Content
- Physiological discharge, which is the norm
- How to notice discharge
- Discharge color in men
- Causes of discharge from the urethra
- Urethritis (inflammation of the wall of the urethra)
- Gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
- Nonspecific urethritis
- Gardnerellosis
- Ureaplasmosis
- Mycoplasmosis
- Trichomoniasis
- Features of the course of urethritis, depending on the pathogen
- Discharge in men with genital infections
- Inflammation of the prostate
- The reasons for the appearance of purulent discharge in men
- Is it possible to judge the cause of the disease by the nature of the discharge
- Standard classification of secretions
- Pus from the urethra after miramistin
- Complications of urethritis
- What doctor deals with discharge in men
- Necessary examination for discharge in men
- Causes of discharge, redness, itching, inflammation, burning
- Treatment
- How is the diagnosis and treatment prescribed?
- Prophylaxis
Allocations in men are physiological and pathological. Physiological related to the functionality of the urethral system. They generally have a color - from transparent to whitish-gray, odorless, or have a certain specific, not pungent odor. And pathological ones are distinguished by an atypical color (yellowish, greenish, etc.), volume, consistency and have an unpleasant odor.

Physiological discharge, which is the norm
Despite the fact that doctors recommend that if they find suspicious discharge in themselves, immediately contact the clinic to get tested, not all of them pose a threat to health. We are talking about a transparent secret, which is considered the norm in urological practice. If such traces are found on the underwear, you should not sound the alarm, because this just shows that everything is in order with the body.
Particularly noteworthy is the consideration of mucus, which begins to bother women of reproductive age. Transparent thickish vaginal discharge indicates that in a few days they will have a period of ovulation. They last about three days, usually without causing significant discomfort. This phenomenon is considered quite normal for the female body, provided that the lingering clots are not white, but transparent, do not have a fetid, putrid odor and disappear in a couple of days.
Changes in the hormonal background become the reason for such a reaction of the body to ovulation. The separation of mucus from the vagina is within the normal range if the process ends in a day or two.
Variants of natural discharge of secretions from the urinary tract in men, from the urethra and vagina in women are considered separately. This is possible in the case of strong sexual arousal after the end of intercourse.
A common scenario for the normal discharge of mucus from the urethra for both sexes and from the vagina in women is considered to be a sharp release of a large amount of hormones. The reasons for such an outcome can be both an extreme degree of arousal of a sexual nature before the onset of intercourse, and some specific stressful situations.
How to notice discharge
It is easy to notice discharge when it appears in abundance during the day and is accompanied by discomfort in the urethra. However, such an obvious nature of the discharge is not so common. Much more common is the situation when the discharge in men appears only in the morning or after a long break in urination. In some cases, the discharge appears spontaneously, and in some only after pressing the urethra. Sometimes the crusts and adhered sponges of the urethra are the equivalent of discharge from the urethra. This happens when there is a small amount of secretions, which, when dry, form a film. Allocations can be regular and occur only after any deviations in the usual way of life - the use of spicy food and alcohol. Some cleanliness men may notice bleeding in their underwear.
If the discharge is scanty, it is difficult to notice it. First of all, because rarely any of the men have the habit of pressing down on the urethra in the morning and maturing to see if discharge has appeared there. As a rule, alertness increases when a man had a casual relationship some time ago and is worried about whether any disease was transmitted to him during sexual intercourse. In some cases, the discharge is so scarce that it can be detected only by examining the morning first portion of urine released into the glass. In doing so, attention is paid to whether the urine sample contains floating filaments and flocs. Filaments and flakes in the first portion of urine appear when there is discharge in the urethra, which is washed off with a stream.
Discharge color in men
Discharge in men can have different transparency and color. These signs are influenced by the intensity of the inflammation, the cause of the inflammation, and the stage of the inflammation. The secretions are composed of fluid, mucus, and cells. The more cells, the more cloudy the discharge. If epithelium predominates among the cells of secretions, the secretions become gray and have a thick consistency. If there are many leukocytes in the secretions, they turn green and yellow. With candidiasis of the urethra (thrush) in men, the discharge becomes white and has a dense consistency. The intensity and stage of inflammation can cause changes in secretions for the same disease at different times.
Causes of discharge from the urethra
If we talk about pathological discharge, their cause may be an infectious disease or inflammation. The color of the liquid turns out to be varied, as well as its constituent elements, smell and level of viscosity. To detect the presence of urethral discharge, a three-hour abstinence from the urination process is required. Then a medical specialist performs easy massage movements.
Several secretions of an infectious nature can be noted:
- spermotorrhea;
- hematorrhea.
If we talk about spermatorrhea, it is represented by the release of sperm outside of intercourse. This sometimes happens when sexual functions are impaired, and the muscle structure of the urethral sphincters has a low tone. It also happens that this happens after a disturbed nervous system. As for hematorrhea, it is represented by a discharge from the urethra with blood impurities. Most often they occur after injuries sustained during:
- medical examination;
- using a catheter;
- sampling of smears.
With this disease, the prostate usually swells.
There are also such secretions that are caused by inflammation. If we talk about the fluid secreted in sexually transmitted diseases, specific reasons may be:
- Gonorrhea - in which the discharge is profuse and purulent;
- Chlamydosis - a clear liquid is released from the urethra;
- Trichomoniasis - no discharge.
As soon as the above symptoms appear, it is necessary to contact a specialist in urology or venereology. They may also suspect such serious ailments as orchitis, prostatitis, epididymitis. The doctor will be able to choose the right therapeutic course and its duration.
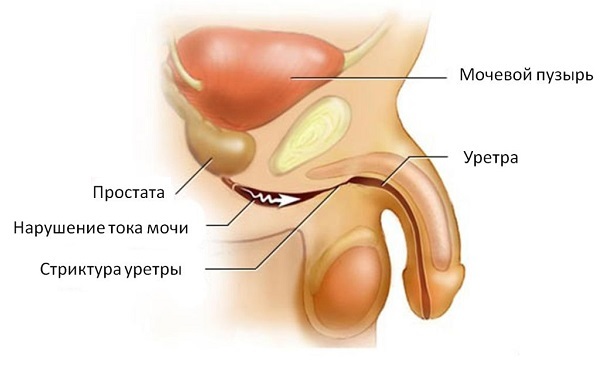
Urethritis (inflammation of the wall of the urethra)
A symptom of urethritis in men is discharge from the urogenital canal, but discharge may be physiological, and urethritis can proceed without discharge, therefore it is important when a discharge is detected see a doctor. Urethritis, along with discharge, is accompanied by dysuria (difficulty urinating) and irritation of the glans penis. Diagnosis of urethritis occurs by examining the first portion of urine and smear. Urethritis is often caused by gonococcus, chlamydia, etc.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea proceeds differently in men and women, but they have in common that the main manifestation of the disease is discharge from the genitals and cutting pains during urination. A symptom of gonorrhea in men is white or yellow discharge from the penis.
The fact that there is no discharge does not mean that there are no diseases. Discharge, as a rule, appears after the incubation (2 to 5 days) period, although sometimes the incubation period is longer - it lasts a month, and sometimes more.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is slowly taking the name of the 21st century plague from many sexually transmitted diseases. The rate of spread of this infection is similar to an avalanche. This disease is mainly sexually transmitted. In men, every second urethritis of chlamydial origin. The symptom of chlamydia in men is discharge from the urethra. Small discharge of transparent color, accompanied by slight pain during urination. In boys, along with the discharge, itching of the penis is also noticed.
Nonspecific urethritis
Nonspecific urethritis is inflammation of the urethra that is caused by other microorganisms other than gonococci, chlamydia, Trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma and virus herpes. In venereology, this is the most interesting and little-studied area. For any symptoms of urethritis (discharge from the penis, pain and burning sensation when urinating), doubts about nonspecific urethritis should be considered.
Gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis is a vaginal dysbiosis and therefore, according to some experts, consider it a direct male disease is impossible, although the fact that gardnerella causes gardnerellez, and this can cause inflammatory processes. Gardnerella enters the male reproductive system during sexual intercourse and since it is not a "legal resident" of the male genital tract, gardnerella can be considered a genital infection. Gardnerella often enters the male body and, as a rule, leaves the reproductive system after 2-3 days.
Rarely, chronic carriage of gardnerella develops, in which the tests are always positive, although no symptoms of the disease are noticeable. In 9 cases out of 10 in men, gardnerellosis is not detected at all and it is so dangerous that the sexual partners of this man become infected and have no idea about it. In the classic case, as soon as the causative agents of this disease enter the urinary canal during intercourse, they cause an inflammatory process of the mucous wall, which proceeds sluggishly. It is possible that the discharge from the penis will be greenish in color, which does not bother the patient much.
Ureaplasmosis
Ureaplasma are microorganisms that are considered as a transitional step from viruses to unicellular ones. Often, infection with this organism occurs through sexual contact. It is also possible for the newborn to become infected from the mother. The incubation period of the disease is usually from 4 days to a month, although it is possible that it will last longer. After the end of the incubation period, the first symptoms of ureoplasm are revealed. It should be noted that often the symptoms of ureaplasma are almost imperceptible. This course of the disease is typical especially in women. The most common symptoms of ureaplasmosis in men are small transparent discharge from the penis, moderate pain and burning sensation during urination. Damage to the ureaplasma of the prostate gland is revealed by signs of the prostate.
Mycoplasmosis
Urogenital mycoplasmosis is clinically not very different from pests of other etiology (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis). Some patients have no subjective findings, while the other part has a whole bunch of symptoms. If the urinary tract is damaged, men have a small discharge in the morning.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas is a unicellular creature that is able to live not only in the body, but also outside the body. Trichomonas, in addition to the harm it causes to the body, is able to absorb gonococci without damaging them. Trichomonas, which has passed from the body of one person to the body of another, carries with it gonococci, which absorbed, and in case of incomplete cure (for example, self-medication) after treatment of trichomoniasis, gonorrheal develops infection. Trichomoniasis is often asymptomatic in men. A man can be a carrier of trichomoniasis all his life, infect partners, and he himself does not experience any discomfort. Very rarely, inflammatory processes are detected in the urethra, in the prostate, seminal vesicles, in the seminal gland. Sometimes a cloudy white liquid flows from the urethra or a trace of blood is noted. It lasts 1-2 weeks, and then the symptoms diminish, although the disease continues and becomes chronic.
Features of the course of urethritis, depending on the pathogen
Bacterial urethritis. The causative agents are: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, gardnerella, etc. Infection into the urethra can enter during sexual intercourse, as well as due to its spread from the genitourinary tract with pyelonephritis, prostatitis, vesiculitis, trauma of the urethra. More than 230 strains of bacteria have been isolated, which, in a certain situation, are capable of causing inflammation of the urethral mucosa.
The average duration of the incubation period for bacterial urethritis is 12-14 days (from 2 to 20 days). More often, their clinical course is malosymptomatic, sluggish. Less often, bacterial urethritis acquire an acute course.
Urethritis caused by diplococci, similar to gonococci (pseudogonococci), usually proceed as acute urethritis.
Gardnerella, as a rule, causes low-symptom urethritis, often resulting in self-healing.
Bacterial urethritis often (in 30% or more) end with complications (balanoposthitis, epididymitis, prostatitis, cystitis, etc.).
Discharge in men with genital infections
Genital infections are most often the cause of the appearance of atypical discharge from the urethra in men. Sexually transmitted infections are a group of diseases that are most often transmitted through sexual contact. Less commonly - through blood, by household or during childbirth. All sexually transmitted infections have both similar symptoms and some differences.
They are most often accompanied by discharge from the urethra (sometimes yellow, green, cheesy, foul-smelling), and are also characterized by burning and itching, pain during urination and during intercourse. Sometimes skin rashes and other skin disorders appear.
The highlights are as follows:
- Chronic chlamydia, uraplasmosis, mycoplasmosis (transparent, viscous discharge of moderate amount). The number of leukocytes in the blood is increased by microscopic examination.
- Acute course of chlamydia, uraplasmosis, mycoplasmosis (white or translucent discharge of mucopurulent consistency). With chlamydia, a purulent substance accumulates on the head of the penis.
- Gonorrhea is characterized by a putrid odor of discharge. They have a thick, sticky consistency, ranging in color from yellow to yellow-green. Microscopic examination shows many leukocytes, epithelial cells from the urethra. In addition, itching, burning, pain during urination are added.
Sexually transmitted diseases often occur in one patient in combination. It can be gonorrhea with chlamydia and gonorrhea, or syphilis and gonorrhea with mycoplasmosis. Any combination is possible. Therefore, the nature of the discharge can be very different.
Urogenital candidiasis (thrush) is not classified as venereal, since it is extremely rare that it passes from a sick woman to a man. More often this is a consequence of a decrease in immunity, trauma to the organs of the genitourinary system. With this disease, the release of a sour odor, curdled consistency. It also causes itching and burning when urinating.
Inflammation of the prostate
Prostatitis often develops in the stronger sex, who have crossed the fifty-year line. With inflammation of the prostate gland, painful sensations in the groin area, pain during urination, weakness occur. The following reasons for the development of prostatitis should be named:
- Irregular sex life.
- Hypothermia.
- Chronic diseases of the genitourinary sphere.
- Venereal diseases.
- Injury to the soft tissues of the pelvic organs.
With prostatitis, the discharge is usually yellow or yellow-green. With an exacerbation of the disease, they are usually accompanied by pain. The patient's body temperature may rise. Sometimes a yellow discharge is also observed with prostatorrhea. This pathology occurs with a decrease in the tone of the prostate. Odorless discharge appears during prostate massage, after heavy physical exertion.
Prostatorrhea is accompanied by itching in the urethra. Prostatorrhea is often combined with spermatorrhea. With this pathology, sperm is spontaneously released from the urethra.
The reasons for the appearance of purulent discharge in men
1. Reaction to impact of any nature:
- chemical or thermal burns, mechanical trauma (for example, damage to the mucous membrane when a catheter is inserted);
- an allergic reaction to a particular substance, most often it is lubricants, condom lubricants, hygiene products.
Pathological discharge from the urethra can appear even after intercourse with a healthy woman, the reason for them is the interaction of the mucous membrane of the external opening of the urethra with the microflora of the vagina. The appearance of discharge when changing a sexual partner is characteristic. But, as a rule, in the absence of a pathogen, that is, one or another infectious agent, the symptoms are mild and quickly eliminated.
2. Infectious factor: specific and non-specific pathogens
- causative agents of genital infections are referred to as specific ones, first of all, these are gonococci, Trichomonas, chlamydia, etc.
- non-specific pathogens are staphylococci, Escherichia coli, Proteus and others. Urethritis caused by nonspecific flora often occurs with less pronounced symptoms.
Is it possible to judge the cause of the disease by the nature of the discharge
The color, consistency, quantity and smell of discharge cannot serve as a reliable sign of the cause of the disease that caused them. Currently, many specific diseases have lost their classic features, and only external signs cannot be used to judge the presumptive diagnosis.
Standard classification of secretions
There are several clinical classifications of a secret that has received deviations from the norm. One of the most important options for separating pathological fluids emanating from the urinary tract is called shading separation. Schematically, the classification includes three categories:
- yellow;
- white;
- transparent.
The first variation can be traced for the most part in men, signaling the onset of prostatitis. A greenish tint may indicate that the patient is developing a sexually transmitted infection that has spread to the entire reproductive system. When the mucus contains impurities of pus, is accompanied by a mild putrid odor, then with a high degree of probability the victim suffers from gonorrhea.
It is promptly necessary to contact a venereologist and urologist if the victim has four typical symptoms at once:
- itching;
- profuse discharge;
- problem urination;
- pain in the kidneys.
Then the applicant is diagnosed with gonorrheal urethritis, requiring immediate treatment.
Women who complain of discomfort in the perineum, as well as who have found white marks on their underwear, strange curdled clots, most likely victims of one of the most common female ailments - thrush. At the initial stage, it is relatively easy to treat. And if the listed signs are found in men, then this is a sign of candidiasis.
A transparent secret does not always indicate the absence of problems with the genitourinary system. In young people, a scanty and stringy discharge may signal an infection transmitted during intercourse.
Occasionally, doctors record the secretion of secretions, which is complemented by soreness in the kidney area. But usually patients in the list of the main complaints, in addition to the unusual abundance of secretions, include other signs:
- increased urination;
- itching, burning;
- a feeling of stickiness in the urethral canal, which intensifies in the morning on awakening;
- bloody impurities;
- pain syndrome, aggravated at the end of urination;
- soreness of the pubic region;
- discomfort in the perineum, bladder;
- fluid from the vagina.
Sometimes several symptoms are confused, and sometimes none of them is present at all.
Pus from the urethra after miramistin
The drug is a cationic surface substance that has pronounced antiseptic properties. Miramistin has a detrimental effect on pathogens of bacterial and viral origin, which makes it possible to effectively fight sexually transmitted infections.
The effect of the drug on cell membranes is due to hydrophobic interaction with lipid membranes, as a result of which their complete deformation and subsequent destruction occurs. The causative agents of infection also die with them. As such, the medicine has no contraindications, but it is worth consulting a doctor first so that there is no overdose. The drug contributes to a significant decrease in purulent discharge after administration.
Miramistin can treat the genitals and urethra. The procedure should be carried out by a competent specialist from our clinic in order to exclude unwanted protective reactions of the mechanism, which can lead to profuse purulent discharge.
Complications of urethritis
In the absence of adequate therapy, the active process becomes chronic with periodic episodes of exacerbation. This, in turn, can lead to cicatricial deformity (stricture) of the urethra at any levels, to the development of balanoposthitis (inflammation of the genital head penis), prostatitis, vesiculitis, orchiepididymitis (inflammation of the testicle with the epididymis) and inflammatory diseases of the upper urinary tract (pyelonephritis). In the case of pyelonephritis, symptoms may be accompanied by hyperthermia (fever), chills, increased pain and general weakness.
The most serious complication of urethritis caused by chlamydial infection is Reiter's syndrome - reactive arthritis (or non-suppurative inflammation of the joints) in combination with conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin transparent tissue lining the inner surface of the eyelid and the visible part sclera).
What doctor deals with discharge in men
All diseases in men, which are accompanied by discharge from the urethra, are dealt with by a urologist. A urologist is a narrow specialist who is in charge of diagnostics and treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system.
The urologist of our clinic has a long experience, constantly increases the level of his knowledge, takes part in practical training seminars.
Men of different ages turn to him for help, starting from birth. All services are certified.

Necessary examination for discharge in men
In case of strange discharge, the patient needs to consult a urologist. The doctor conducts diagnostics according to a specific algorithm.
It includes:
- Visual inspection of the penis, glans, perineum, foreskin. The urologist will see if there are deformities, injuries, signs of inflammation, various rashes, etc.
- Palpation of the lymph nodes in the groin. The doctor determines their size, whether they are hot or not, mobile or tightly in contact with the skin, soft or tight. It also matters whether there are different expressions nearby.
- Palpation of the prostate. With pathology of the organ, the lobes increase. This can be determined by massage through the rectum. If there is a cancerous tumor, then the growths are uneven. Discharge - blood with clots from the urethra.
Instrumental studies are also needed, such as ultrasound of the pelvic organs, urography and computed tomography. They allow you to clarify the diagnosis. Diagnostics is always carried out in a complex, since it is impossible to recognize the exact causes of the disease on the basis of a single test.
Causes of discharge, redness, itching, inflammation, burning
The causes of discharge, redness, itching, and inflammation are varied. All the reasons why something liquid is visible on the head of the penis are divided into physiological, which can be observed normally, and pathological, which are never normal. So, what physiological discharge in men can occur in everyday life?
Treatment

The method of treatment in this case directly depends on the cause that caused such a phenomenon as pathological discharge from the urethra. It is important to understand that self-treatment can cause complications, therefore, it is unacceptable. Allocations can occur due to the penetration of various types of pathogens, which must be dealt with by different methods. Most often, drug therapy involves the use of antibiotics, but their selection should be carried out on an individual basis. As a rule, the following means are used:
| Group | When to use | Name |
| Antibacterial | STDs | "Azithromycin", "Amoxiclav" |
| Uroseptics | Urethritis | Chlorhexidine and collargol solution |
| Sulfanilamide | When bacteria that cause inflammation are found | "Doxycycline" |
| Antimicrobial | Trichomoniasis | "Metronidazole" |
In addition, patients are advised to wash their genitals with broths of knotweed, chamomile, calendula or special antiseptic solutions. Warming applications and electrophoresis give good results.
How is the diagnosis and treatment prescribed?
To identify the source of the problem, as well as to prescribe the most effective therapy regimen, you first need to make an appointment with a doctor. During the initial examination, the doctor will conduct a simple questionnaire to find out how long ago the dangerous signs began to manifest themselves.
To understand the cause, ureteroscopy is additionally involved. This is the name of instrumental diagnostics, which is performed using a cystoscope. It is injected into the urethra to obtain more complete information about the current state of the organ.
Next, the victim is sent for laboratory testing, which requires taking a smear for further study of the composition of microflora for infectious agents and cytological analysis. After receiving the results, it is possible to select an adequate treatment.
Further therapy depends entirely on what caused the deviation. But in most cases, all forms of treatment involve the use of antibiotics. Their appointment on their own is strictly prohibited, since the uncontrolled intake of such strong medications will surely come back to haunt kidney dysfunction.
From non-traditional therapy, preference should be given to sitz baths, which will help eliminate irritation. The use of auxiliary techniques is allowed only after the approval of the doctor. He will tell you which solutions are best to add to the bath.
Usually these are anti-inflammatory, antiseptic pharmaceutical agents, as well as decoctions of medicinal herbs. They are often impregnated with tampons. It will be useful to attract local suppositories. Physicians call physiotherapy, including a course of electrophoresis, an equally effective approach.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of infections consists mainly in:
- avoid casual unprotected sex;
- maintain immunity in a "working" condition, including preventing hypothermia;
- on time and completely heal other diseases, especially inflammation of the small pelvis;
- maintain the balance of microflora in the intestine.
It is also recommended to eat rationally and fully, do not abuse alcohol, do not smoke, lead an active physical lifestyle (exercise, sports).
Sources of
- https://doctor-moskva.ru/napravleniya/vydeleniya/vydeleniya-u-muzhchin/
- https://FoodandHealth.ru/simptomy/vydeleniya-iz-mocheispuskatelnogo-kanala/
- http://ultraclinic.com.ua/simptomy/vydelenija-u-muzhchin/
- https://doct.ru/articles/vydeleniya_iz_uretry.html
- https://mmt.ge/ru/vydeleniya-u-muzhchin/
- https://stojak.ru/mochepolovye-bolezni/zheltye-vydeleniya-u-muzhchin.html
- https://pro-uro.ru/articles/gnojnye-vydeleniya-iz-uretry-u-muzhchin.html
- https://doctor-moskva.ru/napravleniya/urolog/gnoy-iz-uretry/
- https://ProBolezny.ru/uretrit/
- https://sarclinic.ru/o-kompanii/stati/103-vospalitelnye-zabolevaniya-mochepolovoj-sistemy/579-pochemu-vydeleniya-iz-polovogo-chlena-zud-rez-kapaet-gnoj-krov-sperma-mocha
- https://www.celt.ru/simptomy/vydeleniya-iz-uretry/
- https://www.smclinic.ru/diseases/u/uretrit/kandidoznyy/
