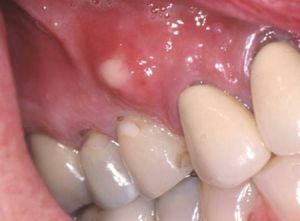
 Periodontal abscess is an inflammatory gum disease of the purulent nature, which is locally limited.
Periodontal abscess is an inflammatory gum disease of the purulent nature, which is locally limited.
This cavity with purulent contents, located in the tissues of the periodontal, looks like a round seal when viewed from the outside.
By the size of the seal can be with a pea, or with a walnut.
Contents
- What causes a painful process?
- Two forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis and treatment
- First-aid intervention
- Surgical treatment
- Recommendations for the post-operative period
- Consequences and complications
- Preventive measures
What causes a painful process?
The main cause of the periodontal abscess is infection, which then affects the gum tissue, the gingival pocket.
Infection is the result of the vital activity of various microorganisms in the gingival pocket. From there, it extends to all neighboring periodontal tissues, causing inflammation. At the site of inflammation, blood, pus, and leukocytes accumulate. The cavity is filled with contents, forming an abscess.
To lead to the development of the pathological process can:
- dental diseases( gingivitis, periodontitis);
- gum injuries( chronic trauma, mechanical damage, various burns);
- improper filling or prosthetics of the teeth( as a result of which the gums are injured).
Two forms of the disease
By the nature of the current, the periodontal abscess can be: 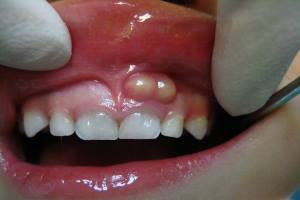
- Acute .Has a pronounced symptomatology. The pain syndrome sharply increases, the pathological mobility of teeth appears, deep gingival pockets are revealed. The patient has a syndrome of severe intoxication.
- Chronic .Symptomatology is erased, the patient is bleeding gums, pain. Mucous in the inflamed area is cyanotic, edematous, the roots of the teeth are bare, in the gingival pockets there is pus. A chronic abscess can become aggravated and become acute.
Symptomatic features of
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, discomfort will be felt. When palpation or chewing food there is soreness.
Over time, the pain will increase, and the chewing process becomes impossible. After a couple of days, a swelling in the area of the inflamed gums will appear. It grows rapidly enough, correspondingly there are constant pains that can irradiate into the area of the cheek, jaw, ear.
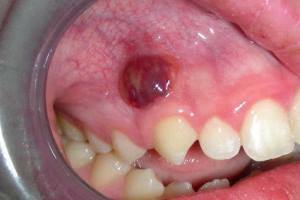
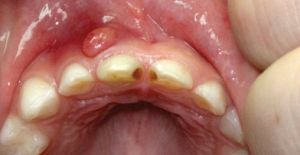
On the photo, a bloody abscess on the gum is a typical picture in the periodontal abscess
The abscess can be opened by itself, then the local inflammation and pain syndrome will subside. The pus flows into the oral cavity, and the wound will heal independently. But without treatment of the oral cavity with an antiseptic, there is a risk of infection of neighboring tissues.
As the inflammatory process develops, there will be a general intoxication of the body. Its severity depends on the stage of the disease. The patient may experience dizziness, fever, headaches, insomnia, a decrease or lack of appetite, a decrease in ability to work, a deterioration in well-being.
With further progression of the disease, the tumor will expand. Appear swelling of the cheek from the side of the affected gums.
Diagnosis and treatment
An abscess on the gums is diagnosed by examining the oral cavity, where a painful seal is found.
Radiography should be performed to ensure that the inflammation does not reach the bone tissue.
General blood test and PCR are done. In the general analysis there is an increase in leukocytes, ESR, the leukocyte formula is shifted to the left. With the help of PCR, the composition of the microflora in the gingival pocket is revealed.
Along with the rest of the methods, a cytological study is performed, with the help of which it is possible to detect a huge number of destroyed neutrophilic granulocytes.
These examinations help differentiate periodontal abscess with acute periodontitis, or exacerbation of its chronic form, with suppuration of the cyst of the jaw, osteomyelitis and other diseases.
First-aid intervention
To treat independently periodontal abscess at home is impossible, becausethis can lead to serious complications. But it is possible to carry out a number of procedures that will help relieve the pain and alleviate the general condition.
You can do the following:
- Rinse the mouth with an antiseptic. It can be potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine or furacilin.
 The temperature of the rinse solution should be between 20 and 25.
The temperature of the rinse solution should be between 20 and 25. - Rinse the oral cavity with herbal decoctions. These include chamomile, St. John's wort, sage.
- Apply cold to the swollen side of the cheek. You can take the ice, after wrapping it in a waffle towel.
- As analgesics, only analgesics can be taken( Analgin, Paracetamol, Tempalgin).
- Cautious cleaning of the oral cavity and diseased tooth in particular from food residues.
The following actions are prohibited:
- Self-administration of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. These groups of drugs are taken only for the purpose of the dentist. An independent initiative can lead to a deterioration of the state. In addition, using the drug before taking a doctor, you can remove some of the symptoms and the dentist can not objectively assess the nature of the disease.
- Pressure, pierce or heat swelling is strictly prohibited. This can exacerbate the inflammatory process, and it will spread to nearby tissues.
Surgical treatment
Periodontal abscess is treated exclusively surgically. The operation is carried out as follows:
- The dentist in the dot method resolves the gum.
- The abscess is drained. Sometimes purification is carried out through the periodontal pocket.
- All pus, dead tissue, blood is eliminated.
- Wound surface and oral cavity are treated with antiseptic solutions.
- Analgesics are prescribed to relieve the pain syndrome. Depending on the severity of the condition, antibacterial therapy may be prescribed. Immunostimulatory therapy is also prescribed to raise the defenses of the body.
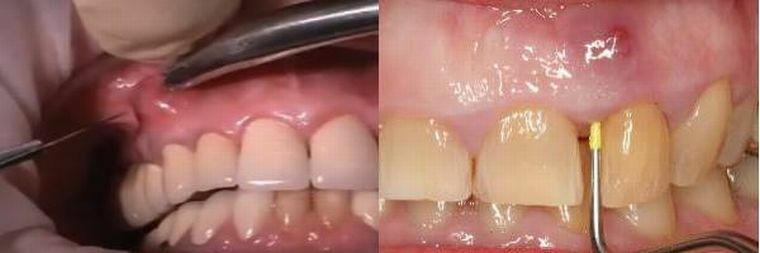
For laser wound healing laser procedures or physiotherapy are prescribed. To be sure of full recovery, it is necessary to repeat the visit to the dentist some time after the treatment( 1-1.5 weeks).He will not only examine the oral cavity, but also give further recommendations for caring for the damaged area.
Recommendations for the postoperative period
To avoid postoperative consequences, it is necessary to adhere to such recommendations:
- not to eat too hard food;
- refrain from consuming alcoholic beverages, smoking;
- not to use other drugs other than those prescribed( except for the treatment of other chronic diseases);
- do not take analgesics without the need;
- with the appearance of pus, temperature, etc., you should immediately go to dentistry.
Consequences and complications of
 The lack of treatment leads to serious consequences. The easiest, among all possible complications of an abscess, is the appearance of a chronic foci of infection. The rest have a more dangerous prognosis and serious treatment.
The lack of treatment leads to serious consequences. The easiest, among all possible complications of an abscess, is the appearance of a chronic foci of infection. The rest have a more dangerous prognosis and serious treatment.
Infection can spread as the nearest tissues - bone, periosteum, and internal organs, including the brain.
Periodontal tissues can be necrotic, loosening of the teeth, then their loss. Also, there is a risk of osteomyelitis of the jaw. The jaw will be deformed, which will lead to a distortion of the face.
Preventive measures
Prevention of abscess on the gums - a daily oral hygiene, treatment of oropharyngeal diseases, timely sanitation and regular preventive examinations at the dentist.
It is also important to prevent gum injuries, do not eat hot food.
If there are unpleasant symptoms, pains and swelling in the mouth, it is important to immediately go to dentistry. Even running caries can lead to other, much more serious diseases.
