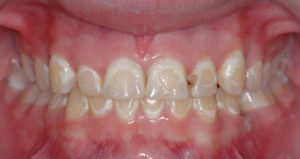
 Odontoclasia is a pathological process in hard tooth tissues, which is characterized by demineralization of enamel areas and is accompanied by the formation of a carious cavity.
Odontoclasia is a pathological process in hard tooth tissues, which is characterized by demineralization of enamel areas and is accompanied by the formation of a carious cavity.
Odontoclasia is one of the varieties of carious lesions and is localized in the cervical zone of the vestibular surfaces of the anterior group of teeth.
The definition of "odontoclasy" of Greco-Latin origin "clasia" means breaking, breaking. A hereditary factor plays a special role in considering the causes of odontoclasia: imperfect amelogenesis or aplasia of enamel and dentin can become a source.
Contents
- Causes and symptoms
- The location of odontoclasia in the classification of caries
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Children's melanodentia
- Prevention of the disease
Causes and symptoms
This is a polyetiological pathology - several factors can cause its development and development, such as:
- unsatisfactory oral hygiene;

- bad habits;
- metabolism;
- general condition of the body.
The main symptom of carious lesions of teeth is a short-term pain when irritating the affected area. Complications of pathology arise as a result of untimely treatment of the dentist.
The carious process can capture deeper layers of enamel and dentin, as a result of which the pulp is exposed. This threatens the development of deep caries. A more extensive influence of the infectious agent can lead to the appearance of periodontitis, paradontitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis and other serious complications.
The place of odontoclasia in the classification of caries
The World Health Organization has approved the international classification of diseases, 10 which was revised in 1989.
ICD-10 caries classification:
- enamel caries, also called caries in the "chalk" or "white spot" stage, with initial caries;
- caries of dentin;
- caries of cement;
- suspended caries;
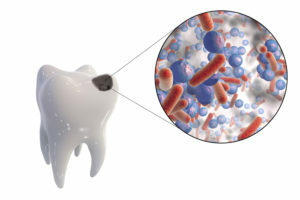
- odontoclase, which includes children's melasma and melanodontoclase;
- caries with pulp outcrop;
- another caries;
- , unspecified caries.
Based on this classification, it can be concluded that odontoclasia actually refers to carious lesions of the teeth and has its own varieties. This disease differs aetiological focus, but the mechanism of development is similar to that of other types of caries. In general, the origin of odontoclasis has been little studied and is of great interest for doctors and scientists.
Diagnosis and treatment
The carious defect in odontoclasis is localized on the vestibular( labial) surfaces of incisors and canines. The short-term nature of pain is a differential sign of a carious lesion of the tooth tissues, but with a high pain threshold of the patient or an early stage of the pathology, pain may be absent.
In addition to subjective pain, the appearance of a pathology may be indicated by a visually distinct change in enamel. With rapid focal demineralization, the defect has a whitish hue, the surface of the enamel loses its luster. The white spot when viewed differs in texture from the healthy enamel.
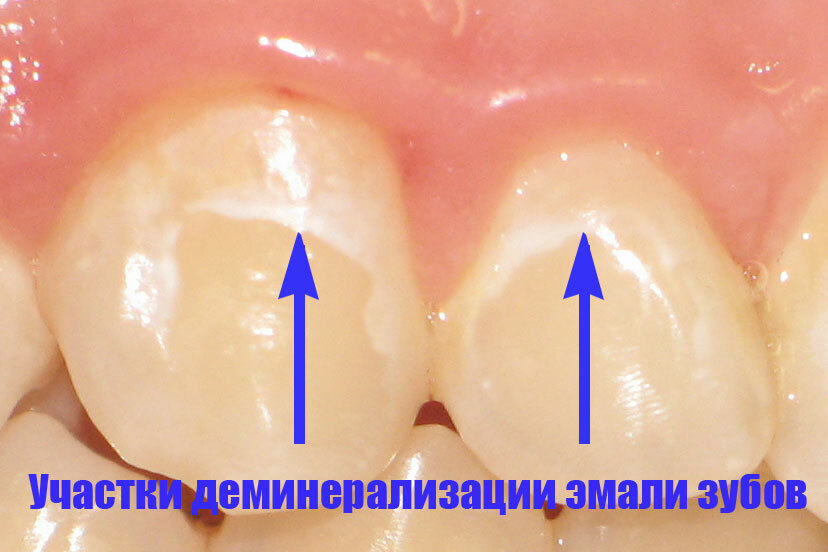
In addition, the vital staining method is used to detect the initial caries. Caries in the stain stage is differentiated from fluorosis and enamel hypoplasia. Slow demineralization is characterized by a brown defect.
At later stages, a carious cavity is visible on the enamel surface, which is determined by sounding.
Treatment of odontoclasis, as well as another variety of caries, consists in excision of affected tissues and filling the formed cavity with filling material.
Sometimes carious lesions of teeth indicate a serious violation of mineral metabolism in the body, since the main component of hard tissues are crystals of hydroxyapatite, which contain calcium and phosphorus.
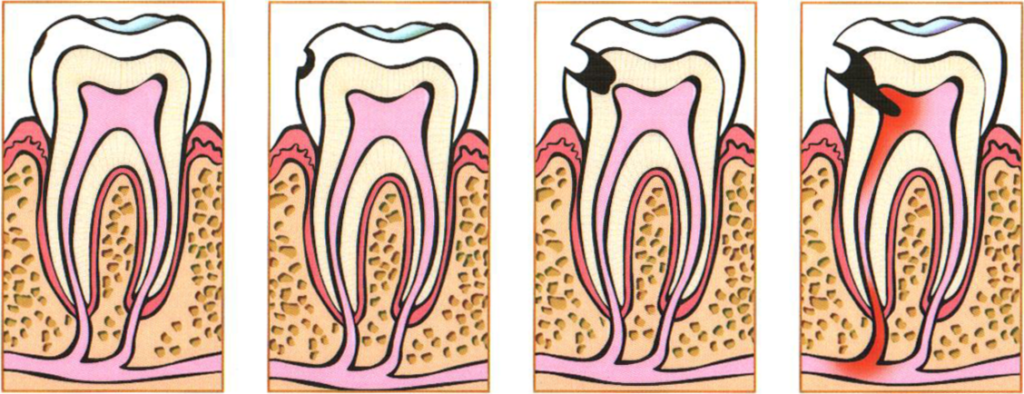
In this case, the patient is required to consult a specialist and prescribe drugs-regulators of phosphoric-calcium metabolism.
The price for treatment of odontoclasis in clinics is 3000 rubles on average. The cost varies depending on the location of the defect according to the classification of Black, the number of affected teeth, the features of the pathology.
Children's melanodentium
Allocate children's melanodendency - a kind of odontoclase. This is a pathological resorption of the roots of baby teeth. Normally, the roots of baby teeth dissolve when the time comes for teething permanent teeth.
 Osteoclasts - giant multinucleated cells that destroy roots by dissolving the mineral component - respond to this process. The temporary tooth loosens and falls out. The change of the milk bite to a permanent at the age of 7 starts.
Osteoclasts - giant multinucleated cells that destroy roots by dissolving the mineral component - respond to this process. The temporary tooth loosens and falls out. The change of the milk bite to a permanent at the age of 7 starts.
The premature activity of osteoclasts may become the cause of childhood melanodentia. If the time of falling out of the milk tooth strongly does not correspond to the timing of the eruption of the corresponding molar tooth, this indicates a baby melasma.
Such a pathology can talk about serious endocrine disorders in the body. The child needs consultation of the endocrinologist and the purpose of appropriate treatment. In this situation, the presence of bone loss in the body - osteoporosis.
In addition, the consequence of early tooth loss may be the development of dentoalveolar anomalies:
- bite anomalies;

- changes the location of the teeth;
- incorrect formation of jaw bones.
Preventing the occurrence of melanodentia in children is the regular passage of a medical examination by the mother during pregnancy to detect violations of fetal development.
For any dental problem, do not forget about the three necessary measures:
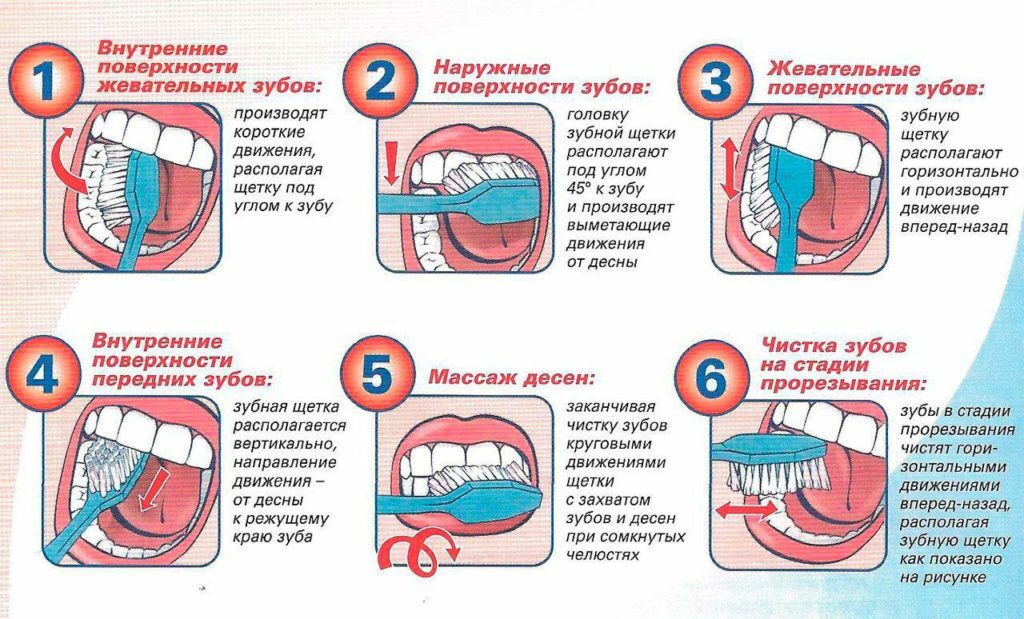
- Careful hygiene of the oral cavity. There are several methods of cleaning teeth, which is easy to teach a child at the dentist or at home. These include, for example, the Leonardo method( from red to white).
- Proper nutrition. Minimizing the consumption of candy, chocolate, baking and other products containing easily fermentable carbohydrates.
- Visit to the dentist at least once every six months.
Odontoclasia and children's melanodentia are varieties of carious lesions of hard tooth tissues. The reasons for the development of odontoclasis and children's melanodentia have not been fully investigated and represent a mystery for dental science.
It is likely that this phenomenon has an origin that has not yet been covered in the literature. The scientific path in this area is open to young scientists who want to shed light on an unexplored dental problem.
Prevention of
It is always better to prevent the disease than to treat it in the future. The basis of dental health is the careful oral hygiene. Brush your teeth two to three times a day for 3 minutes, following the technique of proper cleaning. One of the universal methods - the standard method of cleaning teeth by GN Pakhomov.
The second component of the prevention of carious lesions is a reduction in the intake of carbohydrate foods containing easily fermentable carbohydrates.
Such products include:
- baking;
- chocolate;
- candy;
- chips.
Plaque bacteria break down glucose and sucrose of carbohydrates to organic acids, which cause demineralization of the teeth.
Getting rid of bad habits - smoking, consuming large quantities of coffee and tea - will be a help on the way to healthy teeth.
Prevention of odontoclasia also includes a regular examination with a therapist, endocrinologist and other specialists to detect violations of mineral metabolism in the body. This pathology can be a consequence of the imperfect genesis of dental tissues in the prenatal period, so a woman during pregnancy should consult a dentist and follow all his recommendations.
