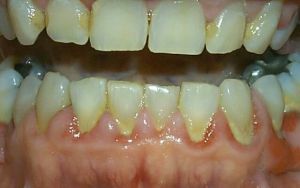
 Generalized periodontitis is an inflammatory periodontal disease caused by the multiplication of bacteria. The disease proceeds with the formation of the gingival pockets.
Generalized periodontitis is an inflammatory periodontal disease caused by the multiplication of bacteria. The disease proceeds with the formation of the gingival pockets.
It is considered one of the most difficult dental diseases. Chronic generalized periodontitis can cause stroke, heart attack, arthritis and other serious disorders that pose a threat to human life and health.
Contents
- The specific and clinical causes of the disease
- Features of the clinical picture
- Other features of the disease course
- Chronic and acute form of the flow of the destructive process
- Degrees of severity
- Diagnostic methods
- Methods of treatment
- Preventive measures
- Features of the clinical picture
Local and general causes of the disease
There are two groups of provoking factors -local and general. Among the local causes of the manifestations of the disease are the following:
- Incorrect alignment of the teeth or broken bite - in this case, the remains of food can accumulate between the teeth, which will become a favorable environment for the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria.
- The plaque on the enamel of the teeth arises from the absence of care for the oral cavity. Under the attack, pathogenic bacteria develop.
- Stones on the teeth - a progressive type of bacterial plaque, which is located on the inside of the dentition. Has a dark color. Due to the dead tissues in the stones, food residues, bacteria, which reproduce in a favorable environment for them, there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Gnashing of teeth - bruxism .During the clash of the dentition, the enamel is erased, resulting in damage to the upper edges of the teeth, which can also cause the first signs of generalized periodontitis.
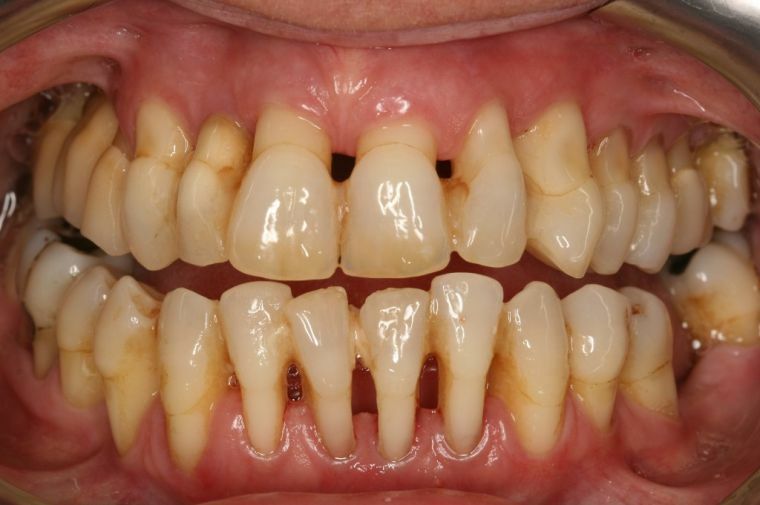
Common causes include diseases that weaken the immune system:
- Gastritis is considered one of the diseases that contribute to the appearance of periodontitis and gingivitis. With this disease, the body has lost the ability to correctly and completely absorb food, because of this in the mouth remain pieces of food that affect the development of bacteria.
- Diabetes is a disease that can exacerbate the inflammatory process in the periodontal region.
- Periodontal disease also causes hepatitis, rheumatism, obesity .All these diseases affect the body in various degrees and weaken it, undermine the protective functions of the body, thereby allowing the bacteria to multiply in the oral cavity.
Features of the clinical picture
Like any other periodontal disease, generalized periodontitis has its unique symptoms, according to which it can be easily identified. The main five:
- Bleeding in the gums , which is most often manifested when brushing your teeth. Unfortunately, most often no one pays attention to it, writing off this symptom for a lack of vitamins.
- Bad smell from the mouth .
- Burning in the gums .
- Change in gum structure .During the development of the disease, the surface of the gums becomes porous, the periodontal pockets appear.
- Appearance of pain when chewing food .Usually this is considered the main factor, indicating that the gums are inflamed, and generalized periodontitis is already in a serious degree of its development.
Other features of the disease course
In the case of the onset of the development of the disease, there is a high sensitivity of the teeth to food temperature changes and irritating nerve endings of the tooth roots, products, for example, after using sweet or hot, sharp pains in the gum area begin.
In addition to hypersensitivity begins the process of loosening of the teeth, there is a deviation from the normal location, the appearance of cracks.
There is often a high fever, indicating the existence of an inflammatory process.
Weakness and general malaise caused by bacteria that awaken all fallen asleep inflammatory processes is another symptom that may indicate the development of periodontitis.
Generalized periodontitis of severe degree provokes a complete change in the structure of the gums and tooth loss, which can only be stopped with the help of surgical intervention.
Chronic and acute form of
disruptive process course Generalized periodontitis can occur in two forms: 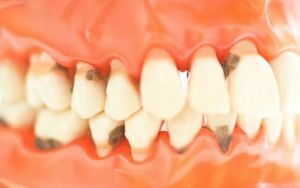
- Acute form of the disease is less common, but it is more rapid and painful. The basis for its development is the careless execution of dental procedures by a doctor. In acute infection, only 1-2 teeth are most often affected, and if the treatment is started on time, it is easy to get rid of the disease.
- The chronic form of generalized periodontitis is much more common. There are periods of "hibernation" and activity. It is the chronic form of periodontitis that is considered common. It is also worth noting that chronic generalized periodontitis is the basis for the development of such a disease as stomatitis. The disease gradually destroys all teeth.
Symptoms of the chronic form of the disease:
- complete inflammation of the gingival surface, expressed in mild form;
- appearance of burning in the gums;
- severe regular bleeding in the mouth;
- pain during meals.
In the sleep mode, chronic periodontitis does not bother a person and creates the feeling that the disease has receded.
However, this stage can be considered the most dangerous, in comparison with the current one. During its course, the inflammation process proceeds in a slowed-down form, but more deeply affects the periodontal tissue. At transition in an operating stage at the patient the temperature rises, the general inflammatory process and a malaise is observed.
Degrees of severity
Generalized periodontitis on the path of development passes through three degrees of progress:
- For the , the light degree is characterized by the appearance of bleeding gums. A change in the structure of the gums begins. Perhaps the appearance of
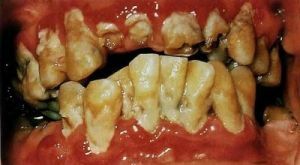 dentogingival pockets.
dentogingival pockets. - In the average degree is observed the appearance of painful sensations when the teeth come in contact with hot and cold food, deepening the pockets in the gums to 5 mm. Also, the middle stage is accompanied by increased bleeding in the gum area.
- In the severe , a disruptive process is accompanied by severe bleeding and the appearance of pus on the surface of the gums. Further deepening of the gingival pockets up to 7 mm also develops. This form should be treated only surgically.
Diagnostic methods
In the process of primary diagnosis and verification for the appearance of periodontal disease, dentists are studying the presence of plaque on teeth and stone deposits, the presence of wounds in the gums and bleeding.
To establish the prerequisites for the appearance of the disease, the patient is invited to check the entire body for inflammatory processes, which can be a favorable environment for the emergence and development of bacteria.
When checking the condition of the oral cavity, the doctor also pays attention to the setting of teeth, on the gap between them and possible displacement, since it is the incorrect bite, as was said earlier, which is one of the reasons for the appearance of periodontal disease.
Methods of treatment
There is a classical scheme of therapy, worked out for years.
 With mild generalized periodontitis treatment means the use of external means, such as, for example, Metrogil Denta.
With mild generalized periodontitis treatment means the use of external means, such as, for example, Metrogil Denta.
In addition to the use of medicines, dental stones and plaque are removed, this is done to exclude a favorable environment. After this procedure, the teeth are ground to remove the damaged parts.
In the second stage, the infected areas of the teeth are removed and the gums are treated by cleaning the pockets formed. If necessary, the cavities are filled. If necessary, it may be recommended to remove inflamed teeth and roots.
Generalized periodontitis of severe degree is treated by a greater degree by surgical methods. Removal of damaged gum sites and extraction of teeth is carried out, biochemical therapy is possible.
A group of anesthetizing injections is done before surgery, and after surgical intervention it is recommended to apply aseptic dressings for a certain time.
When the process is started and there is no treatment, it is possible to lose a large number of teeth, rapid wear of gum tissue and a serious decrease in immunity, which leads to the emergence of new foci of infection.
Preventative measures
As a preventive measure, the following are recommended: 
- regular tooth cleaning;
- preventive check at the dentist at least once a year;
- regular rinsing of the oral cavity after eating to completely purify it of food leftovers;
- formation of a balanced diet for improved functioning of the body and exclusion of the process of inflammation;
- removal or treatment of sick teeth;
- treatment of gums in case of bleeding.
