 The baby's teeth appear first. They erupt in the baby after birth in some sequence.
The baby's teeth appear first. They erupt in the baby after birth in some sequence.
On each half of the jaw the teeth of one name break through. Unlike an adult who has 32 teeth, the child has only 20.
Contents
- How the first teeth are cut
- What is the name of the boys?
- Features of baby teeth
- Why are "first-born" in the mouth?
- When, how and why do they fall out?
- Small spine, yes removal
- As an output of
How the first teeth of
are cut "Milk" have several features:
- is much smaller in size;
- have, in contrast to the adult, much fewer tubercles;
- their eruption begins on the seventh month of life.
The first incisors are lower incisors. The final formation of the dentition ends up to three years of the child's life.
After six years, gradual replacement of incisors, molars and canines with permanent ones begins. The scheme of their location in the child looks like this:
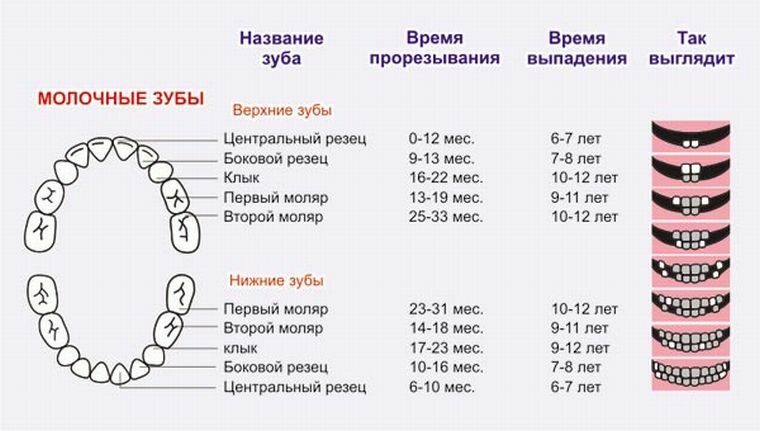
This photo clearly shows all the teeth that erupt in the child in a certain sequence, also their names are given.
The order is as follows:
- Usually cuts the incisors in the lower jaw in six months of , and at seven months the first incisors on the upper jaw erupt. In total, there are four.
- For nine months , one more pair of incisors appears on each jaw. So, to one year the child has a total of eight teeth.
- At the age of one year , a pair of molars on the lower jaw break through, and two months later - on the lower jaw.
- Canines on the lower jaw are formed per year and four months , and a little later - and on the top - also two canines. Thus, the one and a half year old child has 16 teeth.
- In 20 months appears a pair of molars on the lower jaw.
- And by the age of two years the child has a second pair of molars on the upper jaw. So gradually the process of forming a child's dentition ends.
Since the age of six, the process of forming permanent incisors, canines, and then molars has begun. It completely ends in 12 - 13 years. The third large molars of the G-8 finish appearing around the age of 30.
What is the name of the boys?
The first teeth are called as follows:
- central cutter( cut first);
- lateral incisor( cutting it - up to one year);
- canine( term of eruption - up to 23 months);
- the first molar( appears maximum up to 19 months);
- the second molar( the maximum duration of eruption is up to 31 months)
Features of the baby teeth
The child has the following teeth:
- The incisors, the canines resemble the same constants in their structure
- On the upper jaw , the crown of the 1st molar is similar tocrown with the same permanent premolar, has two tubercles
- The second molar of the maxilla resembles the crown of the same permanent molar and has four tubercles
- The first molar has four tubercles on the lower jaw .The lower molar has five tubercles. It is similar to the first permanent lower molar in an adult.
Baby teeth have some differences from permanent ones: 
- they have a white, "milky" hue, "which is why they got their name;
- they have less expressed degree of mineralization, so they are much more prone to tooth decay;
- the cavity of their pulp is larger, and the walls of the crowns are thinner;
- crowns are wider;
- location - strictly vertical, this is due to the fact that behind the roots are placed the rudiments of permanent teeth;
- the size of the baby teeth is significantly less compared to the permanent ones.
Why do you need "first-born" in your mouth?
Baby teeth are very important for a child:
- , he can chew food properly and qualitatively;
- incisors and canines, as well as molars, participate in the formation of speech;
- is the most important part of the oral cavity;
- they "show" permanent teeth a place for eruption;
- are involved in the formation of bite;
- they are of great importance for the formation of the facial skeleton.
When, how and why do they fall out?
Usually, from six to seven years, there is a gradual loss of milk teeth and their replacement by permanent teeth. There may be deviations from these terms, associated with the individual characteristics of the child's body.
But, despite the individual features of such a period, they fall out and are replaced by the constants in strict sequence:
- This process begins not with the fall itself, as some parents erroneously think, but with with the growth of premolars. The appearance of quadruples and fives is associated with the growth of the jaw. But they can not grow with a jaw. If during such a replacement the interdental spaces do not increase, this contributes to the development of bite deformities.
- As the permanent teeth grow, processes are underway to change the existing .They start to wobble and fall out. At first the incisors fall out, and then the molar molars. Fangs change last.
 The most active process for the replacement of incisors, canines and molars is from seven to eleven years old. In this period, a high enough risk of caries development.
The most active process for the replacement of incisors, canines and molars is from seven to eleven years old. In this period, a high enough risk of caries development.
Therefore, during this period it is very important that the child carefully takes care of the oral cavity and does it twice a day - in the morning and in the evening. It is important to check how the child does this, as some children do this very quickly and do not pay enough attention to cleaning the interdental spaces.
The incisor, fang or molar that has appeared is not yet fully formed. Only a few years after the eruption, we can say that its formation is completely finished.
Small spine, yes,
Around this topic there are many myths - for example, that the milk teeth have no nerves or roots. It is not true. They have roots. And many parents do not see them for the simple reason that they dissolve in the process of falling out.
Dental roots in children are widely distributed. They cover the rudiment of a permanent tooth.
It should be borne in mind that the destruction of baby teeth occurs much faster than in an adult. If you delete them much earlier than the time, it will also lead to undesirable consequences. Because of the displacement of the roots, they will begin to shift from their place.
So a permanent tooth begins to be not where it needs to be, which leads to a wrong bite. So parents should know: the roots of milk teeth are, and they should be treated very carefully.
As an output of
So, the baby teeth are very important for the functioning of the digestion of an infant, the formation of its facial skeleton, speech. Parents should closely monitor the timing of their eruption, as well as the timing of their replacement by permanent.
Diseases of the child's mouth are very serious, and in many cases they contribute to the appearance of bite anomalies. Improper development of teeth leads to the development of many problems in the further development of the child.
This means that parents should be very attentive to dental problems in children and to treat dental diseases in a timely manner.
