
Gingivit - fight!
With gingivitis, the tissues located in the immediate vicinity of the tooth base are affected. Painful sensations in the infected area gradually intensify and are accompanied by edema, bleeding gums and other not very pleasant symptoms.
Prevention of gingivitis must necessarily be complex and long-term, since it is impossible to achieve the desired result using any one method.
Contents
- Background of preventive measures
- Step one - find out the causes of the disease
- Methods of primary prevention of gingivitis
- Secondary prevention
- Preventive measures for different forms of the disease
- Child's issue
- Proper nutrition as a health guarantee
The urgency of preventive measures
The chronic form of the disease can act as a harbingermore serious problems associated with the mobility of teeth and their subsequent loss. The inflammatory process continues to spread through the oral cavity, affecting the periodontium and traumatizing the gums. The peri-toothed tissues begin to deform and die off.
Despite the fact that the onset of the disease often does not cause any special discomfort to the patients, it's still not worth underestimating its cunning. 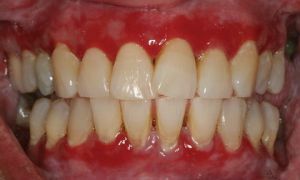
In addition to the catarrhal form, gingivitis can hypertrophy the gum, forming gingival pockets. Manifestations of ulcerative lesions no longer leave any doubt about the need for urgent medical treatment.
And the foci of inflammation are localized both in separate small areas of the oral cavity, and on both jaws. Variations in the course of gingivitis are so diverse that self-medication in this case will not be extremely prudent.
Step One - find out the causes of the disease
Adhering to certain hygienic rules, it is quite realistic to significantly reduce the risk of bacteria spreading in the oral cavity.
However, it is not always possible to solve the problem in this way. There are many factors that cause the infection to become more active, and among them are:
- mechanical mucosal trauma;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- decreased immune function;
- diabetes mellitus;
- chemical and thermal tissue damage;
- deformation of the dentition;
- lack of nutrients in the body;
- plaque and hardened deposits( stone);
- caries( including the cervical).
It is extremely cautious that women who are expecting a child's birth and children of adolescence should take care of their health. Harmful habits also form a certain predisposition to the development of gingivitis.
Hormonal changes that occur in the body, in turn, affect the state of the dentoalveolar system.
Methods of primary prevention of gingivitis
 If a tendency to infectious diseases of the oral cavity is necessary at least twice a year to use the services of a specialist. In solid dental clinics each patient has a separate outpatient card, in which all the features of the history are recorded.
If a tendency to infectious diseases of the oral cavity is necessary at least twice a year to use the services of a specialist. In solid dental clinics each patient has a separate outpatient card, in which all the features of the history are recorded.
This foresight allows doctors to act purposefully and focus on treatment, avoiding unnecessary flow of information.
Working on the result, you need not only carefully and several times a day to brush your teeth, but together with the doctor to select accessories for this procedure.
Of course, tough stubble removes plaque well, but for weakened gums it may not be the best option. In addition, the budgetary toothpaste is also not worth much in terms of prevention.
Electric toothbrush and irrigator greatly simplify the process of cleaning the oral cavity and make it better, therefore, at the slightest financial opportunity, it is worthwhile to think about the acquisition of such useful things.
The main rule for the prevention of gingivitis is timely dental care for anomalies in the development of the dentition, bite defects, the presence of plaque and carious formations.
Secondary prevention of
 In order to prevent the spread of gingivitis, it is necessary to create unfavorable conditions for its development. The use of remineralizing gels, as well as preparations that include fluoride, strengthens tooth enamel and significantly reduces the likelihood of caries.
In order to prevent the spread of gingivitis, it is necessary to create unfavorable conditions for its development. The use of remineralizing gels, as well as preparations that include fluoride, strengthens tooth enamel and significantly reduces the likelihood of caries.
Herbal decoctions, antiseptics, therapeutic and preventive rinse aid and properly selected dental floss will help to remove difficult-to-access areas from pathogenic microorganisms.
Removal of calculus from the surface of the enamel is performed directly in the dental office under the supervision of a professional. In some cases, additional studies( radiographic and laboratory) may be required to better understand the clinical picture.
Preventive measures for various forms of the disease
For the prevention of catarrhal gingivitis, it is enough for an adult to form several useful habits. First of all, it is necessary to adhere to the schedule of routine dental examinations, during which the doctor will be able to assess the general condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning of teeth.
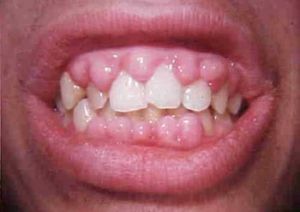
Hypertrophic gingivitis requires special measures to prevent
It should also be remembered that any( even minor) discomfort sensations are an occasion for specialist advice. The initial stage of the disease is much easier to treat.
Hypertrophic gingivitis very often manifests itself in abnormalities of the hormonal background, therefore, during pregnancy, puberty and menopause it is desirable to carefully monitor the ratio of hormones.
The atrophic form of the disease provides for a comprehensive treatment. Severely neglected cases require more serious surgical interventions.
In such situations, dead tissue areas are completely removed, and in their place, healthy cells are transplanted. The engraftment usually passes quickly enough, however, when caring for the oral cavity it will be necessary to refuse the use of a toothbrush on the operated site.
An excellent non-traumatic hygiene option will be rinsers that will not allow germs to penetrate the wound and cause inflammation.
Children's issue
Children's dentists pay special attention to parents that oral hygiene must necessarily be systematic. With irregular and short cleaning it is quite difficult to cope with the bloom accumulated in hard-to-reach places.
The most optimal option would be if the adult by his own example will form a positive attitude to the  hygienic procedures in a child and teach the child to correctly use personal items.
hygienic procedures in a child and teach the child to correctly use personal items.
Do not forget that when choosing a child's toothpaste and brush should take into account the individual characteristics of growth and development of baby teeth. The child will be much more comfortable to use a soft toothbrush that gently cleanses the enamel and does not cause any harm to the gums.
In spite of the fact that little fidgets are mostly sweet, it is extremely undesirable to indulge all their gastronomic whims thoughtlessly.
In many ways, thanks to the sweet food, microorganisms have an excellent opportunity to multiply in a familiar environment. If you limit the baby in his taste preferences for any reason impossible, it remains to control the process of hygienic manipulation.
Proper nutrition is a guarantee of health
When designing a menu, you should consider not only the quantity of products used, but also the benefits that they can bring to the body.
 If possible, it is advisable to select seasonal vegetables and fruits for the menu. Strawberries, zucchini and carrots are excellent at cleaning the oral cavity. Citruses have a beneficial effect on the gums and at the same time improve the color of tooth enamel.
If possible, it is advisable to select seasonal vegetables and fruits for the menu. Strawberries, zucchini and carrots are excellent at cleaning the oral cavity. Citruses have a beneficial effect on the gums and at the same time improve the color of tooth enamel.
Sour milk products enriches the body with calcium, and the fish replenishes the lack of vitamin D. Parsley, dill and salad leaves help fight microbes. Such spices, as ginger and wasabi, disinfect the oral cavity.
As for sweet carbonated drinks and sweets, it is desirable to limit their amount in the diet, as they adversely affect the health of the dentoalveolar system.
