Pregnancy is a test even for a healthy body. And if it occurs against the background of gynecological problems, it requires special control. Among them, dysplasia of the cervix can be found. The disease, although very serious and dangerous, often develops without noticeable signs. Therefore, when both cervical dysplasia and pregnancy are diagnosed at the same time, a woman is closely monitored not only by the gynecologist.
More on dysplasia
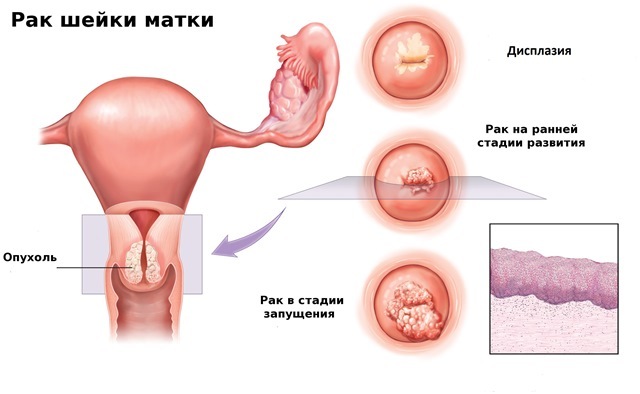
The cervix from all parts of the reproductive system is the most susceptible to changes. After all, it binds the vagina and the organ itself.

A similar condition is called dysplasia and is characterized as a precancer. Its other name is cervical intraepithelial neoplasia( CIN).
Epithelial changes in the disease are not irreversible. If the dysplasia is detected at an early stage, it can be removed with medicines. With the development of pathology, surgical treatment is indicated.
Types of dysplasia
The flat epithelium, which covers the outer part of the cervix, has several layers:
- is the deepest basal;
- following it in between;
- surface functional.
The type of dysplasia in each case of the disease is determined in accordance with how deep the pathological processes went. Normally, cells of all layers have a rounded configuration and the same core. The closer to the surface, the more flat they become. With dysplasia, the outlines of cells are disrupted, they lose their correct form, grow larger, acquire multiple nuclei. If such changes occur:
- in the outer layer of the epithelium, occupying 1/3 of the coverage, the disease has a 1-st degree and is considered to be light;
- in the surface and middle layer, localizing in 2/3 of the mucosa, pathologies are assigned a 2-nd degree, called moderate;
- in the entire thickness of the cervical covering, without touching nerves, vessels and muscles, is already a severe degree of ailment, that is, the 3rd.
Symptoms of dysplasia
The danger of dysplasia is that it does not have clear clinical signs, especially at the beginning. The covering of the cervix changes externally, but only a gynecologist can see it, and an additional examination is needed to establish the culprit for the formation of the pathological site. Further development often leads to infection or the onset of the inflammatory process of .Therefore, all manifestations are caused, rather, by them:
- Allocations are obviously unhealthy. They can be curdled, with impurities of blood, pus, lean or plentiful. Excretions can cause itching and burning or do not have such an accompaniment. In a word, everything depends on concomitant dysplasia of diseases, which are also provocators of cellular changes in the epithelium.
- Pain. This sign is mostly found in the last stage of the pathology. But it can also bother before, if dysplasia is joined by endometritis, adnexitis, salpingitis. Pain occurs against the background of high temperature in the first case, it is very strong in the second, it increases at the end of the cycle in the third. With the transition of dysplasia to the last stage, it is aching, long lasting, supplemented by bloody discharge with odor and unusual consistency.
- The formation of genital warts on the vulva, vagina and anus. This is due to HPV detected in 95% of CIN cases.
Diagnosis of dysplasia
The potential risk of dysplasia and the inability to diagnose by clinical signs require careful examination to determine the disease and the degree of its development. For this use:
- Gynecological examination. Mirror will allow you to see the areas changed in the form of shiny spots, the growth of the mucous membrane.
- Colposcopy. The device makes it possible to consider the disruption of the development of epithelial cells in an increase and with the use of reagents.
- Smear on cytology. The study will confirm or disprove the presence of atypical cells in tissues. They are taken from different sites. In addition, cytology reveals one of the culprits of dysplastic changes - the papillomavirus.
- Histology. The method establishes the potential risk of the disease on the basis of an analysis of tissues taken with colposcopy. The cell structure, morphology and number of layers are considered.
- PCR. The study will let you know about the presence of HPV in the body, determine the type of virus, its concentration.
Planning pregnancy for dysplasia
Whether dysplasia of the cervix is compatible and pregnancy planning should be answered by the doctor, relying on a specific diagnosis. It is necessary to take into account the possible influence of the state on the development of pathology. After all, pregnancy changes the hormonal background, which can stimulate the malformed cells of the cervical epithelium. But this can not be called a 100% provoking factor.
And yet in most cases, the initial and the second stages of dysplasia planning is possible. After all, the disease is able to stay at such a level for a long time that it requires not observation but observation. But before getting pregnant, a woman must:
- undergo another examination on all the existing directions in the diagnosis of dysplasia;
- get rid of concomitant pathologies, especially HPV( the same must be done and its partner);
- determine your own hormonal status.
 We recommend reading the article about the monthly during pregnancy. From it you will learn about normal and pathological discharge in the period of bearing, the causes of the appearance of secretions, the prevention of violations.
We recommend reading the article about the monthly during pregnancy. From it you will learn about normal and pathological discharge in the period of bearing, the causes of the appearance of secretions, the prevention of violations.
If dysplasia is detected during pregnancy
Not everyone responds responsibly to family planning, so the diagnosis of "CIN" is possible after the fact of pregnancy has been established. This does not mean that the future child will have to give up for the sake of saving a woman's life. But pathology considerably complicates the patient's management, since it requires constant monitoring, which is different from what healthy future mothers need. The risks that exist at different levels of the disease development are shared by the doctors as follows:
- At the first stage, they are minimal. The probability of progression of the tumor process and its transformation into cancer is very small. In addition, this type of CIN is susceptible to conservative treatment, which in pregnancy is not contraindicated. And for some, on the background of hormonal changes, the epithelium restores its properties independently.
- Cervical dysplasia of the 2nd degree and pregnancy coincide in 5% of the cases of waiting for the addition. Here, too, medicamental treatment is advisable, but due to more serious changes it does not always give the desired result. A surgical intervention in pregnancy is contraindicated, it is done after childbirth. During this time dysplasia develops to the next degree in 15-20% of women.
- The third stage of CIN in combination with pregnancy is dangerous in that it forces to postpone the only correct surgical treatment for the postpartum period in this case. And if it is absent in 20-30% of patients, it turns into cancer.
Peculiarities of bearing in dysplasia
Pregnancy in CIN makes management of a condition different than that of healthy women. In addition to the usual types of examination that control its course, development of the fetus, those who will inform about the processes in the epithelium of the cervix are needed:
- smears on oncocytology every 3 to 4 months;
- analysis for the presence of venereal diseases( once);
- colposcopy 1 to 4 times, depending on the degree of the disease;
- biopsy and histology in severe dysplasia;
- scraping of the cervical canal if there is reason to suspect cancer;
- cone biopsy in severe dysplasia.

In addition to a gynecologist, the woman is also seen with an oncologist. For the treatment of the first two stages of the disease, a specialist can prescribe locally such drugs:
- Terzhinan,
- Genferon,
- Betadin,
- Livarol,
- Hexicon.
The choice of the therapy period is also left for the doctor, as some of the drugs are undesirable in the first trimester.
Cervical dysplasia during pregnancy does not affect the fetus, it rarely progresses enough. But bearing in mind the complications that it can create for gestation, and the resulting dangers with regard to the health of women, it may be worthwhile to treat the ailment before conception.
