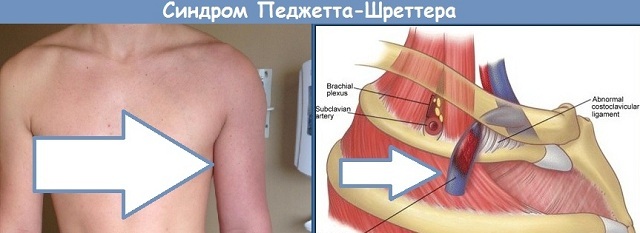
 Paget-Shreter syndrome( venous thrombosis) is a consequence of acute circulatory disorders due to blood clots, the appearance of which can be observed in the deep veins of the shoulder. As a result, the pressure of large veins increases, the supply of small capillaries and vessels is disturbed.
Paget-Shreter syndrome( venous thrombosis) is a consequence of acute circulatory disorders due to blood clots, the appearance of which can be observed in the deep veins of the shoulder. As a result, the pressure of large veins increases, the supply of small capillaries and vessels is disturbed.
Basically, acute thrombosis of the deep veins of the shoulder appears in young people who are exposed to significant physical exertion.
In the risk group are athletes with developed muscles, in which physical exertion falls on any hand. But thrombosis can appear after a long push on the subclavian vein in an uncomfortable position with a hand tucked behind the head.
Pathology was named after a physician who first identified it, as a syndrome evolving from excessive physical effort.
The disease can be acute and chronic. Acute illness means mild, moderate and severe forms, which during the study are detected by venous pressure in mm of water. Art.
In the early days of the disease, there is an increased pressure, which gradually decreases. When the disease passes into the acute form, there is no hypertension with a calm position of the limb, its increase occurs with moderate physical exertion.
Etiology and causes of pathology
High number of causes of acute form of pathology, depending on the provoking factor depends on the choice of treatment and prognosis. There are primary and secondary thrombosis of the deep veins of the shoulder. 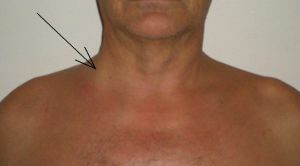
The primary form of the syndrome is associated with the appearance of compressed veins, and the secondary forms due to many etiological factors, including damage to the veins by the installation of a central catheter.
Also pathology develops when the collarbone is injured, with an incorrectly formed bone callus. The appearance of thrombosis affects the level of clotting and some hereditary diseases. Pathophysiological features include slowed-up local blood flow in the vein.
Often there is a violation of the vein in the right shoulder due to high loads on this limb.
Hypertension in the veins of the shoulder is especially pronounced in the early stages of the development of pathology, it gradually decreases with the development of collateral blood outflow, the recanalization of the affected site of the vein.
In a chronic stage in a patient's calm position, the hypertension of the veins is moderately pronounced, but with insufficient muscle strain, insufficient blood outflow is clearly indicated.
Symptoms of the disease
In the clinic of acute form Paget's syndrome, the main symptoms are puffiness of the affected area and the upper zone of the chest. It is rare to find thrombosis, common on the forearm zones.
If you press a finger on the swelling does not appear a fossa( as a result of the expansion of lymphatic and venous vessels, where the fluid flows into the subcutaneous tissue from the vascular bed).In this case, patients complain of a feeling of bursting, tension, weakness and rapid fatigue in the limb.
Another sign of the disease is the subcutaneous enlargement of the brachial veins and vessels in the anterior thoracic region. Such symptomatology of 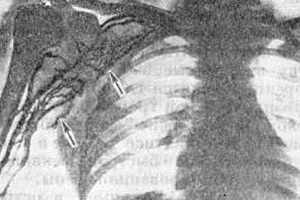 is revealed in a chronic stage. In acute form, subcutaneous vasodilation may be absent or mild.
is revealed in a chronic stage. In acute form, subcutaneous vasodilation may be absent or mild.
Patients note the severity, burning, cooling and flailing of the limb. Sometimes there is cyanosis of the skin.
In comparison with thrombosis of the lower extremities, the symptoms of shoulder pathology are associated not with reflux, but with irregular venous permeability.
It is often possible to detect the appearance of deep vein thrombosis of the shoulder without conducting an examination of the severe symptoms:
- with an intensified pattern of veins whose boundaries can correspond to the spread of edema;
- to constant pains that become pronounced, pulsating and bursting;
- soft tissue edemas;
- appearance of a dense, glossy and tensed shoulder surface.
Diagnostic methods and criteria
Duplex scanning is primarily used for diagnostic research, which, in comparison with phlebography, is characterized by high specificity and sensitivity.
For the detection of deep vein thrombosis, the following methods are used:
- magnetic resonance angiography;
- computed tomography;
- phlebography( to detect the development of thrombosis, the development of collateral circulation).
In addition, the doctor may prescribe dopplerography, X-ray of the shoulder zone, ultrasound of deep veins, etc.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Basically, with deep vein thrombosis of the shoulder, conservative treatment is chosen. In the absence of timely treatment in a few weeks, the resulting thrombus begins to recanalize( dissolve).
The main objectives of conservative therapy is the attachment of a thrombus to the wall, the stopping of blood clots, the cessation of inflammation and spasm, the effect on tissue metabolism and microcirculation.
Treatment of Paget's syndrome is not different from the treatment of thrombi of the lower extremities, since there is no complication of thrombo-embolism. Due to the developed venous network, rapid blood flow compensation occurs and less intensive therapy is prescribed.
If necessary, a strict bed rest is established, the arm should be in a vertical position at rest.
The following drugs are used during treatment:
- Sometimes anticoagulants are prescribed, effective of which are direct-acting drugs. The choice of the dose of Heparin is determined in the calculation of its relationship with plasma proteins. Its action is strengthened together with Fibrinolysin in the ratio
 10/20 thousand units. Heparinotherapy is carried out 3-5 days based on the severity and prevalence of thrombosis.
10/20 thousand units. Heparinotherapy is carried out 3-5 days based on the severity and prevalence of thrombosis. - At the initial stage of treatment flavonoids ( Escuzan, Glivenol, Venoruton, Troxevasinum and Detralex) are prescribed, the action of which is extended to the metabolism of the venous wall. They have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Myotropic antispasmodics and substances that normalize and improve blood flow ( Trental, Xanthinal nicotinate).They are injected intramuscularly and taken with a cocktail. Parenterally, myotropic antispasmodics( Halidor, Papaverin, No-shpa) can be administered.
- Application of compresses with different preparations ( Heparoid, Heparin ointment, alcohol solution, Troquesvazin ointment containing flavonoids) and leeches.
In the absence of contraindications, physiotherapeutic measures( iontophoresis of novocain, heparin, aspirin or trypsin) are used. Initially, it is required to bandage the limb( in the absence of total thrombus formation).
Based on statistical studies, recurrences of the disease can be observed, so antihistamines are prescribed for prophylaxis to patients, regular therapy with drugs is conducted.
Surgical intervention is prescribed for severe pain in combination with severe pathologies of venous outflow. The operation is performed to normalize the blood flow in the deep veins of the shoulder.
 In the first stages, thrombectomy is performed, in chronic stages, a reconstructive intervention is prescribed( with segmental occlusion of the veins with an outflow disturbance).Indications for thrombectomy are signs of gangrene and hemodynamic disorders. The method developed by Professor Saveliev is considered to be the best option, where cuts are made over the sternoclavicular joint with the revision of the vein.
In the first stages, thrombectomy is performed, in chronic stages, a reconstructive intervention is prescribed( with segmental occlusion of the veins with an outflow disturbance).Indications for thrombectomy are signs of gangrene and hemodynamic disorders. The method developed by Professor Saveliev is considered to be the best option, where cuts are made over the sternoclavicular joint with the revision of the vein.
Vascular endoprosthetics and angioplasty can be performed. To eliminate the compression, simultaneous intervention on the tendons, bones and muscles is carried out.
In the treatment of the chronic stage of the disease, surgical procedures are used, creating additional ways for the outflow of blood from the upper limbs.
These methods include anastomosing. For shunts, transplants made from the saphenous vein on the thigh are used.
To eliminate the factors of development of pathology, the rib-diaphragmatic ligament is dissected, phlebolysis is performed, extravasal formations and cervical rib are removed.
In the presence of bluish or redness, severe pain, heat and swelling of the shoulder, urgent therapy is recommended. Otherwise, pulmonary embolism may appear. One of the complications of acute thrombosis is the pathology of chest expiration.
Timely detection and properly selected treatment for the elimination of Paget-Shreter syndrome often lead to positive results. In the absence of a positive effect from drug therapy or in complex forms, an operation can be performed to increase venous outflow.
