 Sometimes, in the way of miracles created by modern orthodontics( for example, if you need to regroup teeth for the purpose of bite correction or for some other reason), there is an obstacle in the form of excessive densities of the jaw bones, in such cases, the specialist receives compotectotomy.
Sometimes, in the way of miracles created by modern orthodontics( for example, if you need to regroup teeth for the purpose of bite correction or for some other reason), there is an obstacle in the form of excessive densities of the jaw bones, in such cases, the specialist receives compotectotomy.
This is the name of the surgical method of rarefaction of the structure of the compact zone of the jawbone. Technically, the procedure looks like the destruction of its integrity - the perforation of the jaw bone( drilling in it a number of holes in the staggered order in the zone of the interluneral septums, the tips of the roots and buttresses).
Contents
- Objectives of intervention
- Contraindications and limitations
- Steps for performing the operation
- Rehabilitation period
- About possible complications
Objectives of intervention
If earlier to reduce the density of bone substance and facilitate the process of movement of teeth, the part of the compact( cortical) layer was removed,intervention, the result of which is the development of an inflammatory reaction in the bone in response to its damage.
Partial demineralization and the start of reparative mechanisms facilitate tissue reconstruction under the influence of the pressure of orthodontic devices used in the second stage of the operation. 
Indications for the operation are pronounced deformations of the dentoalveolar system:
- anomalies in the structure of the jaws( microgenia, progeny);
- or prognathic bite with a forward extension of the lower jaw, or retrognatic with the back of the upper or lower jaw;
- open bite.
Contraindications and limitations
Along with indications for intervention, there are contraindications for it, including the presence of disorders:
- blood clotting;
- mental;
- hormonal( of various origins), including diabetes.
Obstacles to the operation are also:
- the presence of an active or chronic infectious process;
- the age of the patient is less than 18 years( due to the incomplete development of jaw bones to this age);
- features of the location of the teeth in the form of a high degree of their crowding( in view of the high probability of damage to the dental roots).
Steps for performing the operation
The objectives of the orthodontic stage of the operation are:
- correction of the anomaly of the location of the teeth;
- recovery of the size and shape of the dentition;
- achievement of adequate contact between the rows;
- ensuring the guaranteed stability of teeth in the newly created position;
- normalization of the processes of chewing, swallowing, speech and breathing.
 But without a preliminary surgical intervention on the upper or lower jaw( proper compactotestomy) they can not be achieved.
But without a preliminary surgical intervention on the upper or lower jaw( proper compactotestomy) they can not be achieved.
In the process of preparation, oral sanitizing measures are carried out, such as professional cleaning of teeth, treatment of carious and removal of non-treatable bad teeth.
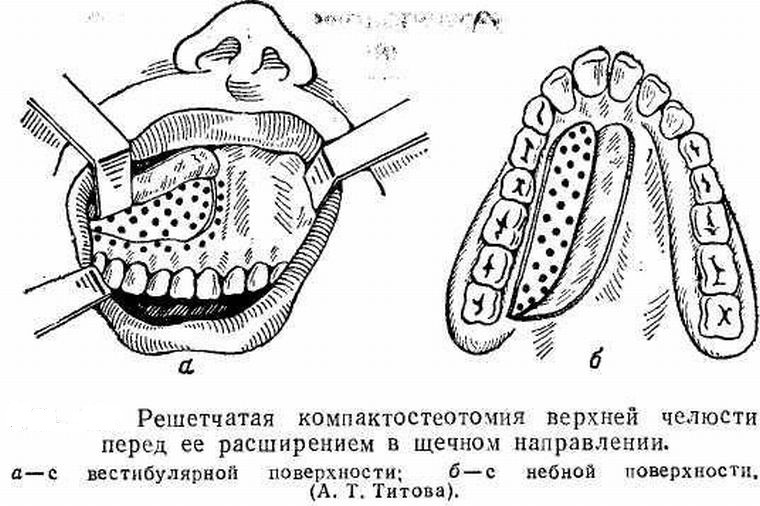
The algorithm for performing latticed compactosteotomy on the upper jaw of Titova includes several stages:
- After an X-ray diagnosis and exclusion of contraindications, anesthesia is performed in a manner appropriate to the case.
- The mucosa is cut through the incision of the gum with the periosteum to the bone between the incisors and the farthest chewing tooth, with a wide exposure of the alveolar process from the vestibular side of the jaw.
- Perforation is performed - boring a number of holes in the outcrop area. They are located "lattice" - in staggered order, with the largest number in the areas of maximum density: in the zone of the pear-shaped aperture, the base of the zygomatic process, with the obligatory involvement of the root zones of the teeth, intended for displacement. The grooves are connected by a common furrow-cut. The resulting wound is sutured with catgut.
- Peel the flap of the mucosa and the periosteum from the side of the oral cavity( in the direction of the central palate) after cutting two to three millimeters below the necks of the teeth and repeat the perforation of the bone of the alveolar and palatine processes with spherical boron.
- Bone wounds are washed with an antiseptic solution.
- After returning to the place of the mucosal-ulterior flap( with the application of seams to fix it), the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution.
- Completes the operation by pressing the tampon impregnated with iodoform solution to the damaged area and applying a protective plate, which is removed 7 days after the operation when removing the joints.
Algorithm of actions for tape compression of the lower jaw in Gavrilov:
- After anesthesia, a cut is made with a scalpel 1-3 cm below the edge of the jaw, exposing the bone from the outer and inner sides and opening the segment from the extreme incisor to the angle of the jaw.
- Perforation of the entire exposed area is carried out with the round boron passing through the entire depth of the compact layer of bone.
- The wound is sealed with suturing, the jaw is fixed with a pressure bandage, which is removed after a day.
Rehabilitation period
Due to the development of the consciously induced inflammatory process in the postoperative period, it is necessary to apply certain measures aimed at limiting it.
The use of:
- antibacterial agents, including antiseptics in the form of rinses;
- anti-edema drugs( diuretics);
- antihistaminic for the purpose of desensitization of the body;
- is a mechanical and chemically gentle diet.
Wearing braces or other orthodontic systems may require a period of 1 to 4 months, and the full period of retention of teeth - from 2 months to 4 years, depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the oral cavity of the patient. The maximum term requires correction options for narrowed dentition.
About possible complications of
Excessive exposure to bone with its perforation can lead to undesirable consequences - more protracted than  is required for treatment, the course of the inflammatory process with further necrosis of individual bone segments due to eating disorders.
is required for treatment, the course of the inflammatory process with further necrosis of individual bone segments due to eating disorders.
In the second retention stage of the operation, the extremely long( more than 2.5 months) effect of the orthodontic device on the "softened" tissue of the alveolar process with a slight degree of mobility of the teeth also supports the inflammation process, resulting in complications in the following:
- bone osteoporosis;
- decrease in the height of the alveolar process( due to the atrophy of its crest) with a decrease in the height of the jaw.
Among other complications, it should be noted the damage to the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw due to the thinness of the spongy layer between the compact layer of bone and the wall of the dental hole, as well as the infection of periodontium due to the loose fit of the interdental papillae, which opens the gate for infection.
Nevertheless, due to the existence of many modifications, this technique can lead to success in the most difficult situations, which require the transfer of significant groups of teeth( together with their cells).
