 Mesenteric vascular thrombosis is the malfunction of mesenteric arteries due to mechanical obstruction of the vessel. Occlusion leads to the emergence of acute ischemia, with the further development of intestinal infarction and peritonitis.
Mesenteric vascular thrombosis is the malfunction of mesenteric arteries due to mechanical obstruction of the vessel. Occlusion leads to the emergence of acute ischemia, with the further development of intestinal infarction and peritonitis.
The upper branches of the mesenteric artery are often affected.
Diseases of are prone to elderly and elderly people , often with a predisposition to this: disruption of the blood circulation system, as well as neoplasm, trauma or surgery.
Contents
- Classification of the disease
- Causes of the disease
- Clinical picture
- Immediate treatment - necessity
- Complications of the disease
- Conclusions
Classification of the disease
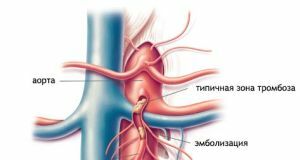
Occlusion defects of the mesenteric circulation subdivide into such specific disorders as:
- embolism;
- thrombosis;
- occlusion resulting from delamination of the aortic wall;
- vascular occlusion due to the onset of a tumor of any etiology;
- weave of blood vessels;
- and the main thing is blockage of the arteries due to atherosclerotic lesion.
There are also so-called non-occlusive disorders, namely, not complete, partial thrombosis or angiospasm.
In the time stages, there are three trends in the disease. Ischemia, heart attack, and then peritonitis.
Clinically, decompensated circulation, subcompensated and compensated. In the last two cases, blood supply, in whole or in part, is restored due to collateral blood flow.
The classification reflects the localization of thrombosis in the upper, middle or lower mesenteric artery.
 Therapeutic exercises for leg varicose must comply with certain rules. Find out the details in our article.
Therapeutic exercises for leg varicose must comply with certain rules. Find out the details in our article.
In folk medicine, chestnuts are widely used for varicose veins. Learn recipes of tinctures based on horse chestnuts and other means for treating varicose veins.
Causes of
The most common and main cause of thrombosis of mesenteric vessels is atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction .
In this case, because of the slowing of blood circulation in the vessels, there is a high likelihood of a thrombus in the mesenteric artery. Also, thrombosis can be caused by stenosis of the mitral valve, aneurysm of the heart or visceral arteries.
A cause of embolism of mesenteric vessels is infective endocarditis.
In rare cases, in younger people, thrombosis is possible when the endothelium of the vessel is detached as a result of a stroke. 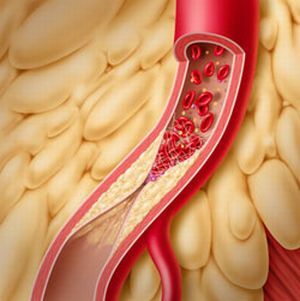
When surgery to remove a thrombus on the aorta, there is sometimes a secondary overlap of the arteries. And also it is possible with polycythemia, cardiac activity, leukemia, portal hypertension, after splenectomy.
Neoplasms in the abdominal cavity, the rudiments of the diaphragm's foot and the possible weave of the vessels, can also lead to the onset of ischemia or intestinal infarction, by squeezing the artery and blocking the natural blood flow.
Clinical picture
Correct diagnosis of mesenteric vascular thrombosis is an extremely difficult task.
The clinic for mesenteric vascular thrombosis depends on the stage.
So the first stage of is reversible and is accompanied by pallor of the skin, sometimes even with a gray-green tinge.
Then vomiting occurs, at a certain stage it can have a feces smell. If the thrombus is in the upper part of the mesenteric artery, vomiting is often with a trace of blood. Diarrhea arises.
In the subsequent stage, diarrhea is replaced by constipation, this occurs with profound destructive changes in the intestine. Blood can be present in the stool, but it should be noted that the abundant blood loss for this disease is not typical.
may appear as a symptom of Mondora - the appearance of swelling below the navel. Sometimes a bradycardia is noted.
When palpation the abdomen is soft, slightly inflated, there is no symptom of muscular protection. Increases peripheral blood leukocytosis. During this period, patients often scream in pain, rush, ask for help.
At the last stage, peritonitis develops, with such symptoms: muscular protection occurs, symptom of Schetkin-Blumberg and other symptoms of abdominal irritation are observed. Paresis of the intestine is noted.
Immediate treatment - the need for
 In the early stages of mesenteric vascular thrombosis, conservative treatment of is possible, namely, the use of thrombolytic agents that dissolve the formed thrombus.
In the early stages of mesenteric vascular thrombosis, conservative treatment of is possible, namely, the use of thrombolytic agents that dissolve the formed thrombus.
In the later stages of , the only possible treatment is surgery. Before the onset of necrosis of the intestine, a part of the mesenteric artery is removed, followed by plasty. If necrosis occurs, the affected area of the intestine is removed.
Complications of
The complications of appear in 100% of cases of in untimely treatment and usually result in death. The most extreme stage, which does not respond to treatment, is diffuse peritonitis and extensive necrosis of the intestine.
Sometimes during the course of the illness, a temporary improvement in the condition of the patient is possible. He stops complaining, a sharp pain stops, the main symptoms become dull, or disappear.
All this can disorient the doctor and the patient, followed by the wrong tactics of treatment and diagnosis. Such a delay may become fatal for the patient.
The age of the patient may be a complicating factor. The older the person, the harder it will be to cope with the disease and, after completing the rehabilitation course, fully recover.
Conclusions
Mesenteric vascular thrombosis is one of the most serious diseases of , both intestines and the entire body.
Sometimes the elimination of pain symptoms is an insoluble task, not to mention the treatment and the subsequent recovery. 
Even a timely diagnosed illness and treatment is not a guarantee of recovery.
The lethality of is on the average 60-70%.
In conclusion, you can add that when you reach a certain age limit, you should regularly be examined by a doctor and be aware of the possible development of atherosclerosis, heart disease, the pathology of the coagulating system of blood and other predisposing conditions.
If these are found, the formation of medical vigilance for such patients is necessary. This will improve the patient's survival.
