Content
- 1 What is and classification of trophoblastic disease
- 2 Causes of trophoblastic disease
- 3 Symptoms of trophoblastic disease
- 4 Diagnosis of trophoblastic disease
- 5 Treatment of trophoblastic disease
- 6 Forecast and possible consequences
- 7 Conclusion
Trophoblastic disease is a diagnosis that occurs during pregnancy or after its termination. The main risk factor is late conception in women. Usually - after 35 years. Trophoblastic disease has an ICD code 10 C58 and combines several variants of diagnoses associated with various forms of proliferative trophoblast neoplasia.
What is and classification of trophoblastic disease
Trophoblastic disease during pregnancy is a neoplastic disease. The development of a malignant neoplasm occurs in the outer layer of the shell of the embryo (trophoblast). In gynecology, this disease is quite rare, occurs in 1.5-2% of cases out of 100. The primary site of tumor localization is almost always the uterine cavity. In percentage terms, the pathogenesis of trophoblastic disease is in the form of:
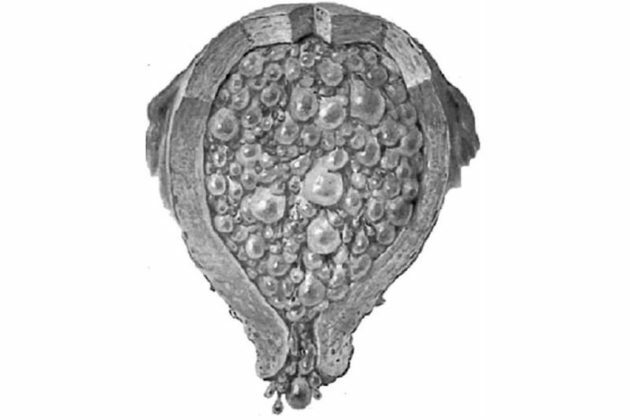
- complete hydatidiform drift - about 72%;
- partial hydatidiform drift - about 5%;
- chorioncarcinoma - 17.5%;
- other options - 5.3%.
Warning! The etiology of trophoblastic disease can be either benign or malignant.
According to the clinical classification, it is customary to distinguish the following types of trophoblastic disease:
- 1 - localization of the neoplasm is limited to the uterine cavity.
- 2 - neoplasia extends to the ligament of the uterus, appendages and vagina, but the formation occurs only within the genitals.
- 3 - not only the genitals are affected, metastases appear in the lungs.
- 4 - in addition to metastases in the lungs, the liver, spleen, kidneys, brain and organs of the gastrointestinal tract are affected.
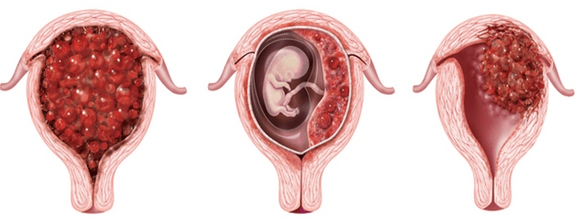
Trophoblastic disease with malignant neoplasia may have a metastatic or non-metastatic clinical course.
According to the histological basis, the diagnosis has the following types:
- partial or complete drift;
- invasive mole;
- syncyial endometritis;
- choriocarcinoma.
Gestational trophoblastic disease is one that has a combination of all of the above types.
Causes of trophoblastic disease
Various types of diagnosis of trophoblastic disease are considered by oncological gynecology as a single process. Among the prerequisites, the influence of various viruses is taken into account, including influenza, the characteristics of the woman's eggs, immunological factors, protein deficiency, chromosomal aberrations and the growth of hyaluronidase.
There are also additional prerequisites that contribute to the development of the disease:
- age over 35, especially over 40;
- a history of spontaneous abortion;
- abortions;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- childbirth.
Chorionic carcinoma often develops after a previous hydatidiform mole, especially its full form.
Important! Trophoblastic disease is more common in representatives of the countries of the East.
Symptoms of trophoblastic disease
Signs of trophoblastic disease depend on its histological type:
- Vesical drift, partial or complete - symptoms of a missed pregnancy, an increase in the uterus, vaginal bleeding. Also, this type of trophoblastic disease is characterized by a high level of hCG.
- Invasive mole - severe pain in the lower abdomen, uterine bleeding.
- Choriocarcinoma - spotting of a dark brown color that occurs outside the menstrual cycle, roughness and swelling of the breast, a violation of the hormones, an increase in the uterine cavity.
- Syncytial endometritis - the presence of bloody discharge.
An important symptom in the diagnosis is the presence of serous-purulent inclusions in the bloody discharge.
If metastases occur in other organs, the characteristic symptoms are:
- intra-abdominal bleeding;
- severe pain in the abdomen, reminiscent of the nature of the fight;
- increase in body temperature;
- secretion of colostrum, enlargement of the mammary glands in the chest;
- if the tumor is in the lungs - cough, pain in the chest;
- in the gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea, general indigestion;
- in the brain - nausea, incoordination, severe headaches.
Additional symptoms of the disease include increased fatigue, decreased appetite, due to which active weight loss occurs, and sleep disturbance. Since trophoblastic disease is directly related to the onset of pregnancy, a change in the emotional state of a woman is possible.
Diagnosis of trophoblastic disease
Differential diagnosis of trophoblastic disease consists in the following activities:
- physical examination;
- blood and urine analysis;
- histology of the tissues of the uterine cavity after scraping;
- control of the hCG indicator;
- conducting an x-ray examination.
As an additional computer diagnostic to establish trophoblastic disease, a gynecologist can perform an ultrasound scan, which will show changes in the uterus. In addition, this method can detect tumors larger than 4 mm. As an additional sign of the disease, the formation of tecalutein-type ovarian cysts is considered.
Warning! By means of histology, it is far from always possible to identify the disease. Sufficiently informative is blood sampling to determine the level of hCG.
X-rays can reveal the presence of metastases to other organs. Additionally, at the initial appointment, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient in order to identify a family analysis of diseases. If the tumors have reached a sufficient size, the gynecologist can feel them by palpation through the cervical canal.
Treatment of trophoblastic disease
The tactics of treating trophoblastic disease according to clinical guidelines in gynecology directly depends on its histological form and stage. As a rule, therapy includes the following types of exposure:
- chemotherapy;
- radiation exposure;
- surgical intervention.
As an antitumor treatment, it is practiced to receive and infuse special preparations through a dropper. With the gestational type of the disease, treatment continues for several weeks, followed by a mandatory break.
As soon as acute symptoms are relieved, two additional courses are carried out for prevention.

After treatment, follow-up by a gynecologist is required for the next two years.
Surgical intervention is indicated for large tumor sizes, as well as for a large number of symptoms of the disease. The main indications for removal of the tumor along with the uterus are:
- Lack of positive dynamics from chemotherapy.
- High pain discomfort.
- Excessive uterine bleeding.
The use of radiation therapy is practiced to relieve signs of the disease, as well as in the presence of metastases in other organs. Treatment in this way is strictly dosed.
Forecast and possible consequences
One of the radical methods of treating trophoblastic disease is the removal of tumors along with the uterus. This, in turn, leads to the impossibility of further functioning of reproductive activity. Accordingly, infertility can be considered as one of the options for the consequences of the disease.
Correct and timely treatment of the disease allows us to hope for a good outcome for almost 100% of patients. Chemotherapy shows fairly good results, provided that it was applied on time, and not at the last stage of the disease, when metastases affected most organs.
Young women often manage to preserve their generative function in the absence of surgical intervention. Further observation and control by a gynecologist will allow in the near future to become pregnant again, endure and give birth to a healthy child.
Warning! In 8% of cases, relapses of the disease are observed.
Conclusion
Trophoblastic disease, characteristic of the gestation period or after its interruption, is a special tumor formation in the uterus. It can be benign or malignant, due to which it is divided into classes and histological types. A favorable prognosis with such a diagnosis is possible only if the patient receives timely assistance - chemotherapy, radiation exposure and surgery, if necessary.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on the information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance or treatment.
