Content
- Acne on the face
- Types of acne
- Open and closed comedones
- Inflammatory elements: papules and pustules
- Inflammatory elements: nodes
- Why do acne develop
- What hormones are responsible for acne
- Androgens and estrogens for the skin
- PCOS and acne
- Analysis of the endocrine status of patients
- When is hormone therapy prescribed?
- Effect of COCs on acne
- The Most Effective Acne Treatments
- Oral antibiotics for acne
- Benzoyl peroxide formulations
- Azelaic acid preparations
- Retinoid-based preparations
- Hormonal drugs against acne
- Study on COC Belar
- Does Jess help with acne
- Can acne come from oral contraceptives?
- How to choose an acne medication
Acne on the face
Acne, or pimples, is a condition of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands that can occur not only on the face, but also on the neck, shoulders or back. All these areas of localization of acne are united by the fact that they contain an increased number of sebaceous glands (from 400 to 800 per 1 cm2). And it is the hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands that is the first and most important factor in the development of acne, which triggers all subsequent links in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Types of acne
Acne is characterized by a large number of different morphological elements that can be inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Treatment of acne on the face will largely depend on exactly what elements are present on the skin. Non-inflammatory elements include only open and closed comedones (acne), while the rest of the acne elements (papules, pustules, nodes) are already inflammatory in nature.
Open and closed comedones
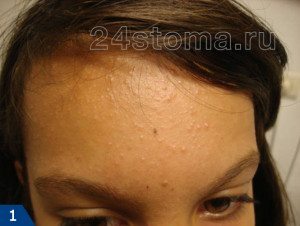
Closed comedones (whiteheads) - These appear as small white bumps on the surface of the skin. Each closed comedone is a hair follicle swollen with abundant fatty content, while the follicle outlet is absent, or almost imperceptible.
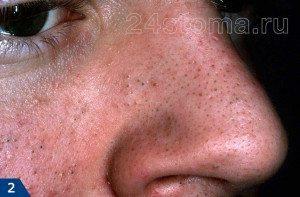
Open comedones (blackheads) appear as blackheads in the pores of the skin. Those. in this case, we visually see fat plugs in the mouths of the hair follicles. The black color of the fat plugs is given by the oxidized pigment melanin.
Comedonal acne: photo
If the patient has only comedones on the skin (without inflammatory elements), then this is called the comedonal form of acne. But most often comedones are only 1 stage of the disease and in their place there are further inflammatory elements - papules and pustules.
Inflammatory elements: papules and pustules
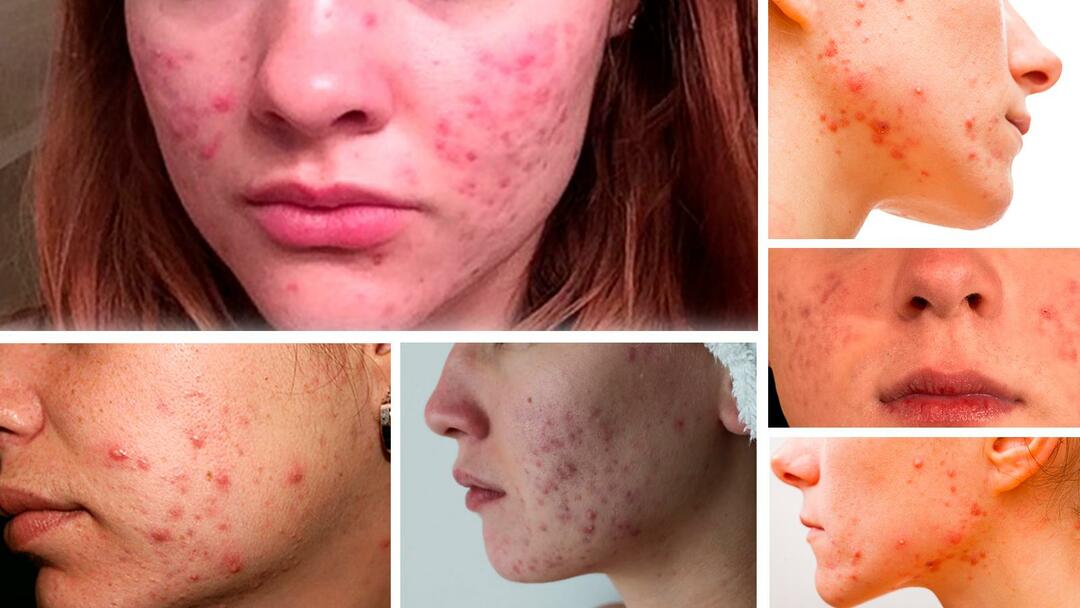
The most common inflammatory elements in acne are papules and pustules (they are called acne). Papules look like inflamed bumps on the surface of the skin, ranging in size from 2.0 to 4.0 mm. Their distinctive feature is that they do not contain pus inside. The full development cycle of papules takes from 10 days to 2 months, after which they either turn into pustules, or spontaneously disappear (with the formation of a weakly pigmented spot).
Pustules are inflammatory formations - in the form of inflamed nodules that rise above the surface of the skin, ranging in size from 2.0 to 4.0 mm (Fig. 4). There is pus in the center of each nodule. Pustules are most often formed from papules, and if they are not squeezed out, then their purulent contents gradually dry up and turn into a crust (a hyperpigmented spot then remains in place of the latter). The form of acne in which the patient has such inflammatory elements is called the papulopustular form of acne.
Papulo-pustular form of acne on the face: photo
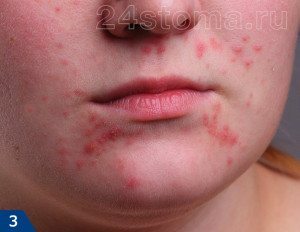
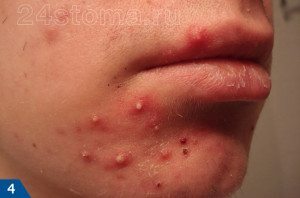
The papulopustular form of acne is mild, moderate, and severe. The differences between them relate to the amount of inflammatory elements in the patient (papules and pustules). Mild degree - up to 15 elements, medium - up to 50 elements, severe - from 50 or more inflammatory elements.
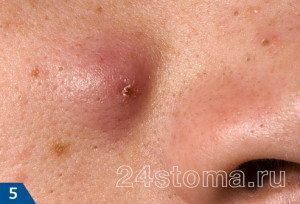
Inflammatory elements: nodes
As a rule, the nodes appear at the later stages of the papulopustular form of acne. They are large cones - most often between 1.0 and 2.0 cm in size. Depending on the type of knots, they can be tight or soft, painful or painless. Previously, the nodes that have a cavity with pus inside were called cysts, but today this term has been abandoned. The full development cycle of the nodes is at least 3-4 weeks, after which they disappear, as a rule, with the formation of scars.
Most often, nodes occur in young girls, and are the result of attempts to squeeze out papules and pustules. As a result, the follicle can burst, and its contents spill out into the depths of the soft tissues, which leads to the formation of a deep inflammatory infiltrate (node).
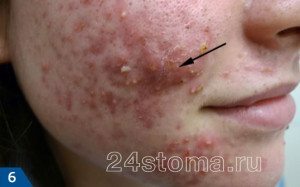
Why do acne develop
At the root of the development of all acne is the blockage of the pores of the skin. Pores are holes that surround each hair follicle, and sebaceous glands secrete their secretions into the follicle. Fatty secretion - sebum - is excreted through the opening of the pore.
When the pores are open, sebum flows freely to the surface and helps to keep the skin soft while protecting it from external influences. But if the pores are clogged with dirt particles, dead skin cells, excess oil, and possibly bacteria, acne develops.
Sometimes, to prevent acne breakouts, it is enough to simply take care of the health of the skin by regularly cleansing it. However, when acne is caused by hormonal imbalances or a medical condition, it can be difficult to manage.
What hormones are responsible for acne
In those people who have a predisposition to acne, the sebaceous glands are large. They begin to form during adolescence. The following types of hormones are involved in the formation of acne:
- androgens
This type of hormone is one of the most important for the secretion of sebum in our body. As they grow up, they allow the production of as much fat as possible, which is why acne appears in adolescents and adults of both sexes.
- estrogens
High levels of these hormones negatively affect sebum production. The sebaceous glands become smaller. Their increase can even at the genetic level affect the regulation of the sebaceous gland.
- progesterone
This type of hormone converts testosterone into the more powerful hormone DHT.
- insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1
It accelerates the growth of the activity of the sebaceous glands. This has already been proven through numerous studies. It greatly affects the work of the adrenal glands.
- corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)
Thanks to it, accessibility to the sebaceous glands is formed, which are its main goal.
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Participates in the formation of a large amount of cortisol.
- melanocortin
Regulates sebocyte differentiation and lipogenesis.
- glucocorticoids
They influence the formation of numerous inflammations.
- a growth hormone
Takes part in the differentiation of sebocytes and increases the rate of conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Androgens and estrogens for the skin
Acne vulgaris (acne) is a dermatological manifestation of diseases often associated with hyperandrogenism and an excess of androgens in the pilosebotic zones of the skin. Acne is most common in adolescents, but often persists into adulthood.

The incidence of acne among women of reproductive age is 12%.
Most acne patients, especially adolescents, are dissatisfied with their appearance, which can cause emotional, psychological, sexual disorders leading to social maladjustment and decreased quality life.
In the pathogenesis of acne formation, the following mechanisms are important:
- hyperproduction of sebum by hyperplastic sebaceous glands;
- follicular hyperkeratosis;
- reproduction of microorganisms.
The balance between androgens and estrogens of the skin is important, which is maintained by specific androgen- and estrogen-synthesizing enzymes of skin cells and activation of androgen receptors.
Prolonged acne, onset after 20 years of age, and resistance to standard dermatological treatments should alert the doctor, making you think about hyperandrogenism, especially if acne is accompanied by hirsutism and menstrual irregularities functions.
PCOS and acne
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine (hormonal) disease characterized by abnormal changes in the structure and function of the ovaries. Commonly used synonyms for PCOS are polycystic or ovarian sclerocystosis.
With this disease in women, insulin resistance is observed, and therefore increased insulin stimulates ovaries to overproduction of male sex hormones - androgens, which disrupt structure and function ovaries.
Androgens have a detrimental effect on the ovulation process, without which pregnancy is impossible, preventing the eggs from growing normally. Irregular periods, delays in menstruation with PCOS can be months or even six months.
In addition to menstrual irregularities, increased hair growth throughout the body (hirsutism) occurs due to the increased amount of male hormones. The skin becomes oily, acne and blackheads appear on the face, back, chest.
Since there are many symptoms of the disease, PCOS can easily be confused with any dyshormonal disorder. At a young age, oily skin, acne and acne are mistaken for natural age characteristics, and increased hairiness and problems with being overweight are often perceived as genetic characteristics.
Therefore, if the menstrual cycle is not disturbed and the woman has not yet tried to become pregnant, then such patients rarely go to the gynecologist. It is important to know that any such manifestations are not the norm, and if you find such symptoms in yourself, you should consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist in person.
The tactics of treating acne with PCOS is determined based on the severity of the symptoms. Usually, therapy is started with conservative methods.
If a woman is obese, then treatment should begin with a correction of body weight. Otherwise, conservative treatment in such patients does not always give the desired result. Further, medical treatment of hormonal disorders is carried out.
Analysis of the endocrine status of patients
Evaluation of the endocrine status is important and is carried out:
- when the acne problem begins after a person reaches 30 years of age;
- acne is not treated with conventional methods;
- acne before puberty;
- acne before your period starts;
- increased content of the hormone androgens;
- increased testosterone content;
- obesity;
- the location of the rash. If they are in the chin area, then the reason lies in hormonal disorders.
When is hormone therapy prescribed?
A sign that a person has an excess of androgens in the body is acne, characterized by:
- the presence of cysts;
- the appearance of nodules;
- the appearance of inflammatory rashes.
Hormonal treatment is indicated for women not only with an increased level of androgens, but with prolonged periods of exacerbation of acne and in cases where the disease is at an advanced stage. It is also used for patients who are not suitable or contraindicated for other treatments. For some women, hormone therapy is used as contraception. The main goals of hormone therapy are:
- reduction of increased secretion of androgens in the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, ovaries;
- suppress androgen receptors of the sebaceous glands.
Acne specialists in Europe recommend the use of hormone therapy for this condition along with antibiotics in severe or moderate cases.
Effect of COCs on acne
Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are often used medicinally to improve the condition of the skin and hair, as they the use is accompanied by an antiandrogenic effect, which is primarily associated with the fact that these drugs contain a combination of estrogens and progestogens.
The estrogenic component of the drugs increases the level of globulin that binds sex hormones. The combined effect of the progestogenic and estrogenic components suppresses the cyclic secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in the hypothalamus, causing antigonadotropic effect and a decrease in the level of secretion of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, as a result of which the synthesis of androgens in ovaries.
Most of the currently used combined contraceptives contain progestogens with low androgenicity or with antiandrogenic properties (cyproterone acetate, drospirenone, dienogest, chlormadinone acetate), which have the ability to direct antiandrogenic action due to competitive blockade of androgen receptors and a decrease in the activity of 5a-reductase, an enzyme involved in the conversion of testosterone into a more potent androgen dihydrotestosterone. The antiandrogenic effect of these drugs leads to a decrease in the effect of androgens on follicular keratinocytes and sebocytes and, as a result, to a 5-fold decrease in sebum secretion.
The Most Effective Acne Treatments
The most difficult part of acne treatment is choosing the right combination of drugs (taking into account the form of acne and the severity of its course). For example, the appointment of different groups of drugs and their combinations will depend on the predominance of certain types of inflammatory elements - these can be comedones, papules, pustules or nodes), as well as from their quantity. The most effective remedies for acne on the face, which we will discuss below:
- topical and systemic retinodes;
- antibiotics;
- benzoyl peroxide products;
- additionally for women - oral contraceptives.
Important: we have not included preparations with azelaic and salicylic acids in this list. They are significantly weaker when compared to topical retinoids. Even for the treatment of the mildest comedonal form of acne (acne), these drugs are only used as 2nd echelon drugs. For the treatment of papulopustular and nodular forms of acne, their use is, in fact, meaningless. Nevertheless, if you are interested in this group of drugs, we talk about them in detail in the article on the treatment of acne.
Oral antibiotics for acne
The daily dosage of tetracycline is in most cases 1000 mg, but with severe acne the dosage can be increased to 3500 mg per day (such doses can be used only under the control of function liver). This antibiotic can be taken only 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after, and the duration of administration is no more than 8 weeks. However, this drug has serious age restrictions, and in recent years, resistant strains of P. acnes have been increasingly found to it.
Doxycycline and minocycline are lipophilic tetracyclines, and much less resistant P. acnes strains have been found. The daily dosage of doxycycline is from 100 to 200 mg per day (orally, the intake does not depend on the food intake), the duration of the intake is up to 8 weeks. But it should be borne in mind that taking doxycycline induces photosensitization in the summer, and for the summer it is not the best antibiotic. Minocycline is taken in the same dosage, but this drug often causes bluish-black pigmentation of the skin (in areas where there is atrophic scars and acne scars).
Antibiotics of the Macrolide group -
for example, it is erythromycin, but now there are many resistant P. acnes strains to it, and therefore it is rarely used recently. The best option (antibiotic of the 2nd choice after doxycycline) is the antibiotic azithromycin, which is prescribed in a dose of 250 to 500 mg (taken only 3 times a week). This drug, unfortunately, can cause antibiotic-associated diarrhea in 2-5% of patients, and therefore it is better to take it immediately together with drugs to restore the intestinal microflora.
Antibiotics of the Lincosamide group -
clindamycin belongs to this group of antibiotics, but it can be used only for external therapy. When taken orally, this antibiotic often causes a severe form of aniotic-associated diarrhea, which is called pseudomembranous colitis (this pathology has a high degree of lethality).
Sulfone group drugs -
drugs in this group (for example, Dapsone) are prescribed only if the patient has P. acnes strains that are resistant to other antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance is assumed in the absence of a response to treatment - after 6 weeks of antibiotic therapy. Moreover, if we assume resistance, then it is extremely important to exclude the patient from gram-negative folliculitis, which may occur in patients with acne due to long-term antibiotic use in the past.
Important: the most painful point of antibiotic therapy for acne is the development of resistant strains of Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Parallel use with antibiotics of topical agents based on benzoyl peroxide, as well as refusal frequent changes in different antibiotics are the best ways to prevent resistance in P. acnes and S. epidermidis.
Important: as you already understood, doxycycline will be the first choice drug, but not any. Given the long-term use of the antibiotic, it is important that doxycycline is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract as quickly as possible and as fully as possible (the worse these indicators are, the more damage will be done to the gastrointestinal tract). For doxycycline preparations from different manufacturers, these parameters differ, and this should be written in the instructions in the "pharmacokinetics" section. Experience has shown that the Dutch drug Unidox Solutab has good fast adsorption.
Important: we need antibiotics to drastically reduce the P. acnes population, but not only antibiotics allow us to do this. The course use of phototherapy and lasers can also significantly reduce the P. acnes population, and in many cases allows you to do - either without the use of external and oral antibiotics, or significantly reduce their duration application.
Benzoyl peroxide formulations
Benzoyl peroxide is a bactericidal component that effectively inhibits the growth of opportunistic bacteria Propionibacterium acne (P. acne), which play an important role in the development of a particularly papulopustular form acne. What is very important - no resistant strains of P.acne have yet been identified to benzoyl peroxide (unlike antibiotics), and how we said above - this component helps to prevent the emergence of resistant strains of P. acne bacteria when applied antibiotics.
Benzoyl peroxide pharmaceuticals are available in gel form. The classic monocomponent preparation is Baziron (with a benzoyl peroxide concentration of 2.5% or 5%). For the first month, it is recommended to use only 2.5% concentration, but when the skin gets used to the effects of the drug, it will be possible to switch to 5% of the drug. If you use more concentrated products at once, irritation will most likely appear on the skin.
Combined drugs -
there are also combination drugs where benzoyl peroxide is combined with an antibiotic or retinoid. Such combinations can be optimal in different clinical situations, for example, depending on what type of inflammatory components (papules or pustules) you have.
- Indoxil (UK) - This product contains 5% benzoyl peroxide and the antibiotic clindamycin 1%;
- Effezel (France) - contains 2.5% benzoyl peroxide + adapalene retinoid.
Azelaic acid preparations
active ingredient azelaic acid. A well-known trade mark is Skinoren. It has an anti-comedogenic, antimicrobial effect. Also, a whitening effect on the skin has been noted with prolonged use. These drugs are considered preferable in the treatment of acne after 24 years, when the amount of inflammatory elements decreases and the number of comedones increases. The healing effect develops gradually over several weeks. It is possible to simultaneously use topical retinoids with drugs, while it is recommended to take a break between the application of drugs in 20-30 minutes.
All of these topical acne medications can be combined with cosmetic products to treat problem skin. However, it is very important to use the products correctly in order to enhance their mutual action and not lead to an increase in skin irritation.
To do this, at least 20 minutes must elapse between washing with a special cosmetic gel or foam and applying the drug, so that the skin has time to dry. And if there is a need to apply a moisturizer specially formulated for oily or problematic skin, then between the application of the drug and moisturizing cosmetics, at least 20-30 minutes.
Retinoid-based preparations
The active ingredient is adapalene, or isotretinoin, or tretinoin, well-known trademarks "Differin", "Klenzit". Lead to a decrease in the production of sebaceous glands, thereby reducing the formation of new elements of the rash. What should you pay attention to? The healing effect is usually noticeable after 4-6 weeks of regular use, while it is important not to apply the drug in a very thick layer, as skin irritation is possible. This type of drug is not recommended for use when pregnancy occurs, and it should also be avoided during periods of increased solar activity (in summer and with a beach holiday).
Hormonal drugs against acne
Acne is not always easy to treat. Depending on the cause and severity of acne, topical treatments may not be effective. In such cases, doctors prescribe a number of oral medications to treat acne.
- Hormonal drugs. Women are prescribed combined contraceptive contraceptives (estrogen + progestogen). These drugs normalize hormones and are effective in treating acne. There are low-dose COCs that do not cause an increase in body weight, a decrease in libido, which is undesirable for women, but, on the contrary, normalize the cycle, eliminate the symptoms of PMS, and menstrual migraine. However, they are used only as directed by a gynecologist and require individual selection of the drug and dosage in order to minimize potential side effects;
- Antiandrogenic drugs. Antiandrogen drugs are used to treat hormonal acne caused by elevated androgen levels. Spironolactone (Veroshpiron) is prescribed, which has antiandrogenic activity, although it belongs to potassium-sparing diuretics. Spironolactone is especially recommended for women with polycystic ovary syndrome, as it allows not only to get rid of acne, but also other androgenic effects, such as hirsutism in PCOS.
It is important to understand that all hormonal drugs are strictly prescription drugs, and are prescribed in the absence of the effect of other acne treatments.
Hormone therapy has a high level of effectiveness, and it doesn't matter if there is an increased level of androgens or not. This method of treatment can be used both as an independent method and in combination with other methods. It is often used in conjunction with:
- antibiotics;
- benzoyl peroxide;
- azelaic acid;
- retinoids.
In order to see the first positive results after using such therapy, at least three months must pass. In many patients, improvements appear earlier.
Three groups of drugs can be used in the treatment:
- AR blockers;
- oral contraceptives;
- 3 glucocorticosteroids;
- enzyme inhibitors.
All drugs used in treatment have a high level of effectiveness. They have already proven themselves from the very best side.
Study on COC Belar
The purpose of this study was to assess the effectiveness of the treatment of acne of varying severity when using combined hormonal contraceptive Belara® and its effect on the indicators of psychological and social state in women reproductive age.
A number of researchers note that the use of COCs containing ethinyl estradiol and chlormadinone acetate within 6 months causes a significant improvement in the condition of the skin and hair.
The study included 123 patients aged 18–45 years who had acne on their face of varying severity. All women were interested in contraception and, after counseling, chose a COC containing 30 μg ethinylestradiol and 2 mg chlormadinone acetate. The patients used COC Belara®, which belongs to the clinical and pharmacological group of monophasic oral contraceptives with antiandrogenic properties. One tablet of the drug contains 30 μg of ethinylestradiol and 2 mg of chlormadinone acetate.
After 3 cycles of taking the drug, questioning and examination were carried out in 112 women; after 6 cycles - in 83. Before the appointment of Belara, 38% of women experienced psychological problems. After 12 weeks, only 7 people experienced severe psychological problems due to acne. patients out of 112, which amounted to 7%, after 24 weeks all women noted the absence of psychological problems. Before the appointment of Belara, 32% of women had problems of social adaptation due to acne.
After 6 cycles of using the drug Belara®, the following indicators of its effectiveness were noted. actions on the skin with acne: recovery was noted by patients in 89% of cases, by a doctor - at 74%. Improvement in the condition of the skin and a decrease in the number of eruptions were noted by 11% of patients, the doctor recorded an improvement in 18%. The doctor found no effect in only 8% of cases.
Does Jess help with acne
Does "Jess" help with acne First of all, it should be noted that the drug is prescribed in adolescence and women in a situation if they are sexually active, since the main purpose of this medication is contraception. Acne therapy is considered only a side effect of its use. Therefore, you can use "Jess" only after consulting a gynecologist and a blood test for hormone levels. The drug is prescribed only in that situation if it turns out that: The level of male hormones is increased. A girl or woman is worried about acne. At the same time, the representative of the beautiful half of humanity leads an active sex life. The woman is not planning a pregnancy. –
First of all, it should be noted that the drug is prescribed for women to prevent unwanted pregnancies, as well as adolescent girls with acne. However, it should be remembered that the main purpose of the drug is contraception, and the fight against acne is only a side effect.
Before taking OK Jess, you need to check your hormone levels. The drug is prescribed only in the following cases:
- there is a hormonal imbalance with acne;
- the woman is sexually active and does not plan pregnancy.
Important! Since the drug affects the patient's hormonal status, it can both cause a rash on the face and remove it.
Can acne come from oral contraceptives?
Researchers from the United States performed a retrospective cohort study that assessed the incidence of the development of acne during the first year after the start of contraceptive therapy in girls and women aged 12-40 years old. All study participants started taking contraceptives for the first time.
The study participants also assessed the severity of acne and the need for topical drugs. and oral tetracycline antibiotics within the first year after initiation contraceptive.
results
- The analysis included 336,738 adolescent girls and women who started taking contraceptives and had no history of acne.
- Compared with the use of combined oral contraceptives, in the presence of an intrauterine copper coil, the risk of developing clinically significant acne increased by 14% (hazard ratio, 1.14; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.29), against the background of an intrauterine device with levonorgestrel, the risk was 9% higher (hazard ratio, 1.09; 95% CI 1.03-1.16).
- Among adolescent girls and women with a history of acne (n = 21,178) versus combined oral contraceptives, intrauterine copper coil was associated with a 44% increase in the use of topical drugs and oral tetracycline antibiotics (hazard ratio, 1,44; 95% CI 1.00–2.06), intrauterine device
How to choose an acne medication
When choosing an anti-acne drug on your own, it is sometimes difficult to understand how they differ from each other and which drug should be preferred.
When choosing a particular drug, it is important to figure out whether it is a drug (for which the requirements for efficacy and safety is much higher) or a cosmetic product and is used not to treat the skin, but to maintain it healthy condition.
The simplest difference is that cosmetics and medicines are on different shelves in the pharmacy. The second difference is the promises on the packaging. On medicinal products, the purpose of the drug and the main active ingredients are indicated. Cosmetics packaging is full of promises about the effectiveness of the product in solving problems.
Medicines for the treatment of acne, with the seeming variety of brands, are divided into only 4 main types, depending on the active ingredient that they contain. It is the active substance that provides the therapeutic effect of the drug.
It is not worth taking hormonal drugs only for acne, because these are quite strong medicines that have side effects. Therefore, consultation of both a dermatologist and a gynecologist is required, and careful weighing of all the advantages and disadvantages.
Sources of
- https://24stoma.ru/lechenie-akne-na-lice.html
- https://unclinic.ru/8-prichin-vozniknovenija-ugrevoj-sypi-u-vzroslyh-i-jeffektivnye-metody-lechenija-akne/
- https://im-b.ru/stati/gormonalnaya-terapiya-akne.html
- https://con-med.ru/eprint/229928/
- https://www.baby-ivf.ru/stati/sindrom-polikistoznykh-yaichnikov-ili-multifollikulyarnye-yaichniki/
- https://zercalin.ru/information/kakoy-preparat-vybrat/
- https://internist.ru/publications/detail/kak-vliyayut-razlichnye-kontratseptivy-na-risk-razvitiya-akne/