 Teeth and gums are constantly exposed to various unpleasant diseases. This is difficult to avoid even with good hygiene, nutrition and lack of bad habits.
Teeth and gums are constantly exposed to various unpleasant diseases. This is difficult to avoid even with good hygiene, nutrition and lack of bad habits.
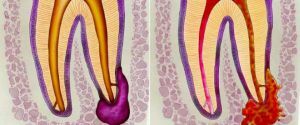
Sometimes just a draft or accidentally brought infection is enough to cause inflammation of the gums, toothache and other significant troubles. One of the most common and serious diseases of the oral cavity is the apical periodontitis.
The disease is accompanied by acute pains that occur in the area of inflammation and spread throughout the oral cavity, as well as the development of purulent foci.
Apical or apical periodontitis is a form of the disease in which the tooth root and the surrounding tissues become inflamed, it can proceed both in chronic and acute form, have both pronounced symptoms, or be for some time almost invisible to the patient.
There is a classification of the disease, depending on the source that provoked the disease. Each type of disease has slightly different symptoms and approaches to treatment.
Contents
- Causes and mechanism of development of
- Causes and mechanism of development of
- Classification and features of clinical picture
- Chronic and acute course of the disease
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Prognosis and prevention
Causes and mechanism of development of
Negative factors that may provoke apical periodontitis:
- Dysfunctional dentist in the treatment of ,when the disinfection of the treated area was found to be insufficient for
 , and dangerous microorganisms got into the wound in the tooth or nearby tissues. This sometimes happens in the treatment of caries and some infectious diseases of the mouth.
, and dangerous microorganisms got into the wound in the tooth or nearby tissues. This sometimes happens in the treatment of caries and some infectious diseases of the mouth. - Running forms of pulpitis , if a person for a long time ignores the need for treatment. As the pulp with time simply perishes, the apical opening opens and becomes accessible for getting into it harmful microorganisms and infections.
- Other factors can also have its negative impact: injuries, improperly installed seals , the use of dental force is not for the intended purpose( snacking of durable materials, opening of cans and packages, etc.).Injuries can be both significant and painful, leading to the development of acute periodontitis, and insignificant, provoking a chronic course of the disease.
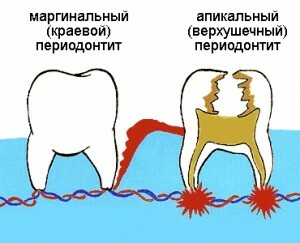
Classification and features of the clinical picture
Apical periodontitis, depending on the triggering factor, can occur in three main types:
- Infectious .Most often is a consequence of neglected caries, as the dental nerve gradually dies and harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity( for example, streptococci, staphylococci and other dangerous bacteria) are able to penetrate into the apical opening. There they spread to the tissues near the tooth and form a strong focus of inflammation around the root. Also, apical infectious periodontitis can be a consequence of inflammatory diseases, for example, osteomyelitis or sinusitis.
- Medicated .Appears due to the fact that in the periodontal tissue fall various dangerous medications, aggressive irritants. In most cases, the cause of this type of disease is the incorrect treatment of pulpitis. Such a negative impact can have a variety of materials and drugs: arsenic and pastes with its content, phenol, formalin, phosphate cement and many others. If, during the course of a visit to a dentist during the treatment, allergic
 was triggered by a reaction to the drugs used, which then provoked immunological reactions, this case also applies to periodontitis medication.
was triggered by a reaction to the drugs used, which then provoked immunological reactions, this case also applies to periodontitis medication. - Traumatic .Another type of disease that develops due to any mechanical or chemical damage. This can be a simple blow, chronic injuries, poorly placed seals and other situations. Fractures of the teeth, jawbone injuries and even micro-traumas refer specifically to this case and actively provoke the development of traumatic periodontitis.
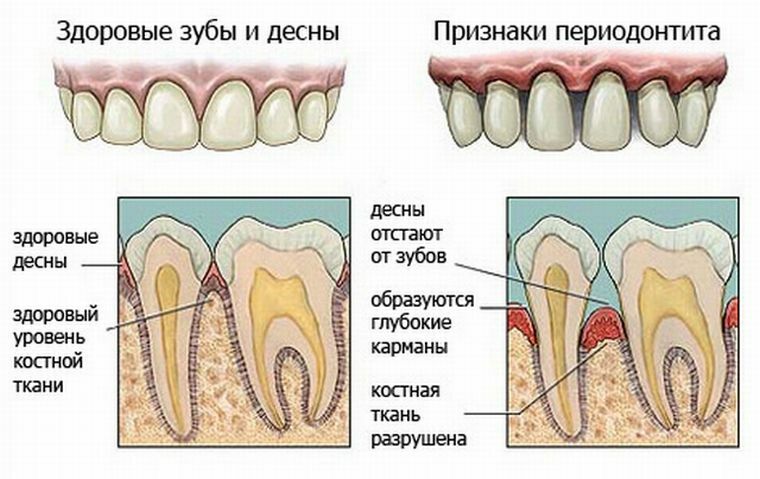
Symptoms of apical periodontitis depend on its shape:
- when infectious, pain occurs when you touch and press on the tooth, redness and swelling of the gums, characterized by an increase in body temperature, the release of pus and serous fluid;
- with medicated in the tooth and jaw felt aching pain, which with food and pressure increases, it seems to the patient that the tooth has become larger and very mobile;
- in the case of a traumatic form there is a constant pronounced pain, there is swelling of the gums at the site of the injury, it can bleed, there may be some mobility of the tooth, it is also possible to stain the periodontal pink.
Chronic and acute course of the disease
The apical periodontitis can have chronic and acute forms of flow. In acute form, there is active inflammation of the tissues near the tooth. In this case, the patient almost always feels severe pain in the tooth and nearby areas, it eventually becomes pulsating, the patient reacts painfully to high temperature. The person's health worsens, the temperature rises, and a headache may appear.
Chronic apical periodontitis usually occurs without pronounced symptoms, the pain appears only occasionally, sometimes when eating. When nakusyvanii on the tooth periodically there may be a feeling of his raspiraniya. On the gums may appear abscess, which after a time disappears by itself.
Diagnosis and treatment
If pain is experienced in the periodontal area, you should consult a doctor to determine the exact causes of discomfort. For diagnosis, X-rays are used, the study of clinical symptoms of the disease, and electrodontometry. But the decisive role in diagnosis is still played by X-ray.

Treatment of apical periodontitis is carried out in several visits to the dentist, as it is necessary to go through three main stages on the way to complete recovery: 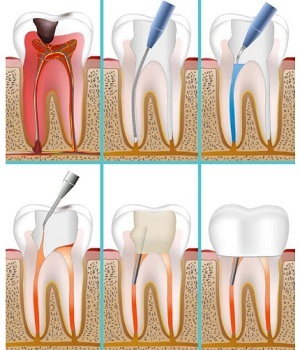
- mechanical preparation of the tooth for treatment;
- treatment of the affected area with an antiseptic;
- canal filling.
During treatment periodontium is opened in the right places, the remains of the dead pulp are removed, caries is treated, the root canals are processed and expanded. It is also important to perform channel disinfection, which is often done with ultrasound therapy.
As conservative treatment, rinses of the oral cavity with decoctions of medicinal herbs, mineral water are used, such drugs as Doxycycline and Cephalexin are used.
Forecast and Prevention
In most cases, apical periodontitis is successfully treated for several trips to the dentist. The most important thing is to call the doctor on time, otherwise serious consequences are possible: the appearance of complications in the form of a cyst, granuloma, abscess and even sepsis. In neglected cases, you just have to remove the tooth.
As far as prevention measures are concerned, constant and high-quality oral hygiene is important here, as well as regular visits to the dentist for the detection and treatment of even small foci of caries. This is usually enough to prevent the appearance and progression of periodontitis.
