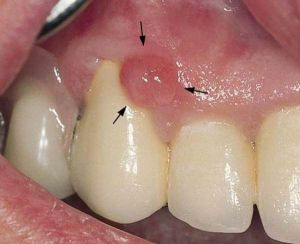
 For the emergence of such a growth on the gums as epulis, serious causes are needed. And in the body they appear in various life situations, giving rise to a tumor structure with rapidly-irresistible and malignant growth, then with a slowly forming body with benign tissue.
For the emergence of such a growth on the gums as epulis, serious causes are needed. And in the body they appear in various life situations, giving rise to a tumor structure with rapidly-irresistible and malignant growth, then with a slowly forming body with benign tissue.
For epulis, also called a superfamily or epulide, is essentially a tumor with an official histological definition: a giant cell granuloma.
Contents
- About
- About
- The causes and symptoms
- Evil VS well: symptomatology difference
- ICD-10 classification
- Features of flow in children and pregnant women
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment of traditional and folk
- About preventive measures
- The causes and symptoms
- About
About the causes of
According to statistics,a neoplasm appears more often.
For women look more important to the appearance and take more resolute measures for the beauty of their smile, hence the more aggressive cleaning of teeth leading to damage to the gums with the deposition of tartar. They are also more susceptible to stresses and hormonal imbalances( during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause).
Often epulis for its occurrence selects a zone of small molars, more often on the lower jaw, because it is in this area that the ducts of the salivary glands open, contributing to the biochemistry of the oral cavity.
The soil for the regeneration of the gingival tissue in the epulis is the presence in the jaw of the tooth with sharp edges injuring the gum and chronic trauma as a result of a defect:
- bite;
- prosthesis;Seals in the root zone.
Clinic and features of the
During a visual examination, the dentist discovers a tumor - a mushroom-like "influx" on the gum with a characteristic leg that, when attached to the 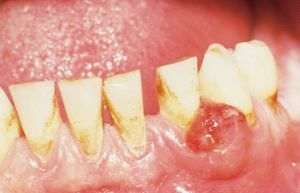 gum, leaves in its tissue, the main body resembling the mushroom cap rises above its surface. The size of education from almost invisible to the eye to three or more centimeters, color - from natural to gum to cherry, brownish-red and cyanotic, with frequent trauma, the surface is ulcerated.
gum, leaves in its tissue, the main body resembling the mushroom cap rises above its surface. The size of education from almost invisible to the eye to three or more centimeters, color - from natural to gum to cherry, brownish-red and cyanotic, with frequent trauma, the surface is ulcerated.
In addition to aesthetic discomfort for the patient, the neoplasm rarely brings him tangible suffering, except for complicated, neglected or malignant cases with more rich symptoms.
Evil VS Well: Symptomatic difference
Malignant process is characterized by rapid growth of the build-up with rapid increase in size, the presence of inflammatory changes in the growth zone( edema, considerable soreness and acute sensitivity, and slight bleeding of the gums), ulceration and cracks with destruction of the root cells andloosening of the involved teeth, as well as changing their position in the jaw.
The X-ray pattern shows the sparsity of the bone tissue and the consistency of the base, the "legs" of the tumor, different from the surrounding structures.
The clinic of benign epulis is very different - the size of the tumor rarely reaches a diameter of more than 2 cm, differing in the development of slow, hardly noticeable for the patient's eyes, often perfect absence of disturbing symptoms, excluding the aesthetics of perception of their appearance.
Classification of ICD-10
Three types of neoplasms were registered in the ICD-10:
- Angiomatous epulis is characterized by the presence on the gums of a rich network of tiny vessels, small-hulled( extremely rarely - smooth)
 surface of unnatural( scarlet) color with a bluish tinge, soft consistency, wide and dense walking, localized near the tooth neck( characteristic appearance in the photo on the left).The tumor is fast-growing, easily bleeding even with minor damage, with a high probability of relapse after removal. The most frequently affected contingent is a person under 18 years of age, mostly children 5-10 years of age.
surface of unnatural( scarlet) color with a bluish tinge, soft consistency, wide and dense walking, localized near the tooth neck( characteristic appearance in the photo on the left).The tumor is fast-growing, easily bleeding even with minor damage, with a high probability of relapse after removal. The most frequently affected contingent is a person under 18 years of age, mostly children 5-10 years of age. - Benign fibrotic epulide is a tumor of dense consistency, round or oval in shape, with a smooth or slightly tuberculate surface that matches color with healthy gingival tissue. Has a wide base, usually located in the premolar zone on the vestibule side of the gum. Bleeding does not manifest itself, it differs very slowly compared with other species of growth, but it can reach considerable dimensions.
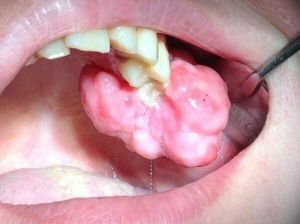
- The appearance of the giant cell on the alveolar gingiva is the prerogative of elderly and senile individuals( from 40-60 years of age and older), mainly women. Tumor of an elastic-dense consistence, oval or round, with a tuberous surface, a shade of bluish-purple to brown. Bleeds seldom and moderately, painful sensations arise from squeezing or other irritation. If the fibrous and angiomatous epulis is formed mainly from the surface structures of the gum due to inflammation from their chronic irritation, the giant cell is able to grow even from the jaw bone, like the central giant cell granuloma.
Features of leaks in children and pregnant women
The overall relapse rate for this contingent is 14%.
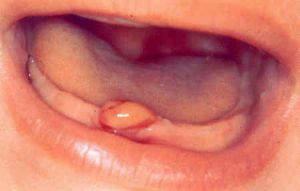
Gum tissue in the child when cutting teeth
In the pubertal period and during pregnancy conditions for the development of tumors on the gums are extremely favorable. For the hormonal background in these moments, which requires the body to exert maximum strength, is unstable, and the body is wounded more than ever.
The moment of teething can also cause a neoplasm. The reason is gum damage, as well as at the age of adolescence, accompanied by frequent injuries to the face and mouth area.
And as teenage girls at this time in their lives begin to use hormonal contraceptives, the tumor develops more often.
Differential diagnosis of
Methods of recognition of a tumor are the study of both visual and:
- histological;
- X-ray, MRI, CT.
Differentiation of epulis follows from other possible tumors, both benign and malignant, including on the gums and jaw.
In case of suspected malignancy of the tissues, an oncologist and other specialist doctors are involved in the diagnosis, a full course of targeted examination is conducted.
Traditional and traditional treatment
Traditional( official) medicine uses excision of the tumor with all surrounding tissues, up to the removal of the periosteum, the jawbone and( if necessary) the involved teeth, since the sanation of the area should be performed to absolutely healthy tissues.
The surgical or laser scalpel is the instrument of choice during the operation. Use of the latter allows to shorten the time of operation and postoperative period, as well as avoid complications that are unavoidable with the usual scalpel technique: development of purulent processes both in the wound and in surrounding tissues, postoperative bleeding.
The method of anesthesia in the manufacture of intervention is either infiltration anesthesia or general anesthesia.
Removing epulis by surgery - the best way out:
Folk treatment in case of epulis on the gum is appropriate only during the rehabilitation period, because it is not able to "deduce" the tumor by itself. 
From the whole arsenal, you should choose dentist-approved disinfectants for mouthwash. These include broths of medicinal raw materials and solutions of the necessary concentration, made from available soda houses or table salt.
As a medicinal raw material for brewing and rinsing, flowers of calendula, sage, chamomile, eucalyptus leaves can be used.
To prepare a rinse aid from baking soda( 3-4 times a day), a teaspoon is dissolved in a glass of warm water. Or, for the same purpose, a tablespoon of food( table salt) is dissolved in a glass of boiling water.
About preventive measures
The consequence of untreated epulis can be not only an aesthetic and cosmetic defect of the face and mouth, but also suppuration, ulceration of the tumor and its degeneration into cancer, in the case of an incorrect operation, a relapse of the disease is inevitable.
Therefore, it is necessary to follow simple rules to prevent its occurrence:
- contain the mouth cavity in proper condition;
- avoid injuries to teeth and jaws.
 If you have the same problems that are not dependent on personal hygiene( scaling, bite defect, difficulties of teething and others), you should visit the dentist's office.
If you have the same problems that are not dependent on personal hygiene( scaling, bite defect, difficulties of teething and others), you should visit the dentist's office.
And not only to visit, but also strictly follow its recommendations to prevent the occurrence of dental diseases.
If there is a concomitant pathology, it should be treated on a regular basis by a specialist doctor.
