Content
- 1 What is postpartum ulcer
- 2 Causes of postpartum ulcers
-
3 Clinical symptoms of postpartum ulcer
- 3.1 What day does a postpartum ulcer occur?
- 4 Diagnostics of the postpartum perineal ulcer
- 5 Postpartum ulcer treatment
- 6 Preventive measures and forecasts
- 7 Conclusion
Among the diseases that occur in the postpartum period, a special place is occupied by the postpartum ulcer, which most often appears in the perineum. Its formation is also possible on the cervical part of the uterus. The diagnosis is characterized by the presence of sutures imposed as a result of ruptures, which, in turn, are infected by various pathogenic microorganisms. The problem requires mandatory medical intervention and medical manipulations. Inaction is fraught with serious negative consequences, in particular, the formation of pus, followed by blood poisoning.
What is postpartum ulcer
Ulcer after childbirth - any wound of the perineum and cervix, as well as the vaginal mucosa, infected with pathogenic microorganisms. It is distinguished by clear boundaries, characterized by infiltration of the tissues surrounding the affected area, edema and noticeable hyperemia of the integument. The bottom of the ulcer has a coating of dirty gray or yellow shades, often there are areas of necrosis.
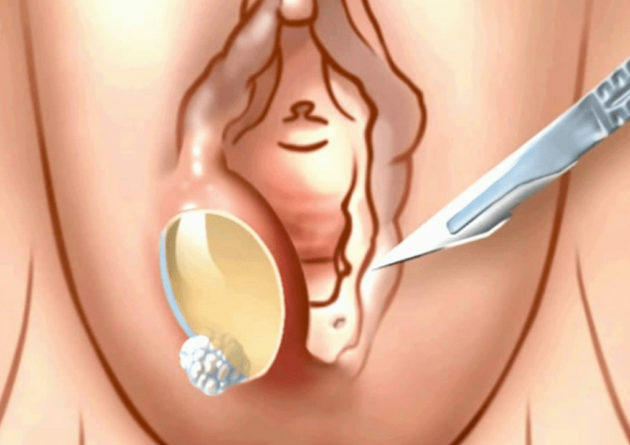
Inflammation of the perineum is characterized by local manifestations, often itching, caused by irritation from the discharge from the wound
Causes of postpartum ulcers
The main reason for the occurrence of postpartum ulcers, in particular, this concerns the cervix, is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the wound formed after childbirth. This applies to breaks, cracks and microdamages. Pathogenic microflora can be formed as a result of activity:
- chlamydia;
- gonococci;
- Trichomonas;
- mycoplasma.
In addition, opportunistic microorganisms, the active reproduction of which occurs against the background of a decrease in immunity, can become the cause of inflammation. Among them:
- anaerobic staphylococci;
- staphylococcus aureus;
- enterobacteriaceae of the lactose-negative type;
- Escherichia coli;
- other associations of microorganisms.
Risk factors for the appearance of a postpartum ulcer, which is localized directly on the cervix, are:
- prolonged labor with a large fetus;
- premature discharge of amniotic fluid;
- bleeding of the uterine type during delivery;
- surgical method of delivery, accompanied by trauma;
- a long period without water during delivery.
Important! The reasons for the appearance of a postpartum perineal ulcer can be considered any complications that have arisen against the background of a violation of sanitary and hygienic standards, an invasive diagnostic method, and surgical treatment.
An additional factor provoking the development of an ulcer is the presence of chronic infectious diseases in a woman in labor.
Clinical symptoms of postpartum ulcer
The symptomatic picture of a postpartum ulcer is exclusively local in nature, manifests itself in the form of a dense purulent plaque of a gray or yellowish tone on the surface of the wound. It is accompanied by severe hyperemia and swelling not only in the place of suppuration, but also in the surrounding tissues.
Additional clinical symptoms of the disease:
- general malaise;
- painful sensations;
- if the cervix is damaged and the ulcer spreads beyond the organ, colpitis and vulvitis may develop with typical symptoms in the form of itching, burning and painful discomfort;
- fever, fever.
Warning! With timely treatment, ulcerative suppuration passes, the wound is gradually cleared of plaque, there is a gradual epithelization of the affected tissues.
What day does a postpartum ulcer occur?
The average time for the formation of a postpartum perineal ulcer is 3-4 days after delivery. Signs of an inflammatory process intensify over the next couple of days and, if inactive, can lead to septic damage to the blood.
Important! With timely treatment, the patient's condition improves already for 4-5 days.
Diagnostics of the postpartum perineal ulcer
A combination of the following examinations and phenomena will help to determine the presence of a postpartum perineal ulcer, in particular the cervix:
- general clinical symptoms;
- interviewing the patient and examining her by a gynecologist to form an anamnesis;
- instrumental examination;
- laboratory tests.
On examination, the gynecologist reveals the presence of a wound defect on the surface of the integument, as well as the presence of purulent plaque, hyperemia and swelling.
The following gynecological examinations are informative:
- General blood analysis. With progressive acute postpartum perineal ulcer, there is an increase in ESR, as well as a noticeable increase in leukocytes.
- PCR analysis, which allows you to identify the type of pathogens. The analysis will help in the future to choose the correct method of therapy.
- Culture of secretions from the cervical canal. Informative if antibacterial therapy is planned.
Additional diagnostic methods, the need for which is determined by the gynecologist:
- Ultrasound;
- colposcopy;
- thermography;
- hysteroscopy.
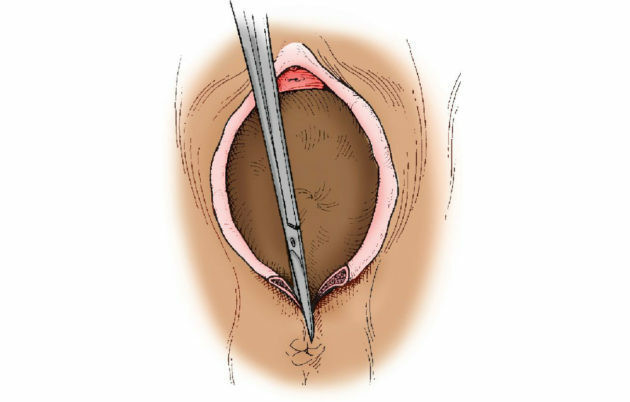
The appearance of a postpartum ulcer is characteristic of tears and incisions of the perineum
Postpartum ulcer treatment
Clinical recommendations for postpartum ulcers are traditionally in the local treatment of the formed abscess. Basic principles of therapy:
- removal of purulent discharge;
- treatment of wounds with antiseptics;
- carrying out activities aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration.
Warning! When treating an ulcer formed on the cervix, a mandatory preliminary removal of the stitches is required.
To cleanse the lesion site from purulent plaque, use:
- 10% sodium chloride solution;
- furacilin;
- applications with antibacterial ointments;
- sedatives, taking painkillers according to indications;
- enzymes of the necrolytic type.
The therapy is carried out until the wounds are completely cleared of purulent plaque. This usually takes several days. General epithelialization usually ends at the end of 10-12 days. If the wound area is extensive, secondary suturing is practiced.
Important! As a result of the healing of a postpartum ulcer, scar tissue can form. In the future, the defect can be eliminated with a laser.
In case of divergence of the seams against the background of the formation of an ulcer, surgical intervention is mandatory.
Preventive measures and forecasts
As the prevention of diseases of the perineum and cervix, the timely treatment of inflammation and gynecological pathologies that arise in patients during pregnancy planning is understood. In addition, the rehabilitation of the birth canal before delivery, rational management of childbirth, as well as the postpartum period will be effective. It also requires proper sanitization of the seams, adherence to the rules of personal hygiene and sanitation.
The prognosis of the diagnosis of postpartum perineal and cervical ulcers in most cases is favorable. With proper and timely treatment, the wound is cleared of pus, complete tissue regeneration occurs, which often does not end with the formation of a scar. If necessary, antibiotic therapy is carried out.
Conclusion
A postpartum ulcer is a pathological process that occurs when there are sutures imposed as a result of tears or incisions in the perineum. The disease requires compulsory medical intervention, which provides for the correct diagnosis and drawing up a plan of complex measures. In the course of treatment, purulent plaque is gradually removed from the wound area, which further leads to gradual tissue regeneration.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance, or treatment.
