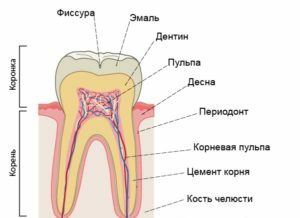
 The structure of the baby teeth is almost the same as the structure of the permanent teeth. One of the important elements is pulp - a cluster of nerve and vascular fibers.
The structure of the baby teeth is almost the same as the structure of the permanent teeth. One of the important elements is pulp - a cluster of nerve and vascular fibers.
When destroying hard tooth tissues, pathogenic microorganisms present in carious contents can penetrate into the pulp, provoking the development of inflammation in it.
Contents
- Features of the development of the disorder
- Forms of the disease and its symptoms
- Features of the acute form of the disease
- Features of the chronic form of the disorder
- Treatment methods - package of measures
- Biological method
- Partial or complete removal of the pulp
- Devital - complete removal of the pulp
- Possible mistakes in the treatment of
- prepare a child
Features of the development of a violation
 Milk teeth are much more likely to develop pulpitis. This feature is due to a more thin layer of enamel, a small amount of dentin and a wide cavity in which the pulp is placed. One contributing factor is also insufficient immune protection.
Milk teeth are much more likely to develop pulpitis. This feature is due to a more thin layer of enamel, a small amount of dentin and a wide cavity in which the pulp is placed. One contributing factor is also insufficient immune protection.
The destruction of hard tissues of the tooth entails the rapid spread of the inflammatory process along the wide dentinal tubules. At the same time, a sufficient width of the tubules ensures an effective outflow of liquid from the pulp, therefore, for a long period of time the process can not externally manifest itself.
One of the characteristic symptoms of pulpitis in children is an unpleasant painful sensation that occurs when chewing or tapping on the tooth due to the shaking of the inflamed pulp.
Forms of the disease and its symptoms
Pulpitis can be characterized by acute or chronic course. The acute form can quickly change to chronic absolutely imperceptibly for the baby and his parents. Prevent critical conditions help regular preventive examinations.
Features of the acute form of the disease
Acute pulpitis is divided into partial and total. Diagnosis of partial pulpitis can be from periodically arising pain without the obvious influence of an external stimulus. Pain can intensify at night. For this stage, the following changes in the state of the tooth and the body as a whole are characteristic:
-

In the photo, acute
infantile pulpitis of the infant teeth is rapid leakage with lesions not only of the coronary but also of the root pulp;
- development of inflammation in periodontitis;
- signs of intoxication in the form of fever, headache, high ESR in a clinical blood test.
The total pulpitis can be determined by the appearance of prolonged intense pain, while the place of localization of pain sensations is not accurately determined.
Features of chronic form of disorder
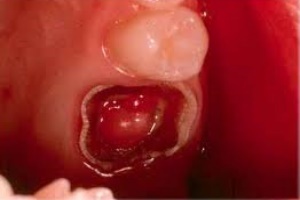
May occur both in the background of acute pulpitis, and as a primary form of the disease, leaking in the form of fibrous or gangrenous inflammation of the pulp. In the first case, during a preventive examination, a carious cavity of a small size is found, in which softened dentin is present. After exposure to heat or cold, the pain quickly fades.
For gangrenous chronic pulpitis is characterized by the absence of pain from hot, the presence of a sharp putrefactive smell and a feeling of "raspiraniya" tooth.
At this stage, signs of periodontal inflammation, swelling may be attached. Probing the carious cavity causes painful sensations.
Treatment methods - a set of measures
When pulping dairy teeth, first of all, you need to eliminate the inflammatory process and prevent a complication in the form of periodontal damage, which can cause the formation of permanent teeth. There are 3 main methods in total.
Biological method
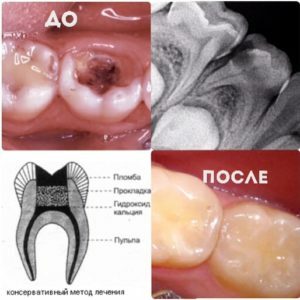 Refers to conservative therapy that does not require surgical procedures. At the first stage, the inflamed cavity is opened, after which its bottom and pulp are tightly closed with a mixture obtained from Shostakovskiy's balm and artificial dentine( in the form of a powder), or they deposit calmetin.
Refers to conservative therapy that does not require surgical procedures. At the first stage, the inflamed cavity is opened, after which its bottom and pulp are tightly closed with a mixture obtained from Shostakovskiy's balm and artificial dentine( in the form of a powder), or they deposit calmetin.
When the material dries, fillings are made using phosphate cement or fluorine-cement pads.
The attitude towards this procedure, despite the creation of the most favorable conditions for the formation of the tips of the roots of the teeth, is twofold because of the possibility of complications and delaying treatment with the risk of spreading the inflammatory process to the periodontal tissue and the rudiment of the permanent tooth.
Partial or complete removal of pulp
Distinguish pulpotomy( partial amputation) and pulpectomy of the pulp. In the first case, the operation removes only the coronal part of the pulp, trying to preserve the root component, which is responsible for protecting the periapical tissues( surround the junction of the tooth canal and the hard apex of the tooth) from the penetration of microbes. Sometimes the procedure requires several visits.
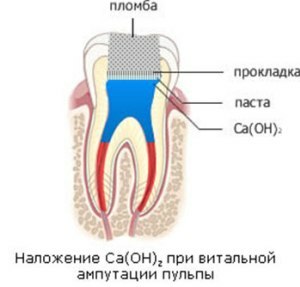 Features of the vital method:
Features of the vital method:
- the need for frequent boron changes when opening the cavity to exclude infection of deep layers of dentin;
- mandatory cleaning of the cavity with an antiseptic;
- the pulp is cut off in the mouth area, then the bleeding stops with adrenaline.
If the bleeding does not stop, diagnose the inflammation transition to the root pulp. In this situation, pulpectomy is performed, completely removing the vascular bundle under anesthesia. It is important not to touch the periodontium.
As a rule, the method is rather long and time consuming, therefore it is extremely rarely used in pediatric dentistry.
Devital - complete removal of the pulp
To eliminate the pulpitis of the baby teeth, the most commonly used is the devital amputation, which is indicated by the inflammation in the common acute common or fibrous chronic form, the lesion by deep caries of the milk molar.
Contraindications include exacerbation of chronic pulpitis and its passage into the gangrenous form.
In general, this method can be used for any variant of inflammation development, obtaining the most effective result.
 Arsenic paste acts as a devitalizing( euthanizing tissue) agent. For the procedure at the first visit, an anesthetic with a 3% solution of dicaine or anesthesin powder is used.
Arsenic paste acts as a devitalizing( euthanizing tissue) agent. For the procedure at the first visit, an anesthetic with a 3% solution of dicaine or anesthesin powder is used.
For the treatment of chronic pulpitis in fibrous form with unformed roots and in case of gangrenous leakage, arsenic is replaced with a tampon with a mixture of formalin and phenol, to which an anesthetic is added.
The duration of the medicine depends on the number of roots in the milk tooth and is a day or two( for teeth with two roots).When using special pastes, the period of exposure can be increased up to 7-14 days.
The pulp is removed during a second visit to the doctor. Immediately after removal, a tampon moistened with resorcinol-formalin liquid is placed in the dental cavity for a couple of days.
As a result, the pulp is saturated with a composition of 2-4 mm and the healthy state of the growth zone of the forming tooth is maintained, contributing to the normal full development of the roots of dairy and successive teeth. Treatment ends at the third visit, applying a resorcinol-formalin paste to the mouth, setting the gasket and sealing the tooth.

Possible errors in the treatment of
Failure to adhere to the rules or poor-quality treatment of pulpitis of the baby teeth can lead to the development of purulent periostitis, periodontitis and acute poliomyelitis. The following errors can be distinguished:
-
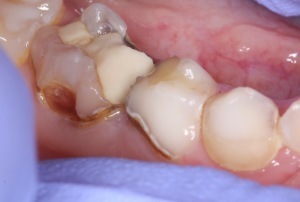 Incorrect evaluation of the pulp condition and consequent incomplete removal of the affected area, fraught with a new exacerbation.
Incorrect evaluation of the pulp condition and consequent incomplete removal of the affected area, fraught with a new exacerbation. - If a temporary bandage with arsenic during the procedure of devital extirpation( complete removal of the pulp) is not applied tightly enough, seepage of the agent can lead to necrosis of the tissues of the cheek, tongue and mucous gum. Dangerous and overdose of arsenic , leading to the development of acute arsenic periodontitis, which requires a long recovery. If periodontitis is acutely manifested during treatment, after opening the cavity and outflow of inflammatory exudate, prescribe sulfanilamides, calcium gluconate and the use of large amounts of liquid.
-
 Poor tightness of the dressing embedded in the carious cavity results in a burn of the mucous membrane of the gums with toxic arsenious acid;
Poor tightness of the dressing embedded in the carious cavity results in a burn of the mucous membrane of the gums with toxic arsenious acid; - Periodontal injury by the root needle , used to clean channels, can also lead to the development of periodontitis.
Sometimes pain can occur as a result of the use of resorcinol-formalin mixture. The child can refuse food because of soreness at nipping caused by periodontal irritation.
For normalization of the condition and effective treatment of pulpitis, therapy should be suspended for some time.
How to prepare a child
 Each child reacts to pain in his own way. The same goes for visits to the dentist. Both physicians and parents should make every effort to minimize the negative impact on the psyche and the development of fear of dentists.
Each child reacts to pain in his own way. The same goes for visits to the dentist. Both physicians and parents should make every effort to minimize the negative impact on the psyche and the development of fear of dentists.
To do this, you need to discuss with the baby ahead of time the upcoming visit, emphasizing that the treatment procedure will be carried out as carefully and painlessly as possible, and mom or dad will always be there.
Positive attitude of the child depends on the approach of the children's dentist. If the doctor sees that the baby is overly stressed, can not relax and is afraid of treatment, he can recommend the use of general anesthesia.
First the child will be given a drink with dissolved water in her, after which the already falling asleep baby will be injected with a means for general anesthesia. As a result, the treatment will pass unnoticed and leave no negative impressions.
 Quite often, children's dentists use such tranquilizers as Mebikar or Sibazon. The choice of anesthetic drug is carried out individually and depends on how much the child is physically developed, whether he has allergic reactions, how emotional he is.
Quite often, children's dentists use such tranquilizers as Mebikar or Sibazon. The choice of anesthetic drug is carried out individually and depends on how much the child is physically developed, whether he has allergic reactions, how emotional he is.
It should be remembered that the pulpitis of the baby teeth is a rather insidious pathology due to for the most part the latent flow of the inflammatory destructive process.
Therefore, it is worth listening to the child, reacting even to the slightest discomfort that occurs when eating or drinking cold and hot drinks. And, of course, in no case should the situation be allowed to run its course.
The causes of the development of pulpitis of baby teeth and possible methods of treatment will tell the children's dentist.
Timely appeal to the dentist will be the key to rapid successful treatment. It is on the treatment to adjust the baby, since the radical method in the form of removing a sick milk tooth in pediatric dentistry is used only in extreme cases, so as not to disrupt the formation of the dentition and bite.
