Leukoplakia is a pathological condition in which inappropriate corneal zones begin to appear inadequately and not typical for the epithelium( thicken, then slough off).This can develop on the external genitalia, cervix and vagina, in the oral cavity and other places. Pathology proceeds little, and a malignant degeneration is often observed. This is the danger of the disease. What contributes to the development of cervical leukoplakia, how to identify and cure an ailment?
Causes of leukoplakia of the cervix
Synonymthe concept of "leukoplakia" - hyperkeratosis. These are absolutely equivalent concepts. There are no exact reasons for the development of the disease. But under the influence of factors, the multilayered flat epithelium begins to cornify.
The following main provocative moments can be singled out:
- Not careful observance of personal hygiene. Recommended washings 1 - 2 times a day. Douching and other such manipulations should be done only as directed by the doctor.
- Random sex and, as a consequence, various infections( trichomonads, gonorrhea, viral lesions, etc.).Often they proceed for a long time, or not completely cure and provoke such changes on the cervix.
- Violation of the endocrine organs, the greatest role is played by the thyroid gland, the reproductive system of a woman.

- Immunodeficiency states, against which many processes in the body of a woman are pathological.
- Serious postpartum trauma to the cervix, its scar deformation.
- Various permanent mechanical injuries of the cervix: violent sexual contacts, improperly installed intrauterine device, numerous abortions, biopsies, etc. These procedures stimulate increased division of cells of the flat epithelium of the cervix, as a result of which malfunctions and mutations can occur.
And here's more about cervical dysplasia.
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia
In most cases, the pathology proceeds unnoticed for a woman. No pain, discharge, etc. Sometimes, after all, you can pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Increase the number of vaginal whites, and often they can have an unpleasant smell. The more extensive the lesion, the greater the excreta.
- If hyperkeratosis affects the external genitalia, itching appears in this area, dryness, scratching. Sometimes a woman marks white spots in places of leukoplakia.
- Also, with pronounced hyperkeratosis of the cervix, bloody contact discharge may appear( after intimate relationships, especially violent ones).
All other signs that a woman can mark are not directly related to leukoplakia, most often they simply reflect the state of the woman's health at the moment.
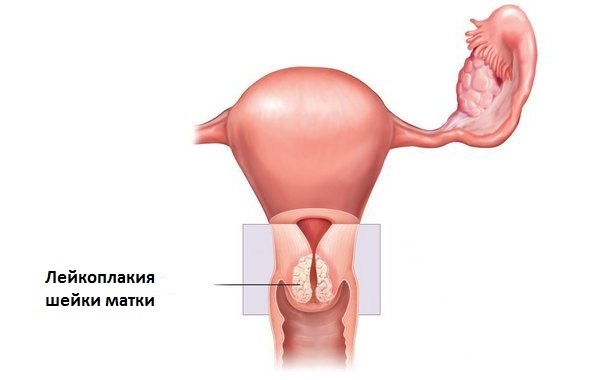
Cervical leukoplakia
Forms of cervical leukoplakia
Leukoplakia can affect part of the cervix or almost all of its surface. In terms of clinical picture, the following forms can be distinguished:
- Plane leukoplakia, which is characterized by the appearance of gray-white areas, while in terms of density, they practically do not differ from the rest of the epithelium. When touching with forceps or another object, the "plaque" is not removed or injured. In histological examination( after a biopsy), acanthosis and parakeratosis are determined.
- Verrux( warty) leukoplakia is characterized by the appearance of "growths", tuberosity. They are formed due to the fact that the constantly keratinized cells of the epithelium do not slough, but remain in place. Upon examination, such "warts" are immediately visible.
- Ulcerous necrotic form, in which tissue defects appear on the site of hyperkeratosis over time. Outwardly, it is difficult to distinguish from ordinary erosion, the biopsy helps to clarify the diagnosis.
Look at the video about cervical leukoplakia:
Diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia
The most common occurrence of leukoplakia is accidental during preventive examinations or against a background of other diseases, most often of an inflammatory nature. Diagnostic measures include the following:
- Inspection of the gynecological chair using mirrors. So it is possible to assume the presence of foci and make a plan for further examination.
- Smear on the flora from the posterior vaginal vault. Helps to identify the infection, as well as distinguish candidal plaque from leukoplakia.
- Bacterial culture of vaginal contents determines the preferred pathogens, their number and sensitivity to the preparations. After a course of properly selected treatment, leukoplakia will be easier to treat.
- Cytological examination is mandatory. After all, leukoplakia is onaccessible, and taking such a smear from the cervical can help determine the severity of the process.
- But the most important step in diagnosis is biopsy - excision of a small area of cervical tissue for subsequent histological examination. This is the only way to exclude / confirm cancer with 100% certainty. Also, a biopsy allows you to know the extent of the process( to what depth of tissue the changes go).This procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, it does not require additional anesthesia.
- Colposcopy helps to detect leukoplakia, even if visually it is not yet determined. Perhaps this is due to the fact that the epithelium "with new functions" does not accumulate starch so intensively or even loses this ability. And with additional staining, these areas are clearly visible. Also, the optimal option is to perform a targeted biopsy - under the control of the colposcope.
- In some situations it is necessary to perform scraping of the uterine cavity and cervical canal with a histological examination of the material obtained. Hysteroscopy can be performed instead of a conventional WFD.In addition to the basic manipulations, it provides an opportunity to visually assess the condition of the organ, as well as conduct additional procedures( moxibustion, removal of polyps, etc.).
Treatment of leukoplakia of the cervix
Approaches to the treatment of leukoplakia depend on many components. The main ones are as follows:
- whether the woman is planning a pregnancy in the future;
- age;
- how widespread the process;
- relapse is either a first-time case and some other points.

If a factor that causes the formation of leukoplakia is found, try to remove it or reduce the effect on the organ. The most commonly used methods are the following:
- Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. Optimum, if the drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the flora and after a complete examination for pathogens.
- Antiviral drugs in cases where HPV, HSV, etc. are detected. Immunomodulating agents - interferons, vitamins, etc.
- Treatment of the cervix with Solkovagin is used against a background of conservative treatment if the site of hyperkeratosis is small, deep tissues are not involved in the process.
- Laser removal can be used even with extensive lesions, relapses with the exclusion of the oncological process. In this case, the site of the cervix is removed, a thermal burn of the tissues takes place. After such treatment, a healing period of 3 to 4 weeks is needed.
- Radiowave conization - excision of tissues with the help of a "radio wave knife".This is one of the popular and relatively sparing methods. It can be used in combination with dysplasia, even to a high degree.
- Cryodestruction - exposure to the affected area with liquid nitrogen, after which a tender scar is formed. Used for small and shallow lesions.
- A method such as DEC( diathermocoagulation) can also be used. It is the most traumatic and requires a long healing period.
- When a combination of dysplasia and leukoplakia or precancerous conditions, with relapse of hyperkeratosis individually, preference can be given to more serious surgical techniques. This is an amputation of the cervix, cone resection or even removal of the uterus( for example, if there are myomatous nodes, non-treatable endometrial hyperplasia, etc.).

But it is necessary to understand that it is unlikely that such treatment will help get rid of pathology. This is nothing more than an addition to the basic therapy regimens.
Prevention of the appearance of cervical leukoplakia
There is no specific prophylaxis for leukoplakia. The main recommendations are as follows:
- Barrier protection methods for sexual intercourse( condoms), especially for sexually active girls, should be preferred. This is the prevention of STIs.
- It should be regularly monitored by a gynecologist( even in the absence of complaints), timely and full treatment is necessary.
- It is advisable to avoid performing abortions, multiple curettage and other procedures that damage the cervix.
- You should also lead a healthy lifestyle. Overweight, smoking, unhealthy foods indirectly contribute to the development of leukoplakia. After all, the disturbed metabolism, the excess of toxins in the body - all this leads to mutations and changes in the properties of cells.
Important questions for patients
When encountering leukoplakia, women usually have many questions, since the pathology is not "on hearing".Here are some of them:
- Cervical leukoplakia is a cancer or not? Hyperkeratosis refers to facultative precursors, i.e.pathology often leads to malignant growth. Each third woman with cervical cancer has histologically confirmed concomitant leukoplakia. The probability of such degeneration is individual, many factors play a role. But in any case, careful and regular examinations at the doctor will help to identify the disease( even if it is cervical cancer) at an early stage, when the likelihood of a radical cure is nearing 100%.
- How dangerous is the pathology of pregnancy? It is impossible to give any specific figures, everything is very individual for every woman. It is important how and when leukoplakia is detected, whether there is concomitant pathology of the cervix, etc. But if hyperkeratosis is found during pregnancy, treatment is performed after childbirth. And during the gestation period, the process is closely monitored.

- Can leukoplakia return? Hyperkeratosis - a disruption of the functioning of cells of the cervix. If the pathological site is completely removed, the provoking factors are minimized, then the probability of recurrence of the pathology is minimal, but it is still preserved. If the most effective treatment is not chosen, or the woman does not follow the recommendations, the risk of getting leukoplakia again is very high.
Prognosis after treatment
With timely detection and competent treatment, leukoplakia does not pose a particular threat. But women with whom it is identified need to monitor their health more carefully, undergo regular examinations and take all the recommended tests. It should be remembered that hyperkeratosis is a precancerous condition, but not an oncological condition.
And here is more detailed about the consequences of cauterization of cervical erosion.
Leukoplakia is a disease in which epithelial cells acquire an unusual quality - keratinization. This abnormal functioning increases the likelihood of developing cervical cancer. Leukoplakia is a mild symptomatic, so it appears more often with preventive examinations or accidentally. Timely treatment helps to identify hyperkeratosis at a stage when malignancy of tissues has not occurred.

 We recommend reading the article on cervical ectopia of the cervix. From it you will learn about the signs of cervicitis and its effect on the cervix, the causes of the development of ectopy and the methods of treatment.
We recommend reading the article on cervical ectopia of the cervix. From it you will learn about the signs of cervicitis and its effect on the cervix, the causes of the development of ectopy and the methods of treatment. 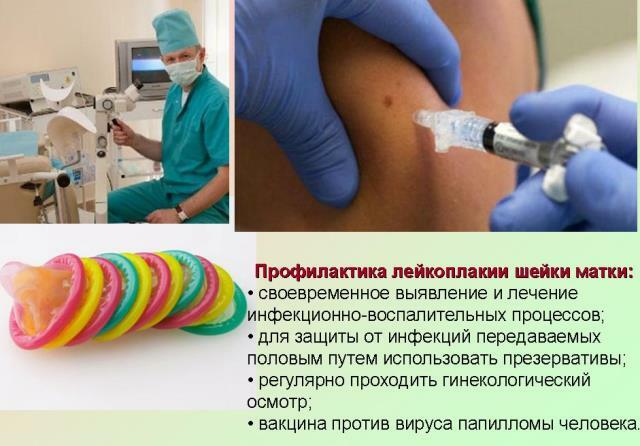
 We recommend that you read an article on the monthly after and after erosion of the cervix. From it you will learn about the violation of the menstrual cycle with erosion of the cervix, treatment of the disease and recovery of menstruation.
We recommend that you read an article on the monthly after and after erosion of the cervix. From it you will learn about the violation of the menstrual cycle with erosion of the cervix, treatment of the disease and recovery of menstruation.