mother?" The fact is that pregnancy without ovulation is impossible, because a woman can become pregnant only when her mature eggs are released from ovary.
Most women have anovulatory cycle once or twice a year. This means that anovulation does not mean a complete inability to conceive a child, but a decrease in the likelihood pregnancy - once or twice a year compared with ten to twelve for a woman with a normal cycle.
Women with irregular cycles during ovulation will have the same chance of pregnancy as women with regular periods.
Ovulatory and anovulatory cycles: what's the difference?
If you have regular periods and feel habitual changes in your body during your cycle (pain at the bottom mid-cycle abdominal swelling, late-cycle breast swelling, or PMS symptoms), you probably have ovulation.
You can check this yourself by tracking changes in basal body temperature or by performing an ovulation test.
Lack of ovulation can be suspected if menstruation is irregular, and the cycle may be too short (less than 21 days) or very long (more than 35 days).
If you often experience delays of more than 2 weeks and cannot determine ovulation with tests or basal body temperature charts, see your doctor.
Possible complications
Persistent impairment of reproductive function is one of the main negative consequences of pathological cycles with an immature egg. In addition to infertility, anovulation often threatens with debilitating uterine bleeding. Their regular repetition leads to hypotension, iron deficiency anemia, physical exhaustion.
Should I see a doctor?
As a rule, a woman starts tracking her ovulation only when she is planning a pregnancy. The anovulatory cycle is the most common cause of infertility. Therefore, it is imperative to seek qualified medical help from a gynecologist.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the lack of ovulation and develop an optimal treatment regimen for restoring sexual function. The gynecologist has at his disposal all the necessary equipment for a complete diagnosis of the pathological condition. Do not neglect routine examinations with a doctor, because it is quite difficult to suspect such a problem on your own.
The volume of blood lost and the regularity of menstruation during anovulatory cycle may be the same as during full menstruation. Regular examinations will identify pathology at an early stage and avoid serious consequences.
Forecast. Prophylaxis
The prognosis for ovarian dysfunction is favorable. However, POI negatively affects not only the reproductive sphere, but also the quality of life, general morbidity and mortality in women.
Timely administration of hormone replacement therapy is the main way to eliminate the symptoms of estrogen deficiency and prevent the risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease [17].
Losing weight and exercising regularly can help reduce the severity of PCOS.
There are no specific methods for preventing excess female sex hormones and androgens. Rational and balanced nutrition, physical activity and smoking cessation will help to avoid the development of concomitant diseases.
Where to get qualified help
Anovulation can be a serious problem for couples planning to conceive. However, with the right approach to diagnostic measures and treatment, pregnancy occurs in most women. That is why it is so important to find an experienced doctor. The easiest way to do this is by consulting a private clinic.
Opinion of doctors
The uncoordinated work of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and ovaries leads to an imbalance in sex hormones. The consequence often becomes the appearance of anovulation - a failure of the maturation process and exit from the ovum follicle. With such suspicions, to track the probable pathology, it is useful to regularly measure the basal temperature. This is an easy way to identify a violation and take action in time.

Anovulation therapy must be supervised by a physician. Additional measures in the form of phytotherapy and other folk methods are allowed, but after consultation with specialists.
Patient questions
How to get pregnant without ovulation?
Unfortunately, I was diagnosed with ovarian anovulation. But after the first disappointment and loss of hope for pregnancy, I heard from a colleague that it is still possible to get pregnant. Tell me, are there any modern methods for this pathology?
Answer
Good afternoon, Varvara! It is very difficult to get pregnant with anovulation. To do this, you must first of all find and eliminate the causes that caused it. If anovulation is accompanied by ovarian cyst, induction or surgery may be used. It is advisable to take a course of hormone therapy. Competent information can be obtained from the gynecology department of our center.
What is anovulation in women?
My classmate was embarrassed to clarify the meaning of anovulation at a gynecologist's examination, this is how he characterized the reason for her long-term inability to become pregnant. Explain to us what it is and how dangerous it is.
Answer
Good day! In gynecology, anovulation is a dyshormonal failure during the menstrual cycle. It is accompanied by the development of the egg, which subsequently cannot leave the ovary. It cannot be called a serious illness. However, with anovulation, there is really no chance of getting pregnant. Since the egg cannot move further in this state, the fusion with the sperm simply will not take place. The doctors of our center can competently tell about the signs and prevention of anovulation.
Sources of
- https://medintercom.ru/articles/anovulyatornyj-cikl
- https://unclinic.ru/otsutstvie-ovuljacii-anovuljatornyj-cikl/
- https://www.mosmedportal.ru/illness/anovulyatornyy-tsikl/
- https://zoj.kz/bolezni-pochek-i-mochepolovoj-sistemy/chto-takoe-anovulyatornyj-czikl-i-kakie-ego-posledstviya.html
- https://MedPortal.ru/enc/besplodie/female/anovulyaciya/
- https://www.medzhencentre.ru/besplodie/jenskoe/anovulyaciya/
- https://ginekologi-msk.ru/info/zabolevaniya/anovulyatornyy-tsikl/
- https://abort-spb.ru/anovuljacija-chem-opasno-otsutstvie-ovuljacii/
- https://flo.health/ru/otslezhivaniye-ovulyatsii/anovulyatornyy-tsikl
- https://miccenter.ru/ovulyatsiya/anovulyatornyj-cikl
- https://www.raduga-clinic.ru/articles/anovulyatornyj-cikl/
- https://ProBolezny.ru/disfunkciya-yaichnikov/
- https://doctor-moskva.ru/napravleniya/ginekolog/anovulyatornyy-tsikl/
- https://doctor-moskva.ru/napravleniya/ginekolog/anovulyatornyy-tsikl/kharakternye-simptomy-anovulyatornogo-tsikla/
