Content
-
1 What is vulvar kraurosis and what does it look like
- 1.1 Stages of vulvar kraurosis
- 2 Causes of vulvar kraurosis
- 3 Symptoms of vulvar kraurosis
- 4 Diagnosis of kraurosis of the vulva
-
5 How to treat vulvar kraurosis
- 5.1 How to treat vulvar kraurosis with folk remedies
- 6 Possible complications and consequences
- 7 Preventive measures and forecasts
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Reviews on the treatment of vulvar kraurosis in women
Atrophic damage to the external organs of the reproductive system is a common phenomenon in gynecological practice. The condition of the skin, as a rule, is influenced by dystrophic processes taking place in the tissues. Such phenomena include kraurosis of the vulva. Often this condition progresses and results in oncology, therefore, it requires mandatory and immediate medical intervention. According to ICD 10, vulvar kraurosis has the code N90.0 and refers to diseases of the vulva of a non-inflammatory nature.
What is vulvar kraurosis and what does it look like
Kraurosis of the vulva is a chronic pathology in women, which is manifested by dystrophic changes in the tissues of the organs. It is usually noticeable in the form of deformation and coarsening of the skin of the vagina and labia. Another name for vulvar kraurosis is lichen sclerosus. In gynecological practice, such a pathology is considered a precancerous condition.
Warning! Since the disease is accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane of the genital organs, this, in turn, leads to a complete or partial dysfunction of the vulva.
Stages of vulvar kraurosis
Kraurosis vulvar disease is usually classified into several stages:
- First - it is characterized by primary changes and deformations of the mucous membranes and skin of the genitals. The process is associated with inflammation and insufficient blood flow to the lesions.
- Second - the external genital epithelium undergoes even greater changes, tissue keratosis becomes visible. Additionally, pigmentation, peeling and the initial stage of deformation of the large and small labia are noted.
- Third - there is an active replacement of the affected epithelium with scar tissue. Practical complete atrophy leads to disruption of the functioning of the vulva - the entrance to the vagina narrows, the labia decreases in size.
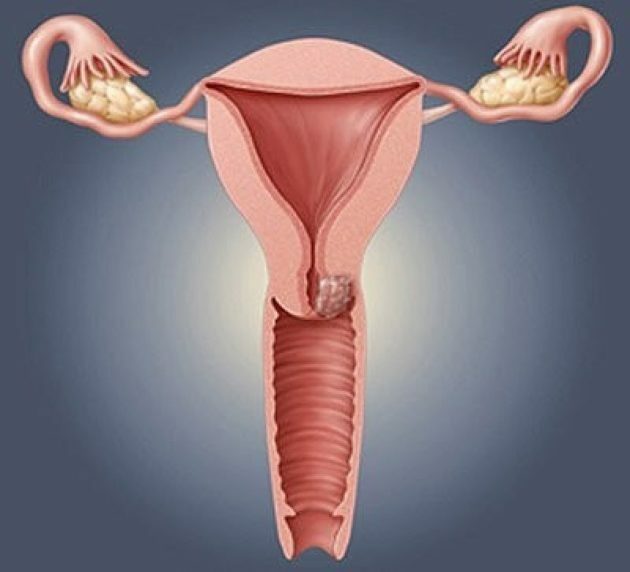
The advanced stage of kraurosis is often accompanied by discomfort during urination.
Important! Kraurosis of the vulva often occurs in women during the development of menopause. However, atrophy of the tissues of the genital organs can also appear after the age of 30 years.
Causes of vulvar kraurosis
At the heart of kraurosis of the vulva, which in the photo looks like soft tissue atrophy, is the response of the epithelium to adverse external factors. Accordingly, the disease is exclusively polyetiological in nature. Often this is an independent diagnosis, which can also be the result of other pathologies such as endocrine system failures or infections.
Possible causes of kraurosis:
- HPV is a sexually transmitted disease. The virus, getting into the skin cells, causes active tissue dysplasia, outwardly this is manifested by the formation of neoplasms - papillomas. Kraurosis can occur against the background of long-term treatment of HPV infection, the combination of which with degenerative changes in the vulva often leads to the formation of malignant cells.
- Endocrine pathologies. Often, signs of vulvar kraurosis are associated with a lack of sex hormones. Additionally, the pathology of the adrenal glands, ovaries and thyroid gland contribute to the development of the disease.
- Infectious diseases of various etiologies, including gonorrhea and herpes. Pathogenic microorganisms of these ailments affect tissues, simultaneously causing inflammatory processes in a chronic form.
- autoimmune diagnoses. In this case, the body's defense system begins to actively attack its own tissues.
Important! According to studies and statistics, vulvar kraurosis is often associated with Lyme disease and hepatitis C.
Clinical guidelines for kraurosis draw attention to the fact that in the diagnosis it is important not to lose sight of risk factors:
- Hereditary history of an unfavorable type - skin and reproductive pathologies in the next of kin.
- Chronic diseases that occur against the background of autoimmune pathologies - diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease.
- Negative factors of psychogenic type.
- Regular traumatization of the skin of the vulva (cuts, burns, sprains).
- Pathologies associated with metabolism, obesity.
- Unprofessional therapeutic and diagnostic measures in the external genital organs.
- Allergic reactions that appeared against the background of hypersensitization of the immune system.
Identification and elimination of the cause of vulvar kraurosis is an important point for effective treatment.
Symptoms of vulvar kraurosis
The primary signs of vulvar kraurosis are usually almost invisible to a woman. Normal are slight tingling in the perineal area, which are accompanied by increased dryness. A progressive diagnosis is characterized by itching, worse at night, deformity of the labia minora and labia majora.
Additional symptoms of genital kraurosis:
- lack of lubrication during sexual arousal;
- noticeable hyperemia of the skin around the vagina;
- thinning of the hairline;
- change in the color of the genitals, the appearance of pronounced pigmentation;
- roughness and coarsening of the epithelium outside the genital organs;
- pain during bowel movements and urination;
- discomfort during intercourse;
- narrowing in the size of the clitoris and labia;
- reduction of the passage into the vagina;
- sleep disturbance, anxiety;
- the presence of small cracks and signs of burst vessels in the genital area;
- decreased concentration and performance.
In parallel, the symptomatic picture of the disease negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of the patient. Particular discomfort delivers a constant burning sensation in the genital mucosa. In addition, the resulting cosmetic defects interfere with normal sexual activity.
Diagnosis of kraurosis of the vulva
The first step to correctly diagnosing vulvar kraurosis is to see a doctor and interview the patient. Even with a detailed examination, the initial signs of the disease can be detected.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Scraping on a smear from the vaginal mucosa. A special swab is used to collect the biomaterial. With the help of cytology, you can exclude or confirm the presence of abnormal cells in the body. Additionally, special nutrient media are used to detect the presence of the pathogen. This is necessary if an infection is suspected.
- Vulvoscopy. It is an external examination of the genital organs using an optical device with multiple magnification. Previously, the site is treated with antiseptic preparations.
- Blood test. Allows you to determine the ratio of enzymes in a qualitative and quantitative sense. Additionally, an immunogram is performed to exclude an autoimmune disease. The purpose of a blood test is to search for antibodies, the formation of which is characteristic when pathogenic cells appear in the body.
- Biopsy. It is a plucking of a small area of affected tissue under local anesthesia. The resulting material is examined to determine the cause of dystrophic changes in the skin of the genitals. With this method, you can reliably see the presence of cancer cells.
With the help of vulvoscopy, you can not only confirm the diagnosis, but also detect signs of oncology.
Important! It is optimal to carry out several diagnostic procedures at once, which will make it possible to make a more accurate diagnosis. In some cases, it may be necessary to consult a dermatologist, immunologist and venereologist.
How to treat vulvar kraurosis
Treatment options for the disease directly depend on the stage of dystrophic changes, the presence of oncology risk, the age of the woman, and concomitant diagnoses. It is important to pay attention not only to the reason why kraurosis occurs, but also to remove external defects of the vulva.
The main methods of treatment:
- Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs. Such a scheme is required when an infection is detected.
- Antihistamines and corticosteroids. Such ointments for kraurosis of the vulva improve blood circulation in the tissues and alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of inflammation.
- Local remedies with progesterone and estrogen. Often with the disease there is a deficiency of such hormones.
- Laser treatment of vulvar kraurosis involves the removal of papillomas. Additionally, cryosurgery can be used.
- Blockade of the nerve of the reproductive system with medication.
- Physiotherapy - warming up promotes rapid tissue regeneration.
- In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment, surgical intervention in the form of ablation or exposure to liquid nitrogen is required.
Important! Additionally, it is recommended to follow a diet, take vitamins and sedatives.
How to treat vulvar kraurosis with folk remedies
As an auxiliary method of therapy, you can use traditional medicine recipes:
- Apply flaxseed oil to the affected areas with a cotton swab at least three times a day.
- Carry out baths with pharmaceutical chamomile - a glass of dry matter in three glasses of boiling water, strain and add to the basin for a future procedure.
- Wash with a solution of soda in combination with tar soap.
- Make a tincture of celandine on vodka for 3-4 days, wipe the areas affected by croirosis with the resulting product.
The use of traditional medicine requires prior consultation with a doctor.
Possible complications and consequences
The main danger of kraurosis of the vulva is the risk of developing cancer. According to statistics, about 35% of women with this diagnosis suffer from cancer in the future.
In addition, advanced forms of the disease cause the formation of deep cracks. Through them, the risk of infection in the body is high.
Preventive measures and forecasts
Prevention of kraurosis can be both primary and secondary. The first includes the following measures:
- hygiene;
- wearing underwear made from natural materials;
- proper nutrition.
Secondary prevention - a timely visit to the doctor, regular vulvoscopy to exclude oncology.
In most cases, it will not be possible to completely restore the skin of the vulva to its original appearance. However, timely complex treatment helps to slow down dystrophic changes in tissues.
Conclusion
Kraurosis of the vulva is a pathological condition, which is a degenerative change in the tissues of the vagina with a partial loss of its functioning. It has an increased risk of developing oncology, therefore, it requires mandatory medical intervention.
Reviews on the treatment of vulvar kraurosis in women
Semenova Antonina, 35 years old, Pyatigorsk
It was possible to notice the makings of a manifesting croirosis at an early stage. The deformation did not have time to become too strong. She took antibiotics, antiviral, smeared with ointments. The doctor believes that the process is stopped.
Petrova Valeria, 40 years old, Moscow
In my case, kraurosis became evidence of the presence of cancer cells in the body. I went through two courses of radiation therapy, at the same time I use ointments and traditional medicine recipes. External deformation is not strong, but noticeable.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on the information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance or treatment.
