Content
- 1 What is vaginal atresia
- 2 Causes of vaginal atresia
- 3 Symptoms of vaginal atresia
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Treatment of vaginal atresia
- 6 Possible complications and consequences
- 7 Preventive measures and forecasts
- 8 Conclusion
Vaginal atresia is a pathological phenomenon, which is an infection of its lumen with connective tissue. There are several forms and types of this diagnosis, in particular, it can be both primary, congenital, and secondary, which was acquired as a result of certain negative factors. According to its distribution, atresia can be both complete and partial, more often the lower third of the vagina. It is a mechanical obstacle to the onset of pregnancy and childbirth, and also makes it difficult or completely blocks the outflow of menstrual blood.
What is vaginal atresia
Vaginal atresia is a common gynecological diagnosis with the ICD code N89.5. With this disease, there is an overgrowth of the walls cervical canal with fibrous tissue, while all organs of the reproductive system - the cervix and uterine cavity, ovaries - continue correctly function.
Depending on the form, clinical gynecology distinguishes the following types of atresia:
- Complete - the entire vaginal cavity is overgrown.
- Partial - fusion of the walls in the upper, middle or lower section (lower third).
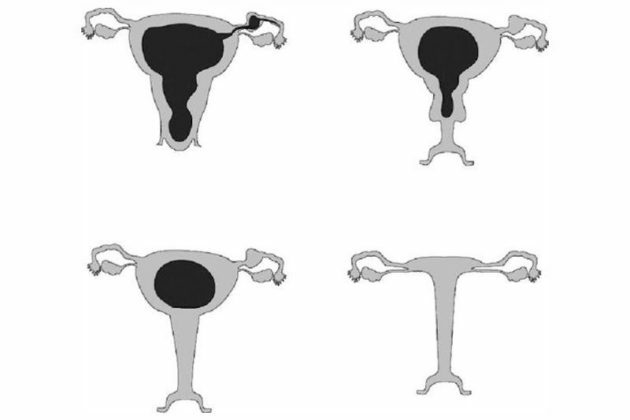
If holes are present in the partitions formed in the vagina, they speak of fistulous atresia
Important! Atresia as a disease is not considered too common; out of 10,000 patients, it is diagnosed in 2-3.
Causes of vaginal atresia
The causes of the disease depend on its form, as well as on the localization of the pathology. For example, primary or congenital atresia results from malformation of the Müllerian ducts that do not merge with the urotheginal sinus. This is facilitated by various adverse factors in the form of sexually transmitted diseases that affect during fetal development:
- trichomoniasis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- herpes genital;
- HPV;
- ureaplasmosis.
The second type of atresia is secondary or acquired, it is promoted by the following phenomena:
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs - colpitis, vaginitis;
- birth trauma of the vagina;
- unsuccessful surgical interventions;
- complicated medical procedures;
- douching with a concentrated disinfectant solution.
The development of atresia is often facilitated by infections carried by the patient at an early age. These include scarlet fever, diphtheria, parotitis.
Symptoms of vaginal atresia
Atresia of the lower third of the vagina has a symptomatic picture similar to any other localization of the pathology. Signs of adhesion also depend solely on the type of disease. In primary atresia, the following symptoms are observed:
- During the period of menarche, girls do not have external menstrual bleeding, but there are regular pulling pains in the lower abdomen.
- Depending on the location of the fusion of the walls, the accumulation of menstrual blood occurs, leading to stretching of the vagina, fallopian tubes and uterus. Accordingly, this leads to the appearance of hematocolps, hematosalpinx and hematometer. In the latter case, in addition to pain, loss of consciousness is possible.
- The congenital disorder can be diagnosed in infants and is usually associated with the child's anxiety due to difficulty urinating.
Secondary atresia, which usually occurs against the background of previous infections or unsuccessful medical manipulations, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- lack of outflow of menstrual blood;
- pulling and aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- soreness during intercourse is observed with partial atresia, for example, of the lower third of the vagina.
As a dangerous symptom of secondary atresia, the development of diseases such as peritonitis, pelvioperitonitis, rupture of the uterine cavity can act.
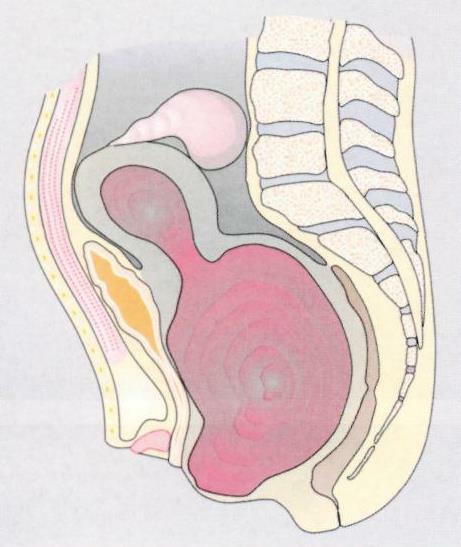
If atresia of the lower third of the vagina occurred during pregnancy, this places the physiological course of childbirth
With the fistulous form of the disease, it is possible to attach infections leading to the formation of pus. The latter, in turn, pours into the abdominal cavity, causing a threat to the life of the patient.
Diagnostics
The following research methods are chosen as diagnostic measures to determine the fusion of the walls of the vagina, as well as the type and type of atresia:
- Primary gynecological examination on the chair, during which the doctor can determine the presence of hematocolpos, which protrudes from the genital gap in the form of a domed formation. Conducting a recto-abdominal examination allows you to detect the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes, which can be high located, enlarged and painful. With the help of probing, the doctor determines the localization of the fusion, the depth of the vagina, which is valuable information for planning further plastic surgery.
- Taking a smear from the vaginal cavity for laboratory testing. This analysis will make sure that antibiotic therapy is necessary when infections are attached.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, which will allow you to visually determine the presence of a hematometer, pyometer, pyosalpinx and find out their size. If they are too small, it makes sense to do an MRI of the pelvic organs.
Modern gynecology uses vaginography and diagnostic laparoscopy as additional research methods. In the presence of pyuria or acute retention, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a urologist. This is especially true with signs of a fistulous form.
Treatment of vaginal atresia
The treatment of atresia of the lower third of the vagina is understood only as a surgical intervention. Usually it is a vaginoplasty, which involves:
- elimination of fusion of the vaginal cavity with fibrous tissue;
- restoration of patency of the genital tract.
A mandatory moment during the operation is the opening of the formed vaginal septum, as well as the emptying of the resulting hematocolpos or hematometers through the cervical canal. After release, mandatory sanitation of the cavity with antiseptics is required, as well as complete excision of the partitions.
As a result of surgery, a wound is formed, the edges of which are sutured with catgut, which makes it possible to achieve not only patency, but also restore the shape of the vagina.
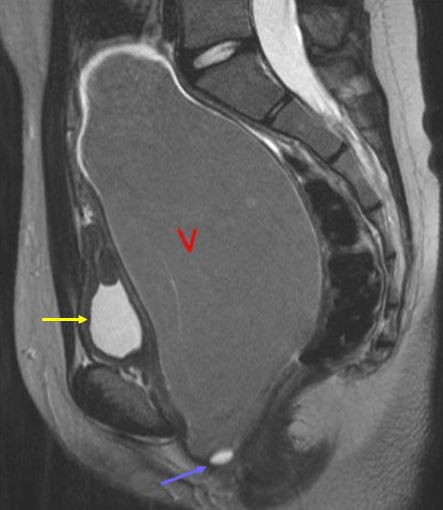
At the last stage, a swab soaked in sterile vaseline oil is inserted into the cervical canal.
If the accumulation of blood has already passed into the fallopian tubes, it is necessary to perform an operation to remove the hematosalpinx through the abdominal cavity. A prerequisite for rehabilitation after surgery is antibiotic therapy. After the recovery period, the woman is shown regular examinations by a gynecologist and an active sexual life.
Important! If there is a threat of re-atresia of the lower third of the vagina, bougienage is performed periodically.
Possible complications and consequences
Among the complications that cause vaginal atresia, the most common are:
- ascending infections, especially in the presence of a fistula;
- sepsis;
- peritonitis;
- re-fusion of the walls of the vagina, their adhesion.
If an infectious complication is present, this is fraught with the release of infected blood into the peritoneal region, which leads to the development of peritonitis. Dangerous consequences threaten the fusion of the vaginal walls in the presence of obstruction of the fallopian tubes. This can lead to rupture of the uterus, the entire contents of which will also be released into the abdominal cavity.
Inflated atresia threatens with accidental wounds in the uterus, bladder or rectum.
A warning! As a possible complication, adhesion of the walls of the vagina, excessive scarring, which often causes recurrent atresia, can be considered.
Preventive measures and forecasts
To reduce the risk of primary atresia in women during the period of gestation, it is important that the course of pregnancy takes place under the constant supervision of a gynecologist. This will prevent and exclude the development of any intrauterine pathologies. This is especially true of possible problems with the hormonal background, in some cases a course of appropriate drugs is required.
To exclude sexual infections, which often cause the development of secondary atresia, it is important to periodically take tests for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. This is especially true during pregnancy, when a woman is prone to sexually transmitted diseases.
As measures for the prevention of acquired atresia, the following are necessary:
- regular examination by a gynecologist;
- scheduled ultrasound, testing;
- timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs;
- accuracy during a medical examination of the genital organs;
- non-traumatic management of physiological childbirth;
- prevent mechanical interventions in the genitals, do not engage in self-administration of medications.
- refusal to douche without the absence of urgent need.
In the presence of gynecological pathologies in girls at an early age, it is also important to visit a doctor regularly, which will help prevent adhesion and fusion of the walls of the vagina.
Conclusion
Vaginal atresia, regardless of localization in the upper, middle or lower third, is the formation of partitions from fibrous tissue. Pathology requires mandatory surgical intervention, as well as competent measures to prevent relapse. Secondary and primary atresia is caused by various reasons, however, if not properly treated, it can cause negative and dangerous consequences.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on the information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance or treatment.
