Hormones are one of the regulators of many reactions in the female body. The change in their composition determines the state of health, biological possibilities and even appearance.
Hormones in menopause acquire such a quantitative presence, which causes a decrease and the gradual disappearance of reproductive abilities. This is expressed by the cessation of menstruation and many other obvious symptoms.
More about climacteric changes
Hormones of  largely determine the sexual development of women. From their sufficient number depends the growth of the breast, the correct formation of reproductive organs in adolescence. First of all, this affects the sex hormones. They also construct cyclical changes in the reproductive system, which are monthly manifested by menstruation, accompanying signs. The main role in this belongs to follicle-stimulating, luteinizing substances, estrogens and progesterone.
largely determine the sexual development of women. From their sufficient number depends the growth of the breast, the correct formation of reproductive organs in adolescence. First of all, this affects the sex hormones. They also construct cyclical changes in the reproductive system, which are monthly manifested by menstruation, accompanying signs. The main role in this belongs to follicle-stimulating, luteinizing substances, estrogens and progesterone.
Hormonal changes in menopause are such that the number of these components gradually decreases. The process begins at the age of 35 when the ovaries no longer have such a supply of germ cells as in earlier years. The activity of these organs slows down, which is accompanied by a decrease in the production of estrogens.
Hormones are bound together in the most intimate way, the deficiency of one substance entails a quantitative fall of the other. Menstruation comes less often, and more often without the formation of an egg. Its absence provokes a decrease in progesterone responsible for the size of the uterine lining. The endometrium is gradually thinner.

Menstruations no longer come, as there are no appropriate conditions for tissue renewal. Internal reproductive organs decrease in size. Ovaries in the last stage of menopause completely stop the production of hormones.
The body's response to the change in the balance of hormones
An important process in the body is the metabolism, which is also regulated by hormones. It affects different areas, but is generally aimed at feeding nutrients to different tissues. This is necessary for normal health.
Hormones with menopause have such a composition, which adversely affects the metabolic processes. In different women, this causes similar reactions, nevertheless manifested in some weakly, others more pronounced:
-

Pain in the heart as a consequence of changes in the balance of hormones in menopause
Reduction in the concentration of sex hormones is important not only for the childbearing system, but affects the work of the brain. The pituitary and hypothalamus, which are its parts, also produce these substances, but now their work is different. The circulation of blood through the body changes, from which there are tides to the upper body, dizziness, nausea, sweating, blood pressure jumps;
- Mineral exchange changes, and as a result of this, a different, lower density of bones and teeth becomes;
- Female sex hormones with menopause can change the functioning of the thyroid gland. It begins to actively and in large quantities produce thyroxine, which increases the heart rate, increases anxiety;
- Failures in the functioning of the adrenal glands due to a drop in the level of female hormones provoke an increase in pressure, pain in the heart;
- Hormones that decrease with menopause affect not the best way for CNS work. Negative manifestations caused by this, hypertrophied emotions, that is, fears, outbursts of irritability, depression, uncaused tears. They do not have any one permanent character, but replace each other.
The level of hormones in the period of "women's autumn"
Some people have to take special medications in order to survive this hormonal reorganization. Others cope themselves. But in order to know how best to do, it is necessary to track the level of substances with the help of analyzes.
Which hormones in menopause have the greatest impact on well-being? First of all, it is FSH, LH and estrogens. Their number and find out if the problems accompanying menopause.
FSG
Follicle-stimulating hormone is a substance by which the approach of menopause can be traced. In young women, its values vary throughout the cycle. The closer to the time of menopause, the higher FSH in the first phase of the menstrual period, when it is at its peak and has the greatest impact on the reproductive system.
This mechanism is provided by natural features of the pituitary-ovary ligament. When the resources of paired organs come to a minimum, they begin to produce estrogen more economically. The pituitary in response to this intensifies activity, giving out more FSH.This is what happens during premenopause, about 40-45 years.
And if the young person has an optimal value of 10 mIU / ml, at a later age the hormone fsg normal in women with menopause is 30-40 mIU / ml. In the future, its level may rise. The longer the interval from the last menstruation, the more likely that FSH will be up to 135 mIU / L.
When it changes due to hormonal failure, the difference in values is not so great. But if a year ago FSG was 15, and now 30, the climax is on the way.
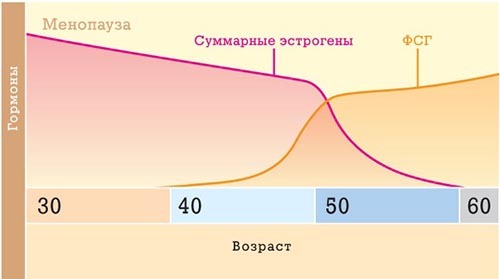
The level of the hormone FSH in the body of a woman with the onset of menopause
Estrogens in the period of menopause
This is perhaps the main group of hormones, the influence of which on the female body is especially great. They ensure the development of the reproductive system in adolescents, the maintenance of its functions and the cycle of renewal in young women, the completeness of metabolic reactions. Most of the manifestations of older age are associated with a decrease in their production.
Estrogens are female hormones, symptoms of deficiency in menopause are as follows:
- Skin becomes drier, thinner, wrinkled. Changes are noticeable externally, the epidermis is peeling, it is easy to damage. The number of moles grows, papillomas in a short time;
- Pressure acquires that high, then too low values. On this soil there are headaches, spasms of blood vessels, leading to coordination disorders, nausea. Periodically, blood supply to the head, neck and chest increases, leading to reddening of the skin, hot flashes, sweating, especially at night;
- The brain does not work so productively, fatigue occurs faster, memory is reduced, it is more difficult to concentrate;
- Bones are made less durable due to lack of calcium. Estrogen deficiency leads to its rapid elimination from the body and poor digestion;
- Heart rhythm is broken in the direction of acceleration.
Estradiol: how does its deficiency respond?
Estradiol in menopause provokes most of the unfavorable symptoms. The lower its level, the more pronounced their manifestations. Most of it is produced by the ovaries and secreted follicles, as well as adipose tissue. With the extinction of their functions, this substance is produced less and less. In some women, the body tries to resist this by increasing the fatty layer. It is at the age of menopause that many learn what excess weight is. Other signs of its decline:
-
The structure of the hormone estradiol in the body of a woman
Dryness and discomfort in the vagina. In sufficient quantity, estradiol regulates the production of mucus by the cervix and its walls;
- Flabbiness of mammary glands. The hormone makes them round and elastic, the norm of estradiol in menopause is such that gradually the chest loses these qualities;
- Decreased libido. Estradiol maintains an attraction for a man at a sufficient level, his fall accordingly affects the sexual appetite;
- The level of cholesterol in the blood rises, and it acquires an increased viscosity;
- Liquid is quickly eliminated from the body. This is manifested by the increased need to urinate and increased activity of the sweat glands;
- Regeneration of tissues slows down. Since many metabolic processes largely regulate estradiol, the norm in women with menopause does not allow it to be done qualitatively as before. Evidence - increased fragility of bones, reduced skin elasticity;
- Emotions go off scale. Previously high values of the hormone provided a good mood and adequate response to any events. Now it can be unpredictable.
Followers of gynecological health regularly do research on the amount of this substance in the blood. Therefore for them the question is actual: Estradiol at a climacterium - norm or rate, it how much? The admissible values are also quite wide, as in FSH, but they should not rise above 82 pg / ml.
What does the value exceed?
The level of this most active female hormone is important at any age. Deviation of values from the norm in the direction of increase with menopause means the presence of a factor provoking the production of a substance. Elevated estradiol in menopause may indicate the presence of:
- Tumors or ovarian cysts;
- Myoma nodes;
- Hyperfunctions of the thyroid gland;
- Liver diseases;
- Neoplasms in the mammary gland.
Other symptoms are obvious:
- Swelling of the tissues;
- Hair loss;
- Notable weakness;
- Digestive problems;
- Insomnia, irritability;
- Tenderness in the mammary glands;
- Bleeding from the genital tract.
If there are these manifestations, the analysis showed an overestimated level of the hormone, you need to be examined further and find out the reason for this. Climax and the previous couple of years are the most dangerous period in which serious ailments can occur, up to malignant tumors.
It happens that going to the age of premenopause, a woman loses vigilance, pays less attention to protection. Menstruation comes less often, but while they are, pregnancy is not excluded. Many late children were the cause of increased estradiol in their mothers. The indicator grows with pregnancy.
 We recommend reading the article about postmenopause in a woman. You will learn about the causes of the appearance of this condition, its symptoms, the nature of secretions and the appointment of medications to relieve the manifestations of postmenopause.
We recommend reading the article about postmenopause in a woman. You will learn about the causes of the appearance of this condition, its symptoms, the nature of secretions and the appointment of medications to relieve the manifestations of postmenopause.
Low level of hormone
The lower limit of estradiol in menopause is 6-9 pg / ml. Minimal values lead to pronounced negative manifestations of this condition. It is those who have a hormone on the lower border or even less, prescribe substitution therapy.
It can be used in the absence of severe manifestations of menopause to maintain health and improve the appearance, if there are no contraindications. But at low values of estradiol it becomes vital.

If you go on about the natural process, it is easy to acquire diseases not only in the field of gynecology, but also endocrine, cardiovascular, oncological. And the fight against aging in the form of proper nutrition, regime, a combination of relaxation and physical activity, and, of course, constant interaction with medicine will significantly improve the quality of life.
