Content
- 1 What is a lochiometer
- 2 The reasons for the appearance of lochiometers
- 3 Lochiometers symptoms after childbirth
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 How to treat a lochiometer after cesarean, childbirth
- 6 Possible complications and consequences
- 7 Preventive measures and forecasts
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Reviews on the treatment of lochiometers after childbirth
Lochiometer after childbirth is a febrile condition in gynecology caused by a retention of lochia in the uterine cavity. This is a physiological wound secret, which consists of blood, decayed and reborn organic elements, as well as mucus. The lochiometer has an accepted ICD code of 10 O90.8 and belongs to the category of postpartum complications.
What is a lochiometer
The formation of lochia occurs as a result of the following processes occurring in the female body:
- After childbirth, blood clots and scraps of the decidual type membrane that remain on the uterine walls are liquefied.
- Erythrocytes, leukocytes, plasma and lymph penetrate through the wound surface into the uterus.
These elements cause the formation of lochia. Normally, this wound secretion should actively flow out of the uterine cavity through the cervical canal into the vagina. Retention of discharge in the body after childbirth is called a lochiometer, the main characteristic of the diagnosis is the high risk of infection of the uterus. Lymph, blood, serum and tissue debris are the best breeding ground for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The postpartum lochiometer often causes the development of endometritis.
Normally, lochia acquire a lacrimal-mucous light consistency three weeks after childbirth.
The reasons for the appearance of lochiometers
The reasons for the development of lochiometers are determined, as a rule, by the presence of mechanical obstacles to the outflow of secretions from the cervical canal. This is additionally facilitated by the low contractility of the uterus, often resulting from a caesarean section.
The reasons for the mechanical obstacles to the appearance of pathology:
- kinks of the uterus;
- blockage of the cervical canal with blood clots formed after childbirth;
- the presence of a large number of exfoliated uterine tissues;
- the presence of residual parts of the decidua of the uterus.
Low contractility of an organ is usually caused by the following reasons:
- Overstretching of the uterine cavity, which appeared due to a large fetus, with multiple pregnancies or due to polyhydramnios.
- Weak or discoordinated labor.
- Cesarean section, planned or emergency.
- Spasm of internal pharynx during opening.
Important! The emergence and rapid development of the lochiometer is also facilitated by forced bed rest after delivery and the low activity of the female reproductive system during childbirth.
Lochiometers symptoms after childbirth
The approximate time of development of the lochiometer is on the seventh day after delivery. The main sign of a pathological condition is a reduction or complete cessation of physiological vaginal discharge after childbirth.
Additional symptoms that indicate the appearance of a lochiometer:
- An increase in the size of the uterus, which becomes much larger than the prescribed norms for the current day after childbirth.
- In the absence of treatment, a febrile state of a woman is observed, it is possible that the body temperature rises to 40 ° C, cramping pains, general deterioration of health, chills, the appearance of cloudy discharge with unpleasant smell.
- Soreness of the uterus on palpation.
At the initial stage of the pathological state, the general objective health of the woman does not change, there are no disruptions in the heart rhythm, in addition, the body temperature remains normal for a long time.
After the temperature rises, its indicators may drop critically after a couple of days, purulent discharge appears
Diagnostics
Timely diagnosis allows you to identify echo signs of a lochiometer. In addition, the doctor will pay attention to additional clinical symptoms during the appointment.
With the help of a standard gynecological examination, the doctor will identify the following signs of the disease:
- painful and unevenly enlarged uterus, which is felt during normal palpation;
- the organ cavity has a dense elastic structure;
- kink of the uterus;
- tight closure of the throat inside.
The main criterion for making a diagnosis is ultrasound, where the signs of lochiometers are seen especially clearly. During the study, the expansion of the organ cavity, the presence of clots and blood, which are hyperechoic in nature, are diagnosed.
How to treat a lochiometer after cesarean, childbirth
Treatment of the disease is carried out on the basis of the cause that caused a violation of the outflow of lochia from the cervical canal. The main therapy regimen is as follows:
- regular application of ice to the lower abdomen;
- injections of antispasmodic drugs that will relieve spasms of the internal pharynx;
- the use of drugs, the action of which is aimed at reducing the size of the uterus.
As antispasmodics with lochiometers, injections of Papaverine or Drotaverine are used
Important! For rapid contraction of the uterine cavity, drugs based on oxytocin and methylergometrine are used.
The basis of physiotherapy with a lochiometer is the regular presence of the patient in a prone position for 1-2 hours. Using this method at least 2-3 times a day ensures a free outflow of lochia from the uterus through the cervical canal.
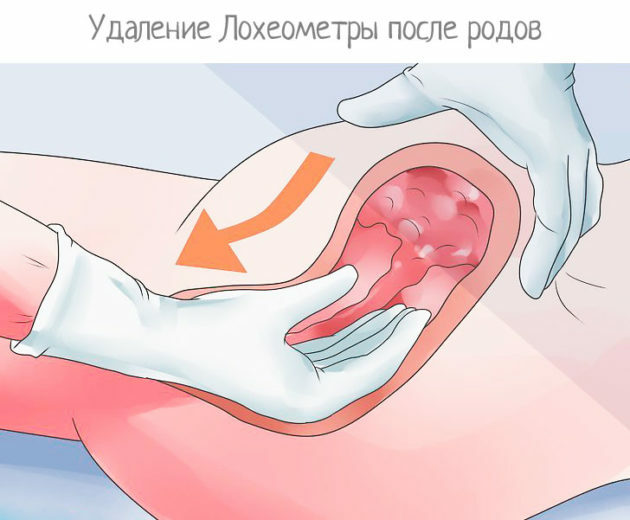
When the organ is bent, special therapeutic exercises are prescribed. If the gynecologist diagnosed a blockage of the cervical canal with blood clots, digital expansion and careful removal are required.
If, despite therapy, the lochiometer continues to progress in the patient's body, it is necessary to carry out instrumental resolution of the pathological condition.
Minimally invasive surgery is performed in two ways:
- Using a gynecological curette.
- Vacuum preparation, the use of which is carried out under the control of hysteroscopy.
A prerequisite after therapy with lochiometers is the collection of a smear for the study of bacteriological culture. In the presence of an imbalance, the patient is prescribed a mandatory course of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs.
Warning! A neglected condition in which there is no outflow of postpartum discharge from the cervical canal can lead to the appearance of pus. This phenomenon is a direct indication for a hysterectomy, which is a complete or partial removal of the uterus.
Possible complications and consequences
Lochiometer, which was not subject to timely treatment, entails the appearance of serious complications. The most dangerous among them are:
- Pyometra - the transition of pathology into a chronically purulent state, fraught with further sepsis.
- Metroendometriosis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the uterus and muscle.
- Intoxication syndrome, in which the body is poisoned with decay products of lochia, which did not leave the organ in a timely manner through the cervical canal.
A running lochiometer is always accompanied by purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Preventive measures and forecasts
Lochiometer is not the most common occurrence, which occurs more often with complicated childbirth, as well as as a result of a forced caesarean section. In addition, non-compliance by the patient with the doctor's recommendations is often a risk factor.
Preventive measures that will help prevent the development of a pathological condition:
- proper preparation of the woman in labor for the upcoming delivery process;
- compliance with the doctor's recommendations, regardless of the type of delivery;
- carrying out postpartum gymnastics;
- breastfeeding the newborn on demand;
- constant observation of the woman by the attending physician after delivery, at the slightest deviation from the norm, the patient should seek medical help.
After giving birth, it is important for the patient to monitor the regular emptying of the bladder and intestines.
The main signals for a patient to visit a doctor are the following symptoms:
- an increase in body temperature a few days after childbirth;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, especially in the uterus after childbirth;
- discomfort after childbirth during urination, radiating to the uterus;
- absence or noticeable reduction in discharge in the first two weeks after childbirth, which is not the norm;
- a sharp change in the nature of lochia.
With timely diagnosis and correctly chosen therapy tactics, the prognosis for treatment of lochiometers after childbirth is very favorable. The eliminated pathological condition does not affect the reproductive function of a woman. Neglected cases always lead to the need to remove the uterus.
Conclusion
A lochiometer after childbirth is not the most common, but often encountered pathological phenomenon that requires compulsory treatment. Depending on the neglect of the diagnosis, the presence of which can only be determined at the reception of a gynecologist, instrumental and surgical intervention may be required. Purulent conditions that have arisen against the background of progressive lochiometers after childbirth are a direct indication for the removal of the uterine cavity.
Reviews on the treatment of lochiometers after childbirth
Elena Ivanochkina, 30 years old, g. Petrozavodsk
After giving birth by cesarean section, the discharge from the uterus was very scarce, on the fifth day it completely disappeared. At the same time, I felt soreness in the lower abdomen. At the gynecologist's appointment for an ultrasound scan, they gave me a lochiometer. Treatment consisted mainly of lying on my stomach three times a day, applying ice to my lower abdomen, and injecting oxytocin. There were no spasms, so they didn't give me painkillers or relaxing injections. Lochia intensified on the third day of treatment, after three weeks they stopped. Repeated diagnostics showed that the uterine cavity was clean.
Maria Krutilina, 28 years old, g. Moscow
I encountered a lochiometer after the first birth, which took place naturally. The discharge completely disappeared on the second day. I did not feel pain or discomfort, it was unpleasant only when examined by a doctor. Prescribed injections and droppers with oxytocin. Active discharge began on the second day of treatment and lasted about a month. Two years later, I gave birth to another child, now there were no such consequences - the discharge was actively leaving on its own within three weeks.
Vasilisa Petrenko, 31 years old, g. Syzran
I did not immediately notice that the lochia after childbirth was too scarce, while they did not disappear completely, however, there was a putrid smell, which I mistakenly took for the norm. A week later, the temperature rose, I was in a fever. On examination, the doctor diagnosed the lochiometer in a purulent phase. As a result, the uterus had to be removed, otherwise the pathology threatened with sepsis.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance, or treatment.
