 A watery formation near the bone tissue of a tooth can appear for various reasons, and sometimes the patient does not even know about its existence. But under certain circumstances, a cyst on a tooth can begin to develop, and thereby make itself felt with a number of symptoms.
A watery formation near the bone tissue of a tooth can appear for various reasons, and sometimes the patient does not even know about its existence. But under certain circumstances, a cyst on a tooth can begin to develop, and thereby make itself felt with a number of symptoms.
Then it is necessary to urgently take action, since the treatment of this, albeit small, education can take years.
Content
- What it is?
- Reasons for education
- Types of formations
- Typical symptoms and signs
- Why is a cyst on the root of a tooth dangerous?
- Approach to therapy
- Surgery
- Preventive actions
What it is?
A cyst is a pathological formation in the area of the apex of the tooth root. Its internal cavity has a liquid or mushy consistency, a dense layer of epithelium forms on top.
The bladder usually consists of an accumulation of pus, dead cells, and bacteria. The most active inflammatory process occurs in the upper jaw, since the roots of the teeth on it have a more porous structure.
Cyst sizes can be from 5 mm to several centimeters. The formation of bubbles at the apex of the tooth root is caused by an inflammatory process. The body seeks to protect healthy tissues by separating pathological areas, this is what contributes to the appearance of cystic formation.
Reasons for education
The main source of cyst formation under the tooth is an infection that affects the inner tissue in the area of the tooth root. All reasons can be divided into two groups: caused by improper oral hygiene and received as a result of an injury in the jaw area. Improper hygiene can provoke a number of diseases, due to which pathological formations appear. Among them:
-
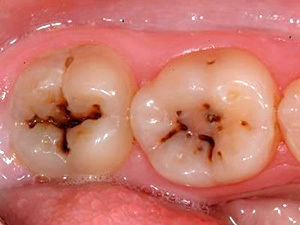 caries;
caries; - complicated pulpitis;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- periodontitis - periodontal inflammation;
- periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum.
Injuries that can cause a cyst to appear include:
- injuries of the face and dentition, which are often found in athletes;
-
 teethingespecially indigenous;
teethingespecially indigenous; - incorrectly installed prostheses;
- incorrectly sealed canals;
- excessive load on the teeth without visible external damage, for example, when biting hard candies, nuts, strong teeth banging against each other.
All of these reasons are capable of provoking an inflammatory process, the focus of which will either be immediately localized in the area of the tooth root, or will eventually deepen from the oral cavity into the tissue.
Types of formations
Depending on the reasons for the formation, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
-
Retromolar occurs with chronic tissue inflammation, most often caused by complicated teething. This type of education is characteristic of the appearance of wisdom teeth, especially with their improper growth, the appearance of an air hood.
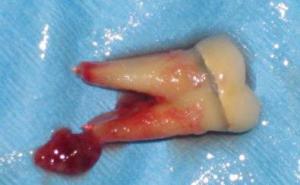
- Eruption cyst is a softened form of the retromolar appearance, it is a small soft formation that appears during teething. Until now, the exact cause of this type of benign cysts has not been identified, therefore it is believed that the reason lies in the defeat of an infection against the background of a weakening of local resistance. Occurs in children in the process of changing milk teeth.
- Follicular appears in connection with the pathology of the development of the molar. It is formed from follicles during the formation of dental tissue during eruption.
- Radicular is the most common type, as it is formed during chronic tissue inflammation. It can be caused by trauma, making early diagnosis difficult.
- Residual formed after tooth extraction. If a piece of root remains in the tissue during the treatment, it will cause inflammation of the tissue and provoke the appearance of a purulent vesicle. Often, a residual cyst contains a piece of the left tooth within itself, and has a complex shape.
- Keratokista formed during pathological formation of the periodontium. Previously, this type belonged to follicular cysts, but in fact it has a slightly different manifestation. The vesicle is formed from the epithelium necessary for the formation of tissue around the tooth, which often interferes with healthy teething.
- Ophthalmic cyst can be caused by complications in the maxillary sinuses, it is localized at the site of inflammation.
Typical symptoms and signs
 The development of a cyst at the root of a tooth takes two forms. When an annular granuloma forms, it is not easy to detect, as there are no signs. Tight bubble does not cause discomfort.
The development of a cyst at the root of a tooth takes two forms. When an annular granuloma forms, it is not easy to detect, as there are no signs. Tight bubble does not cause discomfort.
The patient may complain of slight pain in the tooth and gums when biting, but soreness is often attributed to temperature changes, an accidental reaction that has no cause for concern.
An experienced dentist will be able to detect the formation, but this is not often the case. There are cases when the presence of a cyst at an early stage is known only when an X-ray is taken to treat other teeth.
As soon as the education is influenced by external factors that provoke its growth, the patient will feel pronounced symptoms. Strong pain sensations will appear in the causative tooth, in the gum, and can also be given on the opposite jaw row.
Inflammation will increase significantly, which can cause a rise in temperature. Often there is swelling in the mouth or on the cheeks.
Why is a cyst on the root of a tooth dangerous?
The formation of a cyst is not dangerous for humans, because the body in this way protects itself from infection, trying to keep healthy tissues intact. But in the absence of treatment, a dental cyst will begin to develop, which will provoke the appearance of a huge list of diseases:
-
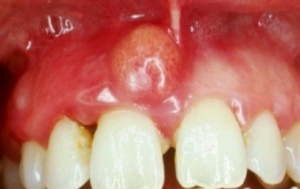
Flux on the anterior upper tooth
Periodontitis can be both a source and a consequence of cyst inflammation. With the spread of inflammation, not only the periodontium suffers, but also the bone tissue, which is fraught with tooth loss.
- Flux accompanied by severe pain and severe swelling not only in the area of inflammation, but also on the face. A large amount of pus is formed at the site of the lesion, which will cause additional complications.
-
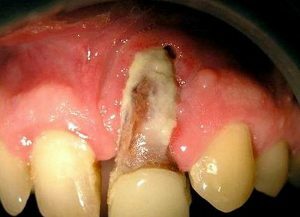
Osteomyelitis of the jaw
Phlegmon spreads to the tissues of the neck and face, accompanied by the appearance of suppuration in the area of inflammation. The disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy, as there is a risk of general infection due to restrictions on treatment.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw bones.
- Loss of diseased teeth.
- Jaw fractures.
- In advanced cases, a cyst can develop into a benign or malignant tumor.
- Blood poisoning.
Approach to therapy
Therapeutic treatment is prescribed in the early stages, when the cyst of the tooth does not yet exceed the size of 1 cm, and also only if the patency of the canals is good. Most often, therapeutic methods are resorted to to treat patients at a young age. Z
The task of the dentist is to eliminate the infection that provokes the formation of the cyst, as well as to establish a solid blockage so that it reappears.
 In the course of treatment, the doctor opens access to the root canals by excising the destroyed tissue or removing the imposed filling. The dentist examines the patency of the canals, direction and length, makes an X-ray with inserted metal instruments to assess the situation visually. The channels are expanded if necessary.
In the course of treatment, the doctor opens access to the root canals by excising the destroyed tissue or removing the imposed filling. The dentist examines the patency of the canals, direction and length, makes an X-ray with inserted metal instruments to assess the situation visually. The channels are expanded if necessary.
Throughout the work with the channels, antiseptic preparations are constantly used. The most popular of these are Chlohexidine and sodium hypochlorite.
After mechanical action and treatment with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs, the apical opening opens, the drug is excreted behind the apex. Use highly alkaline agents, such as calcium hydroxide, to neutralize the acidic environment of the cyst.
This drug destroys the walls of the formation, has an antimicrobial effect, protects bone tissue and promotes early healing.
After removal of the cyst, a temporary filling of the canals is performed. Dentist check-ups are scheduled every week to monitor tissue behavior using x-rays. If the dynamics are positive, each time the canals are sealed to a greater extent until they are fully strengthened in the crown area. Full recovery of bone tissue will last for a year, so it is recommended to visit the dentist in accordance with the prescribed course.

Depophoresis
Recently, depophoresis has been used in therapeutic treatment, which removes infection from all canals of the tooth, even where access is difficult.
The method involves the use of copper-calcium hydroxide as a drug. Inflamed areas are affected by a weak electric current, due to which the drug penetrates deeply, destroying both the cyst and infectious agents.
Usually, a course of at least three sessions is prescribed, at the end of which the tooth is filled like the method described above.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is prescribed if the tooth is properly filled, the cyst has dimensions, exceeding 1 cm in diameter, as well as in cases when there is a crown on the tooth or a root canal is installed pin. There are several types of surgical intervention, depending on the degree of tissue damage and the effect on the cyst.
 It is considered less traumatic to remove only the cyst wall followed by debridement of the affected area, called cystotomy. During the operation, the gum is dissected in the area of the cyst projection, the epithelium protecting it is removed, and antiseptic and regenerative agents are used. The use of drugs works in almost the same way as in therapeutic treatment, but special attention is paid to the postoperative period.
It is considered less traumatic to remove only the cyst wall followed by debridement of the affected area, called cystotomy. During the operation, the gum is dissected in the area of the cyst projection, the epithelium protecting it is removed, and antiseptic and regenerative agents are used. The use of drugs works in almost the same way as in therapeutic treatment, but special attention is paid to the postoperative period.
Cystotomy is used when:
- want to preserve the rudiments of permanent teeth when changing milk teeth;
- the cyst is in contact with the roots of adjacent teeth;
- the cyst is in contact with the jaw bone;
- there are contraindications to other methods due to chronic diseases.
 During a cystectomy, the entire body of the cyst is removed. In a similar way, the gums are dissected in the area of the formation. The edges of the wound are pulled apart, the dentist cuts out the outer bone plate.
During a cystectomy, the entire body of the cyst is removed. In a similar way, the gums are dissected in the area of the formation. The edges of the wound are pulled apart, the dentist cuts out the outer bone plate.
The walls of the cyst are cleaned, the accessible part of the root is removed, if necessary, a filling is carried out to seal the cut. A medicine is placed inside, which accelerates the process of bone tissue restoration. The wound is sutured. If the size of the cyst is large, and the wound is too large, it is not sutured, but blocked with an iodine swab.
In rare cases, they resort to resection of the upper part of the tooth root. This is due to the infection of the bone tissue, so it is not possible to leave the affected part. The dentist performs the operation in the same way as a cystectomy, but in addition to removing the cyst, he cuts the root in the infected zone.
For the operation, it is necessary to prepare the tooth canal by filling it orthogradely. Resection is resorted to only in the case of the strategic importance of the tooth in the absence of positive dynamics in the use of other methods.
Tooth root resection:
One of the modern methods of surgical intervention is laser therapy. With this method of treatment, a tube is inserted into the cut tissue to guide the laser beam. The radiation dissolves the infected tissue, which is removed using a vacuum device. Thanks to this method, a complex effect on pathological tissues is carried out, so the treatment of the cyst is very effective.
 In advanced cases, dentists recommend hemisection (removal of the cyst, root and part of the crown affected by damage) or complete extraction of the tooth together with cyst, but modern methods allow many treatment options to be adopted in order to try to preserve residues even with a severe course of the disease tooth.
In advanced cases, dentists recommend hemisection (removal of the cyst, root and part of the crown affected by damage) or complete extraction of the tooth together with cyst, but modern methods allow many treatment options to be adopted in order to try to preserve residues even with a severe course of the disease tooth.
The cost of removing a radicular cyst in the area of one root in clinics in Moscow starts from 5200 rubles.
Preventive actions
There are a number of things you can do to reduce your risk of developing a cyst, including:
- regular visits to the dentist, at least once a year;
- proper oral hygiene;
- sanitation of the oral cavity, if necessary;
- avoiding injuries to the jaw and teeth;
- support of immunity and lack of stress.
The appearance of a tooth cyst can be triggered by many factors, but with timely treatment, surgical intervention can be avoided and the tooth can be kept intact.
The site is for informational purposes only. Do not under any circumstances self-medicate. If you find you have any symptoms of illness, contact your doctor.
