Content
- Ovarian pain
- Symptoms of Painful Ovulation
- The most common pathologies associated with pain in the ovary
- Oophoritis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Cysts
- Ovarian torsion
- Ovarian apoplexy
- Natural cause of ovarian pain after ovulation
- What the nature of the pain will tell
- Pain after ovulation: what can be confused with
- Can bleeding appear
- Why the ovary on the right side hurts more often than the left
- Pain in the right or ovary as a sign of pregnancy
- How to understand that it is the ovaries that hurt
Ovarian pain
Many diseases of the pelvic organs are localized in the lower abdomen and can radiate to the lower back or thigh. If a woman really hurts the left or right ovary, then most often the pain appears on the affected side, has an aching, pulling or stabbing character. Sometimes it gives off to the leg, perineum or anus. It often happens that it only hurts on one side. This is due to the fact that it was from this side that ovulation occurred, a cyst appeared, or some other phenomenon occurred. Advice on what to do in this case: visit a good gynecologist! The doctors of our women's blade are at your service! Below are typical questions and answers on this topic.
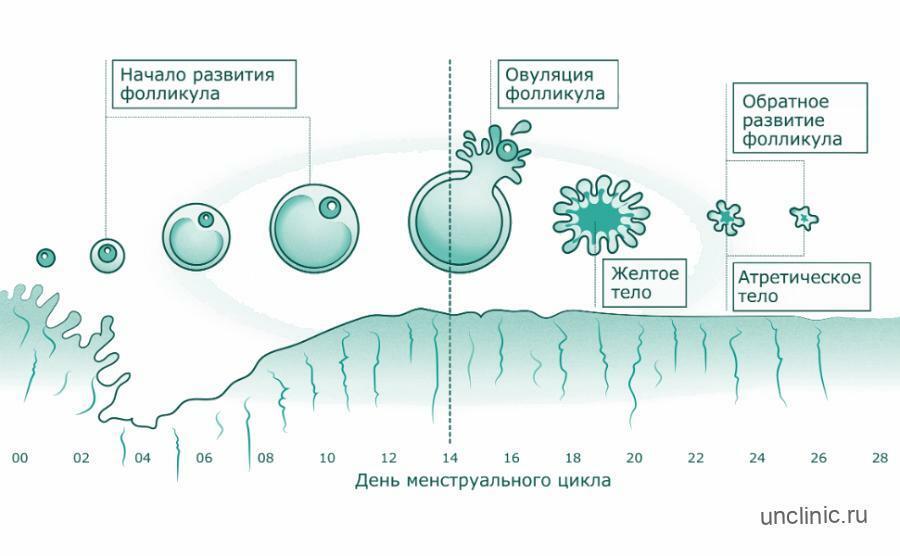
Symptoms of Painful Ovulation
Only in some women is pain during ovulation interpreted as pathological pain in the ovaries. Such a pain syndrome should be alarming and become a reason for a medical consultation. In the vast majority of women, pain is only evidence of the onset of ovulation.
Abdominal pain during ovulation is characterized by the following features:
- abrupt onset - pain occurs suddenly;
- the intensity of pain during ovulation is different, sometimes the painful sensations become so strong that they resemble inflammation of the appendix;
- the nature of the pain, as a rule, changes: first, a stabbing pain appears, which after a while flows into a dull one;
- some women experience pain during intercourse;
- the location of pain during ovulation is primarily the abdomen, in many cases on the right side.
Pain during ovulation lasts about 6-8 hours. There are cases when the duration of painful sensations increases even up to two days. But it is worth noting that not every ovulation is accompanied by pain, most often pain during ovulation occurs in every 3-4 menstrual cycle. Therefore, in case of frequent pain, it is better to check with a gynecologist.
The most common pathologies associated with pain in the ovary
Ovarian pain is not a gynecological disease, but is a symptom that may indicate the presence of pathologies in the female reproductive system.
Oophoritis
Oophoritis is an inflammatory process in the ovarian tissue. It arises as a complication of various inflammatory processes provoked by childbirth, abortion, and various infections. The microbes that cause the inflammatory process can penetrate the bloodstream from the kidneys and other organs, even from diseased tonsils. The disease is manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by pressure on the right side, fever, and sometimes - discharge with an unpleasant odor. The pain can radiate to the lower back, sacrum and right leg.
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous condition in which the embryo, mainly due to adhesions in the fallopian tubes, takes root in the ovarian tissue or in the tubal space. Without treatment, an ectopic pregnancy leads to severe complications, accompanied by dangerous bleeding. Therefore, in the absence of menstruation and abdominal pain on the left side, it is advisable to see a doctor immediately.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the proliferation of endometrial cells, the inner layer of the uterine cavity, on its surface, as well as in the tissues of other organs.
Since the endometrioid tissue has receptors for hormones, the same changes occur in it as in the normal endometrium, manifested by monthly bleeding. These minor bleeding leads to inflammation in the surrounding tissues and causes the main manifestations of the disease: pain, enlargement of the organ, infertility.
Cysts
Functional cysts are caused by a violation of ovulation and are formed from the follicle in which the egg is growing, or the structure remaining from it - the corpus luteum. This disease, in which the left ovary hurts, is not dangerous, in most cases it disappears within 3-4 months.
Congenital cysts (dermoid) are neoplasms with a dense capsule. They usually do not disappear on their own, but in most cases they do not cause problems. If the left ovary hurts, the cyst needs to be removed.
Paraovarian cysts occur in the ligament between the uterus and the ovary. They often dissolve on their own, but can cause pain. In this case, an operation is performed.
Ovarian torsion
Torsion of the ovary is a severe pathology of the appendages that develops when the ligaments fixing the ovary are inverted, the clamping of its vessels and organ ischemia.
In most cases, ovarian torsion develops with an increase in its volume and mass due to various formations - large cysts and tumors, often benign.
Ovarian apoplexy
Ovarian apoplexy is a hemorrhage caused by a ruptured vessel. This condition is triggered by an increase in blood pressure within the pelvic organs. Since the right ovary is better supplied with blood, apoplexy occurs in it more often. In 94% of cases, this situation occurs in the second half of the cycle. The disease is manifested by severe pain in the lower abdomen on the right side, weakness, dizziness, vomiting, nausea, fainting. The disease is accompanied by internal bleeding and requires urgent medical treatment.
Natural cause of ovarian pain after ovulation
After ovulation, pain can cause cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle (ovulatory syndrome).
This pathology is caused by rupture of the follicle, which accompanies the release of the egg.
This process is accompanied by the outpouring of a small volume of blood, which irritates the nerve receptors of the peritoneum.
Before the menstrual cycle, ovarian pain can be caused by a decrease in estrogen levels, which provokes slight endometrial detachment. This, in turn, can be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge, which are observed for 1-2 days.
What the nature of the pain will tell
If the right or left ovary pulls right after ovulation, it is more likely due to rupture of the follicle. But soreness can increase due to inflammatory processes and pathology of the reproductive organs. For example, when a cyst ruptures, a sharp spasm is felt.
When the ovary tingles some time after ovulation, this may indicate pregnancy or gynecological disease.
The pain can be of a different nature. More often, the ovulatory process is accompanied by a pulling or aching pain, sometimes cramping. In case of stabbing or cutting pain syndrome, it is better to see a doctor, as this may be a sign of a disorder of the reproductive system or a violation of ovarian dysfunction.
Pain after ovulation: what can be confused with
Often, women confuse ovulatory pain in the right side of the peritoneum with symptoms of acute appendicitis. Incorrect diagnosis in this case threatens with serious complications. With inflammation of the appendix, in addition to abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and pale skin appear. The diagnosis is made after palpation of the peritoneum. When pressing on an area 2 cm below the navel, the pain syndrome will intensify. If appendicitis is suspected, emergency medical attention should be called.

Some women have pain in the left ovary. Ovulation may have nothing to do with this process. Among the possible causes of ailment, diseases of the digestive system are distinguished. In this case, stool is disturbed, appetite disappears. Pain can spread to the epigastric region.
Can bleeding appear
A slight release of blood in the form of mucous blood streaks or spotting is permissible in the first 1-2 days after ovulation. Drops of blood can enter the mucus from the wound formed at the site of rupture of the follicular walls, as well as the wound surface of the walls of the uterus, to which the egg is attached.
In case of profuse bloody or brown discharge, as well as bloody smears lasting more than 2 days after ovulation, it is necessary to urgently go to the hospital, since the likelihood of internal bleeding is possible.
Why the ovary on the right side hurts more often than the left
The reason lies in the anatomy of the reproductive organs. The blood supply to the right ovary is carried out by a large vessel - the abdominal aorta, and the left one feeds the blood of the smaller renal artery. In addition, the appendicular-ovarian artery is often involved in the blood supply to the right organ.
As a result, the ovary on the right receives much more blood and nutrients. Therefore, it is usually large and ovulates. But he also hurts much more often than the left one.
Another cause of pain in the right ovary is the transition of the inflammatory process from the appendix - the appendix - to the reproductive system. Since the appendix is located on the right side, only the adjacent ovary suffers from inflammation. As a result, adhesions caused by appendicitis and inflammation of the ovary itself - oophoritis - occur more often on the right.
Pain in the right or ovary as a sign of pregnancy
A pulling pain in the ovary can be considered an indirect sign of pregnancy. The fact is that during pregnancy, any inflammatory processes, including those occurring in the ovarian tissue, are exacerbated, which can cause pain. However, in most cases, it is not the ovary that hurts during pregnancy, but the ligaments of the uterus, which stretch as the fetus grows. As a rule, over time, these unpleasant sensations disappear. Most often, the ligaments hurt in primiparous, especially in young women.
The right or left ovary during pregnancy hurts due to the presence of the corpus luteum - a special structure that secretes progesterone and ensures the course of pregnancy. Over time, the function of the corpus luteum is taken over by the placenta, it gradually disappears, although in some women it remains until delivery. Therefore, from 10-12 weeks, the unpleasant sensations on the right side disappear.
The reasons why the right ovary hurts in women may be different. To exclude an ectopic pregnancy and inflammation, a woman needs to consult a gynecologist and do an ultrasound.
How to understand that it is the ovaries that hurt
If a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen, she involuntarily begins to doubt which organ is suffering from discomfort.

For example, if the right ovary hurts, you can easily think about an attack of acute appendicitis.
Is it possible to somehow independently determine what is the cause of the discomfort, women are interested.
Alas, it is impossible to do this without medical intervention.
Only an experienced doctor will be able to tell which organ caused the discomfort and what to do about it.
If a woman is worried about the discomfort caused by the uterine appendages, then the pain will most likely be localized in the lower abdomen.
It can be characterized in different ways.
One woman will say that the discomfort is cutting in nature, while the other, on the contrary, will draw the doctor's attention to pulling characteristics.
From the description of the symptom, in some cases, the doctor can guess the cause of the problem.
It often happens that a woman complains of discomfort on only one side.
For example, the left ovary or only the right ovary often hurts, and this allows the doctor to suspect a one-sided disease.
For example, it could be a tumor or cyst.
Sources of
- https://unclinic.ru/bol-vo-vremja-ovuljacii/
- https://nevromed2016.ru/o-klinike/stati/pochemu-bolyat-yaichniki-prichinyi,-simptomyi,-raznovidnosti.html
- https://Ovulyaciya.com/ovulyaciya/bolit-yaichnik-posle-ovulyatsii
- https://karpov-clinic.ru/articles/ginekologiya/3760-posle-ovulyacii-tyanet-zhivot-kak-pered-mesyachnymi.html
- https://unclinic.ru/pochemu-bolit-pravyj-jaichnik/
- https://kvd-moskva.ru/bolyat-yaichniki/
- https://www.ivf-nn.ru/about/articles/551/
