Content
- 1 What is salpingitis
- 2 Can salpingitis be cured?
- 3 Causes of salpingitis
-
4 Signs of salpingitis
- 4.1 Allocations with salpingitis
- 4.2 Pain with salpingitis
- 5 Types of salpingitis
- 6 Complications of salpingitis
- 7 Diagnosis of salpingitis
-
8 Treatment of salpingitis
- 8.1 Treatment of acute salpingitis
- 8.2 Treatment of chronic salpingitis
- 9 How much salpingitis is treated
- 10 Is it possible to have sex with salpingitis
- 11 Is it possible to get pregnant with salpingitis
- 12 Prevention
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Feedback on the treatment of salpingitis in women
Salpingitis is one of the most common diseases in gynecology, representing inflammation of the fallopian tubes. An isolated diagnosis is rare, as a rule, the ovaries are also involved in the infection, which entails oophoritis. Together, both diseases are usually combined into a common group called salpingo-oophoritis. The diagnosis can be supplemented by extensive inflammation of the uterus at advanced stages. Symptoms and treatment of salpingitis in women are determined by the stage of the disease, but in any case, it requires medical intervention.
What is salpingitis
The diagnosis is an inflammatory process localized in the fallopian tubes, one of the most common pathologies that occur in the pelvic organs. It can be bilateral, when it affects two sides at once, and one-sided.
Left-sided or right-sided salpingitis develops mainly in women of childbearing age, more often up to 25 years. In some cases, it occurs even after the onset of menopause.
First, infectious inflammation affects the mucous membrane of the pipe, after which it becomes chronic and goes into the deeper layers of the organs.
Important! Acute bilateral salpingitis develops more often in nulliparous women.
Can salpingitis be cured?
Even chronic bilateral salpingitis can be cured if you see a doctor in a timely manner. A mild form of the disease can be treated conservatively. If the symptoms of chronic salpingitis indicate a severe course of the disease, hospitalization may be required.
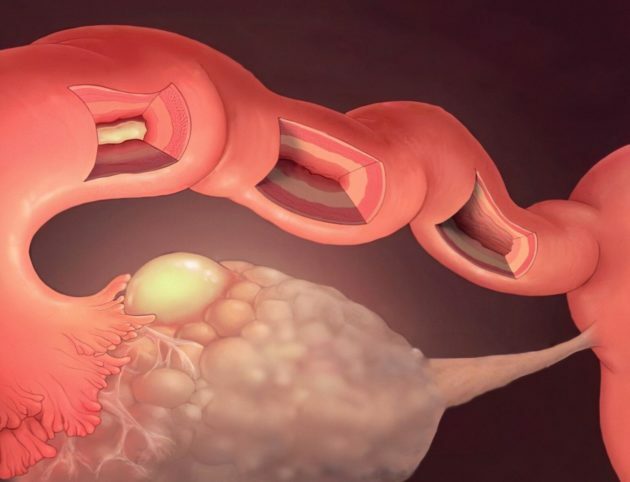
With the formation of pus, surgical intervention is urgently required
Causes of salpingitis
The reasons why acute salpingitis occurs, which later flows into chronic, lie in the activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. These include:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- chlamydia;
- enterococci;
- mycoplasmas;
- gonococci, etc.
There are also a number of additional factors that contribute to the development of the disease in the fallopian tubes:
- The presence of focal infections in the body. Even a simple sore throat can contribute to the development of salpingitis.
- Decreased immunity due to other reasons.
- Abortions and miscarriages with curettage.
- Gynecological diseases of an infectious nature.
- Surgical intrauterine interventions.
- Injury due to childbirth.
- Unprotected intercourse, non-compliance with hygiene standards.
- Any anomalies in the development of the fallopian tubes and uterus.
- Incorrect installation of the contraceptive spiral.
- Frequent stress, depression, unhealthy lifestyle, the presence of bad habits.
Signs of salpingitis
As a rule, acute symptoms of salpingitis in women appear at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, immediately after the end of bleeding. They are expressed by the following signs:
- fever, chills;
- violation of the menstrual cycle;
- weakness and dizziness, headaches of unknown nature;
- nausea, bloating;
- panic attacks, especially when stressed;
- inability to get pregnant, miscarriage;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, painful discomfort when urinating.
Acute and subacute salpingitis, unlike chronic, is always accompanied by general malaise. The latter is characterized by a periodic sensation of a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
Allocations with salpingitis
Allocations in gynecological disease are often purulent in nature. They can be interspersed with mucus, and in advanced cases and with the addition of a secondary infection, even blood. The discharge is quite intense and at the same time has an unpleasant odor.
Pain with salpingitis
Painful sensations with such a diagnosis are of a specific nature, which depends on its form. In acute salpingitis, such signs are most pronounced, while in chronic salpingitis they are practically not felt.
Warning! Pain in the chronic form of the disease tends to intensify during intercourse.
Types of salpingitis
In addition to division, depending on the extent of the spread of the inflammatory process, the disease can be classified according to the nature of development:
- Cheesy. This process of inflammation is accompanied by necrosis of the cells of the fallopian tube, it requires surgical intervention.
- Exudative. With such an inflammatory process, a serous or purulent fluid is formed in the tube.
The caseous form of the disease is much less common than the exudative form.
Accordingly, downstream the inflammatory process can manifest itself in three forms:
- Acute - characterized by a rapid course and development, a vivid symptomatic picture - fever, profuse uncharacteristic discharge from the vagina, severe pain in the abdominal cavity.
- subacute - is formed when the acute form subsides, the symptoms of the disease are less pronounced.
- Chronic - characterized by a long period of flow, which may be accompanied by acute stages, when a woman feels pulling pains in her abdomen.
Warning! The chronic form always manifests itself as a continuation of an untreated acute disease.
Complications of salpingitis
If acute or chronic salpingitis is not treated, the disease is fraught with the following complications:
- Infertility. It occurs due to the chronic form, which leads to the formation of scars and adhesions on the surface of the fallopian tubes.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic area, usually this phenomenon is associated with the further spread of infection.
- Ectopic pregnancy, which is also associated with the formation of adhesions that destroy the normal muscular activity of the fallopian tubes. Their formation prevents the movement of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity.
- Chronic pelvic pain. They are especially pronounced during intimacy or any physical activity.
Both chronic and acute salpingitis are dangerous during pregnancy. It often causes miscarriage or fetal death.
Diagnosis of salpingitis
Primary diagnosis of the disease begins with an appointment with a gynecologist and anamnesis. Next, an examination takes place on a chair with palpation, during which a smear is taken for laboratory research. This analysis is required to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen that caused salpingitis to the antibiotics that will be used in the treatment.
Additional research options:
- General blood and urine tests, which can detect the presence of inflammatory processes.
- X-ray examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- PCR analysis, which will reveal the DNA of the pathogen.
- Ultrasound, which allows you to highlight the accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tubes, adhesions and scars.
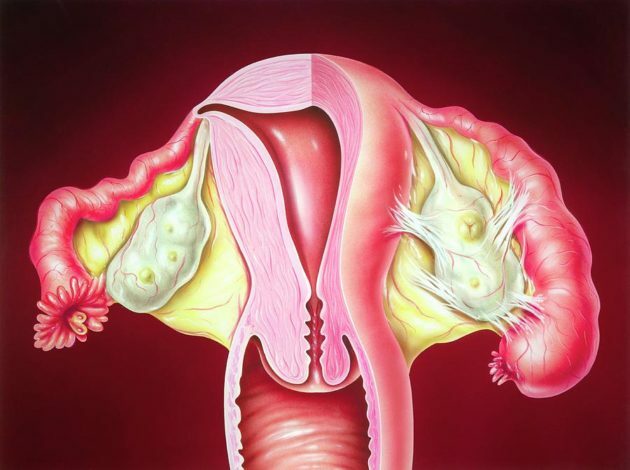
Laparoscopy is a necessary diagnostic method when it is required to study the state of the inflammatory process from the inside.
Treatment of salpingitis
Treatment of salpingitis can be both conservative, medications, and through surgery. The treatment option depends on the form of the disease and the stage.
Treatment of acute salpingitis
Acute salpingitis and its chronic form in an exacerbated version require inpatient treatment. Mandatory conditions for quality therapy are diet, cold on the abdominal cavity and bed rest. The choice of antibacterial drug is based on the result of the analysis for the sensitivity of the pathogen.
The use of almost any form of antibiotics is practiced:
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- tetracyclines;
- macrolides, etc.
Additionally, the introduction of anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs, vitamins, immunomodulator, antifungal agents is required.
Treatment of chronic salpingitis
The treatment regimen for the chronic type of the disease is similar to the acute one, but in the first variant, the patient can undergo therapy at home. The main condition for recovery is strict adherence to the schedule prescribed by the gynecologist, while it is important to undergo regular examinations in order to verify the effectiveness of the chosen direction.
If the chronic form of the diagnosis is accompanied by acute pain syndromes or occurs against the background of pregnancy, hospitalization is required.
How much salpingitis is treated
The duration of treatment depends on the form of the disease and the presence of aggravating factors. On average, at least 10-12 days of taking antibacterial drugs are required.
Is it possible to have sex with salpingitis
Intimacy is allowed only after the suppression of the acute phase of the disease and the elimination of the infection from the body. Otherwise, the risk of infecting a partner is high.
Is it possible to get pregnant with salpingitis
It is quite possible to get pregnant with salpingitis in any form, but this is strictly not recommended by doctors. The presence of any infection that caused the inflammatory process in the fallopian tube poses a threat to the life of the unborn child.
Prevention
All preventive measures are similar to other infectious diseases. It is important to visit a gynecologist at least 1-2 times a year, to beware of stress, to be tested for STDs.
In the presence of any unpleasant symptoms and painful sensations, it is recommended to consult a doctor for examination
Conclusion
Symptoms and treatment of salpingitis in women require mandatory medical intervention. The disease can be caused by various pathogens of an infectious nature and poses a threat to the reproductive function of a woman. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist and be tested for STDs.
Feedback on the treatment of salpingitis in women
Koshneva Maria, 28 years old, Moscow
I found out about the disease by accident, there were pains in the abdomen. It turned out that in the chronic stage. She passed the tests, was treated at home with antibiotics. After the ultrasound, everything is normal, the infection is gone, the pain too.
Mironova Alevtina, 23 years old, Krasnodar
Discharges with an unpleasant odor appeared, an analysis for infection showed mycoplasma, and right-sided salpingitis developed against its background. Because of the acute form, I had to go to the hospital. But relief came immediately after therapy. There was no particular pain.
The information and materials on this site are provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely on the information as a substitute for actual professional medical advice, assistance or treatment.
