Content
- What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- The mechanism of development of polycystic ovary syndrome
- Classification
- What causes PCOS
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
- Overweight
- Hyperandrogenism
- Skin problems
- Failure of the menstrual cycle
- The appearance of stretch marks
- Fertility problems
- How to distinguish PCOS from adrenal pathology
- Consequences of polycystic ovary
- Polycystic ovary disease and infertility
- Polycystic and IVF
- Medication for polycystic ovary disease
- Non-drug weight correction
- Surgical treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Physical activity with polycystic ovary
- Relapse prevention
- How to normalize the menstrual cycle with polycystic ovary
- Improving the psycho-emotional state in PCOS
- Polycystic ovary syndrome in women 40-55 years old
- Forecast and prevention
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or Stein-Leventhal syndrome is a pathological gynecological disease of the ovaries in a woman in which cysts and benign tumors develop. It is caused by the growth of cystic growths inside and outside the ovaries. It appears as a result of a malfunction of the ovaries, pancreas or pituitary gland. The disease can be congenital, appear in adolescence even before the onset of the menstrual cycle.
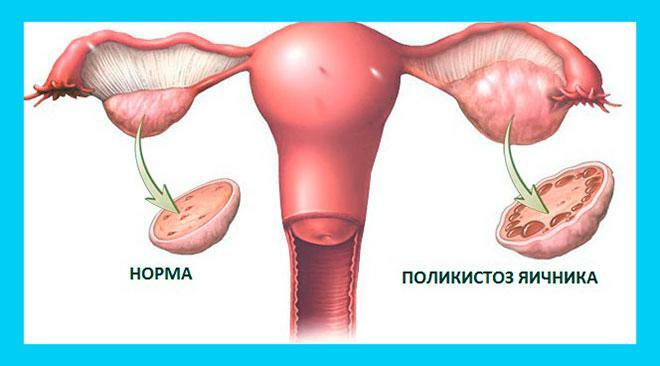
In its shape, the ovary is somewhat similar to a peach bone - dense with an uneven surface. The ovarian membrane consists of protein, it is here that the follicles are contained, together with the maturation of which the maturation of the egg itself occurs. The follicles burst during the period when ovulation occurs, after which the egg is released from the ovary.
In cases where the function of the ovaries is impaired for some reason, we can talk about hormonal changes. The disease itself looks like the formation of cystic formations. There are a lot of them, and these neoplasms begin to affect the tunica albuginea of the ovaries. As a rule, the menstrual cycle begins to loosen at the same time, various irregularities occur. One of the consequences of polycystic disease is infertility in women.
The mechanism of development of polycystic ovary syndrome
The pathogenesis of Stein-Leventhal syndrome is based on the excessive secretion of male sex hormones by the sex glands in the female body. There are a number of hypotheses for the development of polycystic ovary syndrome, the most relevant of which are central, peripheral and insulin. According to the hypothesis of the central origin of polycystic ovary syndrome, excess production of androgens is associated with an increase in the frequency and amplitude of secretion of luteotropic hormone by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland as a result of the formation of macro- and microadenomas. The hypothesis of the peripheral origin of polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with defects in the adrenal glands or ovaries, as a result of which hyperproduction of androgens develops and the effect of follicle-stimulating hormone on ovaries.
The insulin concept of the development of polycystic ovary syndrome is considered the most modern hypothesis. Excess insulin in the body stimulates the synthesis of androgens in ovarian cells. An increase in the concentration of androgens leads to inhibition of cells that produce estrogens - female sex hormones, and to the proliferation of androgen-producing cells. As a result of the formation of such a vicious circle, complete atresia of the follicles develops, leading to the absence of ovulation and disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Classification
By origin, polycystic ovary disease is classified as primary (PCOS) and secondary (concomitant with known nosological forms). Scleropolycystic disease is divided into two forms - with obesity and with normal or reduced body weight. In addition, there are 4 phenotypes of PCOS, which are based on symptoms that are diagnostic criteria:
- Phenotype A (classic). Combination of hyperandrogenism with anovulation, polycystic disease. The frequency of occurrence is 54%.
- Phenotype B (anovulatory). With hyperandrogenism, ovulatory dysfunction, without polycystic disease. Prevalence 29%.
- Phenotype C (ovulatory). Hyperandrogenism and polycystic disease. The frequency of occurrence is 9%.
- Phenotype D (non-androgenic). Anovulation and polycystic. The incidence is 8%.
What causes PCOS
The main mechanism for the development of this disease is disruption of the endocrine system (ovaries, adrenal glands, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pancreas and thyroid glands). Often, polycystic disease is associated with increased production of insulin by the pancreas. Its excess affects the adrenal glands and causes them to produce more of the male sex hormone androgen. The result is an imbalance between androgens and estrogens (female sex hormones) that causes PCOS.
The factor of heredity plays an important role. It has been proven that the cause of polycystic disease is often a genetic predisposition to this disease. Therefore, there is a high probability of developing polycystic ovary disease in women whose older relatives (mother or grandmother) suffered from this disease.
The cause of polycystic disease can be chronic inflammatory processes and infectious diseases, including those suffered in childhood. For example, patients with PCOS often have tonsillitis or mumps (colloquially called mumps) in their history.
Risk factors are also considered abrupt changes in climate and environmental conditions, as well as stress that can cause hormonal disruptions.
Diagnosis of the disease
Any diagnosis needs confirmation. In this case, the following surveys are used for these purposes:
- Ultrasound. With its help, you can visually verify the existing changes in the structure of the ovaries (changed size organ with too thick outer wall in the direction of increase, many filled with fluid cavities).
- Blood test. The hormonal background is being investigated - with PCOS, there is a high level of luteinizing hormone, male genital hormones (in particular, testosterone), while during the second phase of the cycle, it may be too low progesterone.
- Blood chemistry. Allows you to identify violations in the metabolism of increased levels of fats (triglyceride, cholesterol, etc.), glucose.
- Biopsy. Used to examine endometrial specimens if genital endometrial tumors are suspected. In most cases, the procedure is necessary to determine the possibility of combining PCOS and pregnancy.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
The difficulty in making a diagnosis of polycystic ovary disease or Stein-Leventhal syndrome is that that the clinical manifestations inherent in the disease are observed in many endocrine-metabolic violations. Let's consider the most obvious ones.
All symptoms can also be supplemented by severe premenstrual syndrome, depression, drowsiness, increased nervousness, decreased performance, and blurred thinking.
Overweight
As a rule, patients with the disease have insulin resistance - a violation of the metabolic response to insulin produced by the pancreas. In turn, insulin resistance leads to obesity.
With chronic insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular complications can occur.
Hyperandrogenism
This condition is characterized by excess production of male sex hormones. A characteristic sign of a violation is the appearance in women of male secondary sexual characteristics:
- growth of male-type terminal hair. Excessive hair growth appears on the chin, upper chest, abdomen, back;
- coarsening of the voice;
- increased sweating with a pungent odor;
- decrease in the size of the mammary glands;
- enlargement of the clitoris.
Skin problems
Due to the imbalance of hormones, women often complain of the appearance of blackheads, acne, pimples. Excessive dryness of the skin may also be noted.
Failure of the menstrual cycle
As a rule, with a disease, the menstrual cycle becomes long: it lasts 35 days or more. In some situations, menstruation becomes very rare, the break between them can be 3-6 months.
In 20% of women with the disease, the menstrual cycle is not disturbed, but ovulation still does not occur.
The appearance of stretch marks
Stretch marks are stripes where the skin is excessively stretched. They appear due to a sharp increase in body weight, and are localized mainly on the abdomen, hips, chest. A hormonal imbalance contributes to the formation of striae, against which the skin loses its elasticity.
Fertility problems
As with menstrual irregularities, fertility problems can be very varied. Some women are simply not able to become pregnant against the background of their PCOS, and some are able to become pregnant, but they are not able to bear the fetus before the time from which it becomes viable.
How to distinguish PCOS from adrenal pathology
Often, PCOS has to be distinguished from adrenogenital syndrome (AGS), a hereditary pathology of the adrenal glands, in which the content of male sex hormones also increases. But in PCOS, unlike AGS, they are synthesized in the ovaries, not in the adrenal glands.
To establish the diagnosis, tests are performed with glucocorticoids (prednisolone, dexamethasone, cortisone), which are deficient in adrenogenital syndrome and absent in PCOS. In adrenal pathology, after the administration of the missing glucocorticoid, the levels of androgens, their intermediate products and metabolites (DHEA, 17-OC, 17-OP) are normalized. There is no such effect in PCOS.
Currently, genotyping of the 21-hydroxylase gene mutation is performed to establish the diagnosis of AHS (CYP21A2), which allows to identify a deficiency of this enzyme, which is the cause of congenital pathology adrenal glands.
Consequences of polycystic ovary
What is the danger of polycystic ovary disease in a woman? If the disease is not treated, then it leads to the following consequences:
- overweight (due to a malfunction of the hormonal system, it is very difficult to fight the appearance of excess weight, therefore, such women often suffer from obesity);
- first, insulin resistance occurs (body tissues become immune to it), and then type 2 diabetes mellitus develops;
- the formation of blood clots in the arteries, which can lead to their complete blockage and the inability to supply blood and oxygen to vital organs;
- problems with conception and infertility;
- inability to carry a child;
- atherosclerosis;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- breast or endometrial cancer.

Today, it is possible to cope with PCOS. Yes, this is a long-term process that requires a broad approach, but eliminating the symptoms of the disease will help solve many of the patient's health problems and give a chance to become a mother.
Polycystic ovary disease and infertility
PCOS can lead to infertility. Hormonal disturbances negatively affect the ovary's ability to release a mature egg, which must be fertilized for pregnancy to develop. But a woman can still get pregnant both naturally and after a course of treatment that includes normalization of weight, menstrual cycle, therapy with follicle-stimulating drugs, and if it does not work out - after IVF.
Don't panic. Fear of infertility leads to the development of a long-term mental disorder, which, on the one hand, worsens the course of the syndrome, on the other hand, can cause disorders of the neuroendocrine system, which stimulates the onset and development of PCOS, even if a woman does not actually have it It was.
Polycystic and IVF
The most difficult cases of polycystic disease are those in which ovarian tissue does not respond to hormones due to receptor pathology. This condition is called ovarian resistance syndrome. Treatment in such patients does not give any effect, therefore, natural pregnancy is impossible. To help a woman in such cases, assisted reproductive technologies, IVF, are used. Since it is not possible to obtain high-quality mature eggs with resistance syndrome, donor material is used for in vitro fertilization.
Medication for polycystic ovary disease
Typically, therapy for polycystic ovary syndrome is aimed at restoring fertility.
First of all, the following drugs are recommended for treatment:
- Letrozole - prevents androgens from being converted into estrogens, leading to a decrease in estrogen levels, a compensatory increase in FSH, followed by the development and maturation of the dominant follicle.
- Clomiphene citrate - stimulates the production of FSH and LH, causing the dominant follicle to mature.
- Metformin - makes tissues more sensitive to insulin, decreases insulin resistance - a key factor in the development of PCOS. Can be used as an independent drug to stimulate ovulation in patients with polycystic ovaries, obese or of normal weight, and as an adjunct to clomiphene citrate with insufficient efficacy the latter [17].
- Gonadotropins are hormone preparations that mimic the natural peaks of LH and FSH required for the final maturation of follicles and ovulation [18]. These include:
- FSH, LH and their combination - human (obtained by special purification of the urine of women during the period menopause) or recombinant (synthesized by special producer cells in which DNA is embedded hormone);
- urinary or recombinant hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a pregnancy hormone similar in structure to LH, capable of stimulating ovulation [1].
Gonadotropins can be used in conjunction with metformin, but only after excluding the pathology of the uterus, fallopian tubes and male infertility [1]. Treatment is costly.
In the process of stimulating ovulation, ultrasound monitoring of the state of the endometrium and maturation must be carried out follicles (less than three mature follicles are safe), obstetrician-gynecologist observation and hormonal control. This is necessary to exclude the development of possible complications:
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome - an overreaction of the body, in which the size of the ovaries increases due to their pronounced edema and multiple cysts;
- multiple pregnancy, etc. [1] [18] .
Secondly, the following treatment methods are recommended:
- Conservative treatment with gonadotropins in women who have not responded to therapy with clomiphene citrate in combination with metformin.
- Laparoscopic ovarian surgery - performed in the absence of the effect of drug therapy. These include drilling and wedge resection of the ovaries.
Non-drug weight correction
For women with PCOS, it is extremely important to achieve the maximum approximation to the norm of metabolic processes and weight, as this is a reliable prevention and tangible help in the treatment of complications insulin resistance. For this it is recommended:
- give up bad habits, in particular smoking, alcohol abuse;
- normalize sleep patterns;
- reduce the calorie content of the daily diet with a BMI of more than 25.0 to 1200-1500 kcal, switch to a healthy diet;
- increase the level of physical activity, including passing at least 10 thousand daily steps, and also devote at least 30 minutes to intense physical activity, provided there are no contraindications from the cardiovascular system.

If a lifestyle correction for 3 months does not lead to visible results, drug therapy may be recommended for women. As part of it, drugs may be prescribed that reduce appetite and interfere with the absorption of fats in the intestines.
Surgical treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
If, despite the hormonal therapy carried out for 3-6 months, ovulation is still absent, surgery is performed. When choosing an access, preference is given to laparoscopy. During the operation, either small incisions (wedge-shaped resection) or holes (cauterization) are made in the dense membrane of the ovaries through which the egg can leave the ovary and fertilize. After the intervention, the menstrual cycle becomes ovulatory. This effect lasts up to a year, during which time a woman can become pregnant.
PCOS treatment takes a long time - from 3 to 12 months. But if it is selected correctly, the effect is good, and pregnancy occurs in most patients.
PCOS is not a tragedy, not a sentence, but just a barrier that temporarily prevents the achievement of an important goal in life. However, thanks to modern advances in medicine, you will be able to overcome this barrier. You just need to contact leading experts, be patient, and the meeting with the baby will take place!
Physical activity with polycystic ovary
To eliminate the symptoms and causes of polycystic ovary disease, insufficient nutrition and drinking regimen. To burn and eliminate fat efficiently, you need regular cardio workouts.
Physical activity should not complicate the work of the heart, lungs, and musculoskeletal system. Moderate exercise is recommended in accordance with the capabilities of the woman's body.
Hiking in the fresh air in any weather and the following sports are useful:
- swimming in the pool;
- yoga for beginners;
- Pilates is a fitness technique for strengthening the muscular system, improving coordination and balance, relieving stress;
- short runs.
If polycystic ovary is left untreated, it progresses up to menopause. 15% of patients develop type 2 diabetes mellitus, impaired fat metabolism, hypertension with frequent pressure surges.
Relapse prevention
Existing treatments for polycystic ovary syndrome most often do not allow for a permanent cure. The reason is the impossibility of eliminating the main pathogenetic links of the disease. Symptoms and structural ovarian changes recur within five years after surgery, necessitating supportive treatment.
For the regulation of the menstrual cycle, prevention of endometrial hyperplasia, hirsutism and hyperandrogenic dermatopathy on on an ongoing basis until menopause, patients are prescribed combined hormonal contraceptives or gestagens in the second phase cycle. This tactic also contributes to the preservation of reproductive function in some patients.
How to normalize the menstrual cycle with polycystic ovary
Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are used to prevent the progression of the disease. The preparations contain antiandrogens. They reduce the production of male sex hormones, against the background of this, ovulation appears and the likelihood of pregnancy arises.
If the COC course passes, and the ovulatory function has not returned to normal, hormonal drugs are prescribed to stimulate ovulation with a gradual increase in dosage. Additionally, drugs with an antiandrogenic effect (cyproterone acetate, spironolactone) can be used.
Patients note a decrease in skin oiliness and acne, and an increase in the intensity of hair growth. As an adjunct to drug therapy for hirsutism, it is recommended to use cosmetological methods for removing unwanted hair, for example, photoepilation.
Improving the psycho-emotional state in PCOS
If the arising hormonal imbalance in polycystic ovary and the ensuing changes in appearance (obesity, hirsutism, alopecia, acne) led to the onset of a depressive or anxiety state, the woman is shown a psychological support. In more complex cases, antidepressants, anxiolytics are prescribed, but their selection requires special attention, since many in these groups can influence the rate of weight gain and exacerbate existing Problems.
Polycystic ovary syndrome in women 40-55 years old
Older women (40 years old) have different priorities - they are concerned about the possibility of having children. And here all the efforts of doctors will be aimed at regulating the menstrual cycle and restoring fertile function. A special therapy is prescribed to stimulate ovulation. If it does not have the desired effect, then a woman can be offered a surgical method for treating polycystic ovary syndrome - minilaparoscopy. This is a gentle surgery that restores the ovaries' ability to ovulate.
At the age of 45-55 years, polycystic ovary syndrome gives women problems of a completely different kind - high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, uterine bleeding, diseases of the cardiovascular system, the risk of oncology. And in this case, the priority is the treatment of these particular PCOS complications.
Forecast and prevention
Since polycystic ovary disease is a chronic disease, recurrence of clinical manifestations is possible even after a successful pregnancy and childbirth. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures:
- lead a healthy lifestyle that includes healthy sleep, healthy eating and regular physical activity;
- COC therapy or intermittent use of progestins to prevent endometrial hyperplasia and cancer for cycles longer than 90 days;
- conduct screening tests for depression for the timely detection of pre-depressive conditions;
- during pregnancy, be sure to be under the supervision of specialists, given the increased risk of adverse outcomes for mothers and children.
Sources of
- https://endoinfo.ru/theory_pacients/ginekologiya/sindrom-polikistoznykh-yaichnikov.html
- https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/polycystic_ovaries
- https://gutaclinic.ru/articles/sindrom-polikistoznykh-yaichnikov/
- https://www.ivf10.ru/patsientam/spkya-i-beremennost-otvety-na-chastye-voprosy.html
- https://zn48.ru/articles/sindrom-polikistoznykh-yaichnikov-chem-opasna-patologiya-dlya-zhenshchin/
- https://www.diagnos.ru/diseases/ginec/endocrinologiya_v_ginekologii/spkya
- https://www.k31.ru/service/ginekologiya/sindrom-polikistoznyh-yaichnikov.html
- https://www.Endocrinolog.by/to-patients/polikistoz-yaichnikov-spkya-chto-eto-takoe/
- https://unclinic.ru/9-rasprostranennyh-mifov-o-spkja-i-fakty-kotorye-dolzhna-znat-kazhdaja-zhenshhina/
- https://AltraVita-IVF.ru/vse-o-besplodii/zhenskoe-besplodie/113-sindrom-polikistoznykh-yaichnikov.html
- https://ProBolezny.ru/polikistoz-yaichnikov/
- https://institut-clinic.ru/polikistoz-yaichnikov-chto-eto-simptomy-i-osobennosti-lecheniya/
- https://www.imma.ru/polezno/ginekologiya/polikistoz-yaichnikov
- https://oxy-center.ru/stati/patsientam/polikistoz-yaichnikov-kak-vernut-ovulyatsiyu-i-mozhno-li-zaberemenet-s-etim-diagnozom/
- https://mosmed.ru/mosmed-klinika-funktsionalnyih-narusheniy/programmy-ginekologiya/sindrom-polikistoznyh-yaichnikov-spya-spkya
