 To understand what should be the complex and effective prevention of periodontitis, you need to have an idea of what periodontal is and why its diseases develop.
To understand what should be the complex and effective prevention of periodontitis, you need to have an idea of what periodontal is and why its diseases develop.
In contrast to periodontitis - detachment from the necks and roots of the teeth of the gingival tissues, due to their atrophy, periodontitis is a disease of an aggressive-inflammatory nature, leading to rapid destruction of periodontal structures.
While periodontal disease is a slow process and therefore not so destructive, periodontitis is a dangerous disease, fraught with rapid development of rapid loss of teeth.
Since the incompleteness of the chewing apparatus leads to the development of a chronic disorder in the process of assimilation of energy and substances for body building, the prevention of the appearance and development of periodontitis is one of the main tasks of dentistry, which serves the purpose of preserving and protecting human life.
Contents
- About the causes: what contributes to the development of the disease
- About nutrition rules to reduce the risks
- Three stages of preventive measures
- Armor is strong - the primary measures
- "Exit in the same place as the entrance" or about the methods of secondary prevention
- "Not everything is gone", or tertiary measures
- Features of prevention in childhood
About the causes: what contributes to the development of the disease
Because the "gates" through which the life of teeth and gums enters the periodontitis, are periodontal, or tooth-gumpockets, 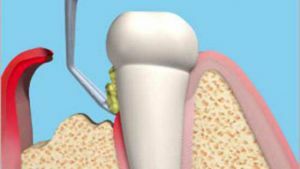 special attention should be given to them. More precisely, their health.
special attention should be given to them. More precisely, their health.
For penetration of infection deep into the periodontium leads to the beginning of its destruction - chronic inflammation at the beginning of the disease leads in the middle of the process to a rapid weakening of the connection of teeth with gums and loss of teeth in its finale.
Therefore, in order to keep dentogingival pockets and gums in a proper state, one should at all avoid the causes of their mechanical damage:
- by rough or hastily eaten food;
- objects, because of the habit, clamped between the teeth during the performance of work or leisure( nails, matches, etc.).
Neglect of cleaning teeth during and after food, as well as the difficulty of cleaning due to incorrect positions of the teeth - another reason for the appearance of periodontitis.
In addition to mechanical damage to gingival structures, there is a danger of their inhibition by physical and chemical methods.
The first is the effect of extremely low or high temperature, or sharply contrasting changes in it, to the second - a blood circulation disorder in the gums using substances that cause their ischemia.
These include nicotine cigarettes, which has a direct vasoconstrictor effect, alcohol and other poisons that enter the oral cavity during breathing or are secreted by its glands during their work from the blood flowing through them.
In the course of chronic diseases, many under-oxidized substances with toxic properties are also formed, negatively affecting the structure of the gums.
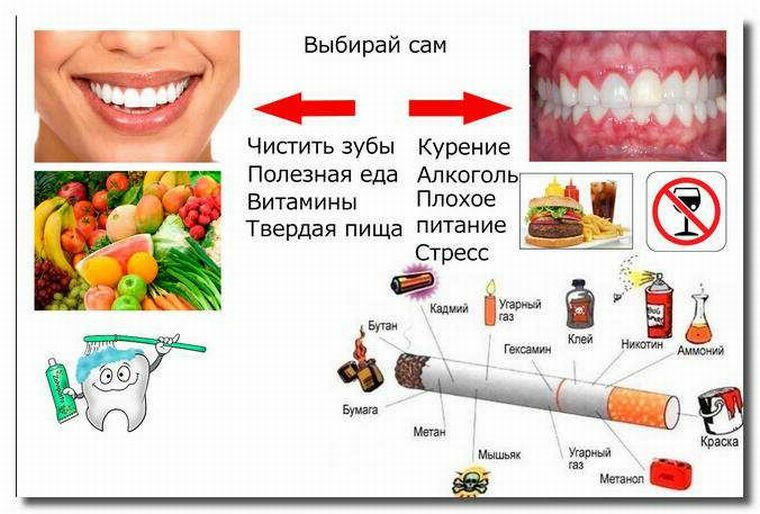
About nutrition rules to reduce the risks of
Both children and adults should be aware that when eating hurriedly, hurriedly, without paying attention to the quality of food and its properties, not only is jammed food remains between the teeth, but also getting them intospace between the gum and crowns.
If systematic neglect of food safety measures and subsequent thorough cleaning of these formations, due to the constant presence in the periodontal pockets of food residues in them, various kinds of microbes will rapidly multiply.
Microbes excrete acids, which enamel destroy slowly and gradually, cement and dentin are much more quickly.
To the destruction of gingival structures lead acid, not only released by microbes, but also in excess contained in the most eaten food, especially in carbohydrate. Therefore, the excess in the diet of sweet, like flour, in turn leads to problems in the oral cavity.
 Fans of gnawing nuts and other solid foods should also refrain from such "heroism", because overstrain of the ligamentous apparatus of teeth also leads to their loss of balance, loosening and subsequent loss.
Fans of gnawing nuts and other solid foods should also refrain from such "heroism", because overstrain of the ligamentous apparatus of teeth also leads to their loss of balance, loosening and subsequent loss.
Separate censure deserves a habit of abrupt temperature changes in the oral cavity during food intake, when the taste of ice-cold ice cream follows hot coffee and the like. Because in addition to the formation of microcracks on the enamel, such experiments lead to uneven blood supply to the gingival structures - gum ischemia and other undesirable results.
Three stages of preventive measures
The measures necessary to avoid periodontitis and other periodontal diseases can be conditionally divided into:
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary.
Each stage of prevention implies the implementation of a set of measures at a certain stage of a person's life.
If the first stage of prevention is the prevention of the onset of the disease, the second is the treatment of the emerging pathology of the periodontal disease and prevention of recurrence of the disease, the third is the restoration of the health of the dentofacial structures damaged by the periodontitis itself and the factors provoked by it, that is, the treatment of the consequences of the disease, inincluding remote ones.
Armor is strong - primary measures
Prevention measures to prevent the very possibility of periodontitis include the use of various devices and methods for cleaning teeth and the oral cavity in general.
But the first of these is the education of children for a food culture, but for adults who have not yet "met" with dental and gum problems, this is retraining, with the inculcation of new eating habits. Eating should be a solemn ritual, conducted in silence and focusing attention on the food.
 When solid food or foreign particles enter it between the teeth or under the edge of the gum, they must be removed immediately, and all remains of food after it is taken are carefully removed with a brush, dental floss and the like.
When solid food or foreign particles enter it between the teeth or under the edge of the gum, they must be removed immediately, and all remains of food after it is taken are carefully removed with a brush, dental floss and the like.
Thorough mouth rinsing after eating should become a habit since childhood. This can be done with simple water, a weak solution of soda or a special rinse aid.
If you can not use a brush or rinse aid, you can neutralize the effect of acids on the enamel by chewing gum without sugar.
The indicator of correctly chosen tactics is the absence of bad breath and a noticeable smoothness of the surface of the enamel.
If it is not possible to clean the enamel completely, and when roughness appears on it, you should resort to professional cleaning, which the dentist will perform.
The congestion and other changes in the bite anomaly should also be timely eliminated using the orthodontic methods.
From the habit of grasping between the teeth objects that are not related to food, also should wean the child in childhood.
"Exit in the same place as the entrance", or about the methods of secondary prevention
 Secondary prevention includes professional treatment of the already existing pathology of periodontal disease and prevention of recurrence of the disease.
Secondary prevention includes professional treatment of the already existing pathology of periodontal disease and prevention of recurrence of the disease.
"Sealing" the entrance gate of infection - sealing various methods of weaknesses in the teeth and gums - the final stage of treatment. But it can become both initial and intermediate in the process of therapy, depending on the methods used in this period.
Treatment includes:
- release of gingival structures from both the infection itself and the products of its vital activity;
- strengthening of ligamentous apparatus and compaction of mucous gums;
- general measures of influence on the body, including its vitaminization and mineralization.
After the completion of professional dental orthopedic treatment it is acceptable to use the secrets of traditional medicine to maintain the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
"Not everything is gone", or about tertiary measures
Tertiary prevention means the restoration of the proper state of the maxillofacial connection after treatment of the periodontitis itself and the elimination of the factors provoked by it.
It implies a deep, cardinal intervention involving the entire arsenal of dental and orthodontic means, including: 
- moving or removing individual teeth and their groups;
- use, if necessary, bone grafting to fill bone deficit or osteoplasty to fill the resulting pathological bone cavity.
In essence, this is the preservation of the newly created tooth profile, in which the former natural structures remained very few.
A patient who has undergone such a full-scale treatment should re-learn all the basics of oral hygiene to prevent a possible repetition of very unpleasant experiences.
Features of prophylaxis in childhood
Prevention of development of periodontitis in children differs from that for adults by the possibility of developing hygiene skills from childhood, and in an easily perceived game form.
To the period of changing teeth, when the horizon of the child is significantly expanding, his reluctance to specifically pay time to clean teeth is understandable.
Therefore, it is desirable to turn this process for him into an exciting adventure, telling the kid about the complex life of the tooth, the dangers that lie in the interdental spaces and spaces under the edge of the gums, as well as the immense gratitude of the rescued tooth of his  to the small master.
to the small master.
The habit is consciously, giving the maximum attention to food, and not twisting your head in the sides, you should also bring up from the early years. It should be explained to the child that food does not appear out of nowhere - it must be cooked and lovingly spread out over plates.
To whom should I express my gratitude? And what is the best way to do this, if you do not taste the taste of the food you eat?
Having acquired the skills of correct behavior at the table and dental care, the child, by the age of puberty, when the processes of both growth and tooth decay occur very rapidly, will be ready for the difficult tests of the growing period, which does not cloud the loss of teeth.
