Content
- 1 What is cervical pregnancy
- 2 Causes of cervical pregnancy
- 3 Cervical pregnancy symptoms
- 4 Diagnosis of cervical pregnancy
- 5 Treatment for cervical pregnancy
- 6 Preventive measures and forecasts
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 Reviews on the treatment of cervical pregnancy
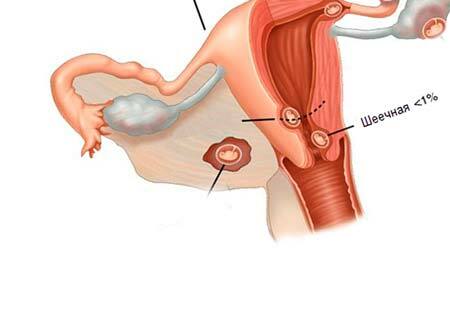
Cervical pregnancy is a type of ectopic fertilization where an egg is attached to the cervix. It is a dangerous pathological condition that entails the risk of extensive bleeding due to possible damage to large arteries concentrated in the walls. Cervical pregnancy has an ICD code 10 O00. Such a pathology occurs relatively infrequently, but it is one of the most pressing problems of gynecology.
What is cervical pregnancy
Cervical pregnancy (SB) is literally the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the cervix. Its development takes place in the cervical canal or directly in the isthmus zone.
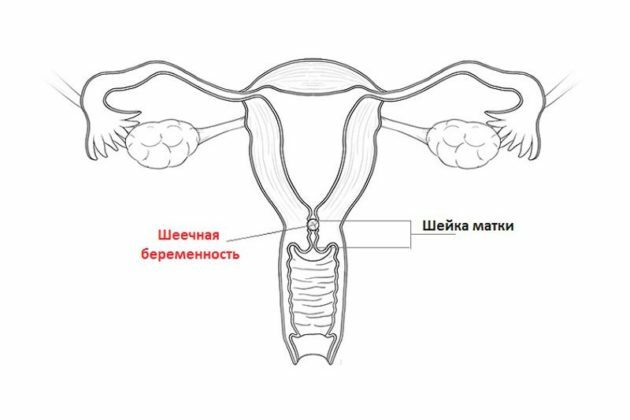
In most cases, SB is characterized by the presence of bleeding as a symptom.
Causes of cervical pregnancy
As a rule, cervical ectopic pregnancy occurs as a result of inadequate development of the endometrium and with an immature trophoblast to the required level. It is the latter that facilitates the attachment of the fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus.
In addition to the main reasons, it is important to take into account the risk factors:
- complications after a previous birth;
- previous delivery by cesarean section;
- a history of surgical abortion;
- any surgical interventions in the uterine cavity;
- artificial insemination;
- fibroids, adhesion formation processes;
- any abnormality of the reproductive organs that is congenital.
Important! Clinical guidelines for cervical pregnancy provide for mandatory surgery. Otherwise, there is a high risk of rupture of the cervical canal as the fetus grows and develops.
Cervical pregnancy symptoms
The characteristic signs of cervical pregnancy are similar to normal, normally developing conception. The expectant mother may experience characteristic malaise, nausea, increased appetite and swelling of the mammary glands. A conception test shows a positive result. However, due to the enlargement of the cervical canal, frequent urge to urinate may be among the possible symptoms. They become painful if an inflammatory process is connected to the cervical pregnancy.
The pathological process, like any conception, is accompanied by a delay in menstruation. However, in most cases, there is spotting from the genital tract. They can be of the following nature:
- smearing;
- moderate;
- very abundant.
Bloody discharge, as a rule, is observed in the first days of cervical pregnancy. As it develops, they stop. However, in the future, a miscarriage often occurs, and the bleeding turns into a profuse form.
Important! The profuse bleeding resulting from SB and subsequent miscarriage requires compulsory medical intervention. Otherwise, there is a risk of death.
Cervical pregnancy, judging by the photo, differs from the usual only in the place of localization of the fertilized egg.
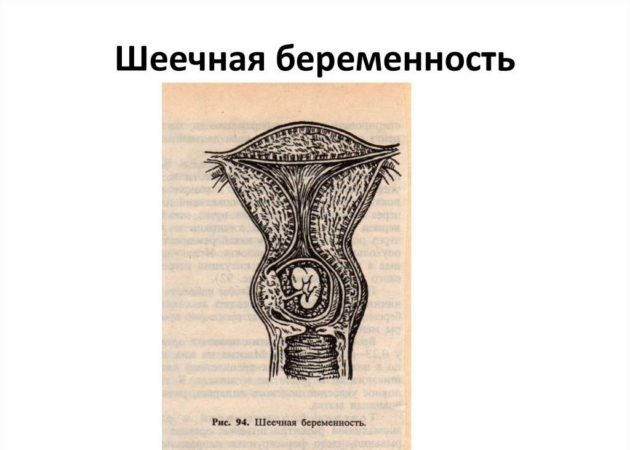
With SB, a woman, as a rule, does not feel any discomfort.
In practice, the symptomatology of a pathological condition can manifest itself only with bleeding of varying intensity. Otherwise, the signs of SB are very weakly expressed. It can only be diagnosed at a specialist appointment.
Diagnosis of cervical pregnancy
Any diagnostic measures begin with interviewing the patient in order to identify the nature of the menstrual cycle, as well as to determine the fact of the presence of pregnancies and their outcomes. Additional important information is the presence in the history of chronic diseases and surgical interventions in the uterine region. This will reveal the presence of risk factors for the development of cervical pregnancy.
The main diagnostic methods that allow you to identify pathological attachment of a fertilized egg:
- A blood test for hCG is a hormone produced by the chorionic membrane of the embryo. It appears after the fertilized egg is attached to the uterine cavity. Normally, its amount should increase daily. With any ectopic pathology, the hCG hormone practically does not increase.
- Gynecological examination, during which the condition of the cervix is assessed.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Allows you to accurately determine the pathological condition at an early stage of pregnancy.
A visual examination of the patient on the gynecological chair helps to identify the following pathological signs:
- cyanosis of the cervix;
- an increase in the size of the cervix;
- displacement of the throat.
Warning! If an ischemic attachment of the ovum has occurred, a gynecological examination may not give results for a diagnosis. The clinical picture will resemble placenta previa.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs is the only way to detect the presence of cervical pregnancy, even at an early stage. With its help, it is easy to detect:
- Pathological expansion of the cervical canal.
- The presence of placental tissue in the canal.
- The absence of the ovum or the embryo itself in the uterine cavity.
- The presence of hyperechogenicity of the endometrial lining.
- The uterus is shaped like an hourglass.
- The internal pharynx remains closed.
- The myometrium has a heterogeneous structure.
Cervical pregnancy on ultrasound is noticeable from the moment the fertilized egg is attached. However, this diagnostic technique is often not performed until 12 weeks after conception. As a result, it is possible to detect SB only at a later date.
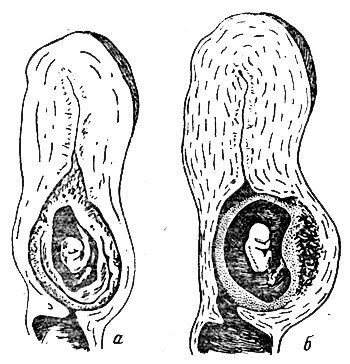
Cervical pregnancy can progress up to 16 weeks
Treatment for cervical pregnancy
The main and only tactic for cervical pregnancy involves mandatory surgical intervention. Previously, surgical practice provided only one method of treatment - extirpation of the uterus. Modern techniques allow you to preserve the organ, respectively, even pregnancy after a cervical pregnancy is quite real.
Treatment of SB involves embolization of the branches of the uterine artery, which are responsible for supplying the cervix. At the same time, the ovum is removed from the cavity by means of a special gynecological instrument - a curette.
Important! Only a specialist of special qualifications can carry out the manipulation to extract the ovum, since it requires jewelry precision.
After surgery, the patient is required to show the following drugs:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics. They avoid the risk of infection after surgery.
- Iron supplements in combination with folic acid. With the help of such a tandem, it will be possible to avoid the risk of anemia.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. They help to quickly recover after surgery and establish all systems of the body's functioning.
Warning! For the next six months after cervical pregnancy, oral contraceptive use is strongly recommended.
Additionally, the use of physiotherapy procedures is recommended. The following treatment options after cervical pregnancy surgery will help reduce the risk of adhesions:
- UHF - the use of an electromagnetic field, which is characterized by an ultra-high frequency;
- diadynamic therapy - the use of currents of different power and frequency;
- magnetotherapy - the effect is through a magnetic field;
- electrophoresis using magnesium and zinc.
Prescribing drugs and drawing up a treatment regimen for SB are strictly individual
Preventive measures and forecasts
Not a single even the most highly professional gynecologist can guarantee that a cervical pregnancy can be avoided. Nevertheless, according to statistics, it is extremely rare in gynecological practice. To reduce the risk of its formation, it is recommended to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Follow the doctor's instructions after any surgical procedure.
- Use contraceptives correctly.
- Planning a pregnancy in advance, treating conception responsibly so that you do not have to resort to abortion.
- Maintain an individual menstruation schedule in order to determine its delay in time.
Despite all the danger of SB, thanks to modern methods of therapy, it is possible to eliminate it practically without consequences.
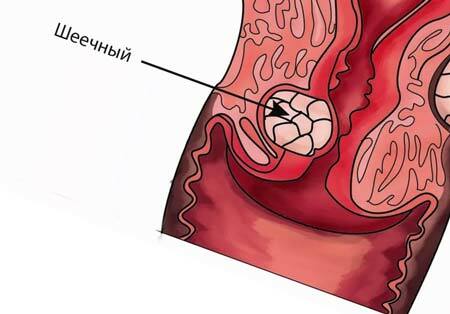
As a rule, with timely surgical intervention during SB, fertility is fully preserved.
Conclusion
Cervical pregnancy is a rather dangerous pathological condition that occurs due to the attachment of the embryo outside the uterine cavity. It is difficult to diagnose early and requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Reviews on the treatment of cervical pregnancy
Olga Skolova, 35 years old, Saratov
By some miracle, I was able to detect an ectopic pathology at an early stage. There was a delay, but hCG did not grow at all. The operation was carried out quickly and recovered without any problems. The doctor said that the reproductive function is preserved.
Elena Martynova, 25 years old, Moscow
I went through the operation to remove the SB a couple of years ago. All organs and reproductive function have been preserved for me. Since then I have fully recovered and in a couple of months I will become a mother.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance, or treatment.
