 Thrombosis is one of the most dangerous diseases affecting both venous and arterial vessels.
Thrombosis is one of the most dangerous diseases affecting both venous and arterial vessels.
This is an disease resulting from the formation of a thrombus and the clogging of the vessel. Curled blood clogs the blood vessels, disrupts their patency, and hence the normal supply of blood to various organs.
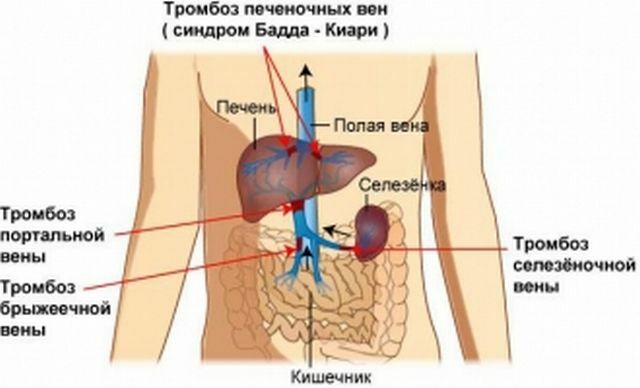
Although thrombosis is often considered a disease of the veins of the lower limbs, it often infects other vessels, such as the intestinal veins, the liver and even the retina of the eyes. And such a dislocation of thrombosis at times more dangerous and difficult to identify.
The portal vein is a vessel in which blood is collected from the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. Through the portal vein, blood is distributed to all the other veins of the liver. As a result of the development of thrombosis in the portal vein, a thrombus is formed, which gradually can completely clog the vessel.
Many doctors claim that portal vein thrombosis is more a complication than an independent disease, given the most common causes of its development( more about these we will discuss below).
Contents
- Prognostic factors and causes of the disease
- Types of the disease
- Symptoms of the pathology
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment methods
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical treatment
- Complications and prognosis
- How to prevent the disease
Provoking factors and causes of the disease
Every day we are affected by thousands of environmental factorsenvironment. Meanwhile, our everyday affairs and habits can involuntarily provoke a dangerous disease!
Many do not suspect that the causes and provoking factors for the development of portal vein thrombosis may be the most unexpected:
- Sitting or standing work, a sedentary lifestyle, lack of regular physical activity.
- Harmful habits, especially smoking.
- Some drugs that increase the blood's ability to clot.
- In addition, often the cause of thrombosis of the vessels becomes overweight.
The disease also develops very often due to surgical intervention in the work of the abdominal organs.
Elderly patients are often prone to this type of thrombosis.
The development of thrombosis is always based on three main factors:
- quality and composition of blood( for the development of thrombosis is favorable increased blood clotting);
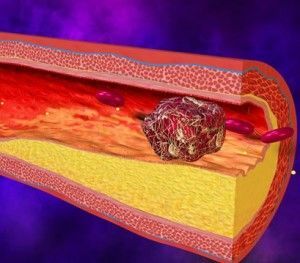
- blood circulation( slowing circulation can trigger thrombus formation);
- strength and vascular tone.
Now, more specifically, we will discuss the causes that provoke thrombosis of the portal vein.
Depending on their age, they can be:
- Thrombosis of in newborns: , an infection caused by an umbilical cord can become a provoking factor.
- Child age: is the most common cause of portal vein thrombosis - appendicitis. Infectious infection can lead to inflammation of this vessel and, as a consequence, to the formation of a thrombus.
- Adult age: As a rule, thrombosis of the portal vein causes surgery or malignant neoplasms in the pancreas or liver.
In addition to these main causes, portal vein thrombosis can be caused by congenital defects in the body, inflammatory processes in the body.
Sometimes this disease can provoke pregnancy, severe dehydration, vascular trauma.
It is important to note that in about half the cases, it is not possible to establish the cause of the disease.
Types of the disease
Depending on the location and size of the thrombus are distinguished:
- The first stage is the minimal thrombosis. Less than 50% of the vessel is blocked by a thrombus. The thrombus is located above the site of the portal vein into the splenic.
- The second stage is the spread of thrombus to the superior mesenteric vein.
- The third stage - thrombosis affects all the veins of the abdominal cavity, however, the blood flow is not significantly affected.
- The fourth stage is massive thrombosis. All veins of the abdominal cavity are affected, the blood flow is severely impaired.
There is also an acute and chronic thrombosis of the portal vein, which are different in their symptoms and consequences. More on this further.
 Why is the diet of thrombophlebitis so important and what principles of nutrition you need to know in order to avoid possible complications you can learn from our material.
Why is the diet of thrombophlebitis so important and what principles of nutrition you need to know in order to avoid possible complications you can learn from our material. What is the danger to the health and life of thrombosis of the cavernous sinus and what prevention methods exist? Also in detail about the symptoms and treatment of pathology.
Symptoms of pathology
The danger of the disease is that it often passes unnoticed until the consequences are no longer too serious. In about a third of cases, thrombosis is not detected in the initial stages.
There is a list of the most common symptoms that can become an alarm and a sign that you should consult your doctor. Symptoms of acute portal vein thrombosis:
- lack of appetite;
- severe abdominal pain, left hypochondrium, bloating;
- flatulence;
- vomiting with blood, diarrhea;
- constant drop in blood pressure;
- if there is cirrhosis of the liver, a symptom of thrombosis may be jaundice.
In chronic thrombosis for a long period, the liver may remain normal. The disease manifests itself mainly during periods of exacerbation, which manifest in about the same way as acute thrombosis.
A characteristic feature is gastrointestinal bleeding. In advanced cases, the liver can increase in size, with palpation it becomes painful and bumpy to the touch.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is impossible to diagnose thrombosis of the portal vein, it is done only on an outpatient basis with the use of special equipment.
To begin with, the doctor carefully examines the patient, revealing the symptoms inherent in thrombosis of the portal vein. If such symptoms are present, the patient is referred for further diagnostic procedures. First of all, this is ultrasound, CT, biopsy and MRI.
A comprehensive study allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis even in the most complex clinical picture.
In some cases, phlebography can be performed, a procedure in which a special radiopaque substance is inserted into the venous vessel, followed by radiography.
Blood and urine tests are also mandatory, but without clinical studies, they are not enough to make a diagnosis.
Methods of treatment
As mentioned above, portal vein thrombosis is a truly dangerous disease that requires timely treatment.
At the initial stage, anxious symptoms can recede on their own, giving confidence that there is no cause for concern. However, if you observe such symptoms repeatedly, it is better to undergo a medical examination and begin treatment, if necessary.
The aim of the treatment is to counteract the complete blockage of the veins and the disturbance of normal blood flow in the abdominal cavity, as well as to prevent the onset of the consequences of portal vein thrombosis.
Let's look at what treatment can be used for this disease.
Conservative treatment of
The objective of this method is to dilute the blood and reduce its ability to clot.
The doctor prescribes anticoagulants( for example, heparin, acenocoumarol, phenyldione) and thrombolytics( streptodecase, fibrinolysin).If necessary, antibiotics of a wide spectrum and beta-blockers( for preventing bleeding) can be prescribed.
If bleeding has already begun, it should be stopped only in a clinical setting with special therapeutic procedures and with the use of hemostatic agents.
In chronic thrombosis, conservative treatment shows the patient a special regimen: reducing the intensity of physical exertion, preventing pressure on the walls of the abdomen.
Surgical treatment
 It is used if conservative methods do not give a positive result.
It is used if conservative methods do not give a positive result.
The task of this method is the early restoration of normal blood circulation.
The essence of the operation is to provide new connections between the thrombosed vein and the remaining vessels. This operation is particularly difficult and a long period of rehabilitation.
Complications and prognosis
Thrombosis of the portal vein is dangerous not only in itself, but also its consequences.
The result of neglected diseases can be liver abscess, hepatic coma, purulent peritonitis, extensive gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal infarction, abscess sub-adrenal or subdiaphragmatic, hepatorenal syndrome.
This is especially true for complete thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein, which in most cases ends in a fatal outcome.
How to prevent
disease Prevention measures are simple and accessible to almost everyone. And special attention to these simple methods should be addressed to those who fall into the risk group, because it is subject to the influence of disease-provoking factors.
So, the methods of prevention include:
- Transition to the correct and balanced diet , the intake of sufficient quantities of essential elements and vitamins. And do not forget about enough fluid to prevent dehydration.
- Physical load .Regular exercises stimulate blood flow and increase the tone of blood vessels. Pay attention to cardio surgery, if there is no contraindication for them. Do not forget about walking on the open air.
- Discarding bad habits of .This will not only reduce the risk of developing portal vein thrombosis, but will also improve the body overall.
And finally, it should be noted that the most important in the treatment of portal vein thrombosis is timeliness. Do not wait for the anxiety symptoms to recede, consult a specialist.
This will help to avoid serious consequences and keep your health.
