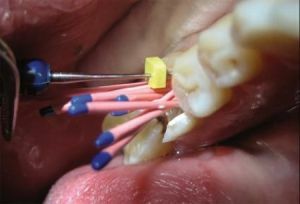
 Dental canal treatment takes a special place in dentistry. Qualitative root filling affects the duration of treatment and the life of the teeth in the future.
Dental canal treatment takes a special place in dentistry. Qualitative root filling affects the duration of treatment and the life of the teeth in the future.
When voids form in the channel due to its poor filling, this favors the creation of a pathogenic microflora. Inside the root, microorganisms can accumulate, particles of food can enter it. All this provokes the onset of an inflammatory process that destroys bone tissue, which threatens to completely lose the tooth.
Because of this, the quality of root treatment is high. Throughout the century, one of the most effective materials for endodontic treatment in dentistry is gutta-percha and pins on its basis. Its main advantage is the ability to keep the shape even after melting.
Contents
- Characteristics of endogermetics
- Main advantages and some drawbacks
- Endo sealing pins - composition and purposes of their use
- Treatment steps
- Method of lateral condensation
- Method of vertical condensation
- Possible complications
Endogermetics characteristic
Gutta percha is a material that is obtained by processing the lactate juice of gutta-percha plants. Its composition is very similar to latex. Has a white color with a characteristic yellowish tinge. The material is hard and at the same time differs in plasticity.
It becomes soft and lends itself to the necessary molding under the influence of high temperature. With the help of this substance, it is possible to fill qualitatively the dental root itself, as well as its numerous branches. If there is a need for re-treatment, the sealant is easily removed.
Gutta percha is divided into two types:
- Alpha;
- Beta.
The first material has increased tackiness and improper fluidity. 
The most common use is the beta version, due to less fluidity and good adhesion. This kind of material is also used to produce gutta-percha pins. This component occupies 20% of the entire composition of the pin. Another 1% occupy radiopaque substances, and the rest of the volume is filled with special mixtures for obtaining plasticization and dyes.
In modern dentistry it is impossible to meet a specialist who has never worked with gutta-percha. An experienced dentist, even with a curved canal trajectory, can quickly and easily block it with a substance.
Main advantages and some drawbacks of
The main advantage of the sealant is the radiopacity and predictability of channel obturation. This plays an important role for quality and effective treatment, due to the fact that it is possible to track the correctness of the filling.
Gutta percha excellently cope with the sealing of all root branches and is best suited for the qualitative filling of channel voids. The material has many advantages:
- excellent biological compatibility with dental tissue;
- high strength and elasticity;
- low toxicity;
- tight sealing of the root canal;
- the ability to quickly remove;
- safety, hypoallergenicity;
- takes on the necessary shape when hardened;
- indifference( retains its properties throughout the life of the product);
- radiopaque( allows to control the quality of filling);
- predictability of obturation.
All of the above indicators have made gutta-percha the number one tool in tooth filling. But it is worth noting that this  substance has several drawbacks:
substance has several drawbacks:
- is neutral and has no bacteriostatic effect;
- has a risk of deformation due to lack of control over the depth of administration;
- lack of rigidity( there is no possibility of fixing in a narrow cavity);
- without root sealant is not applied( there is no adhesion to the root walls);
- is the probability of displacement of the filler in the case of violation of the sealing technique.
Despite a number of shortcomings, the advantages at times prevail. To date, guttagermetik is mainly used for the treatment of roots.
Endo-sealing pins - composition and purposes of their use
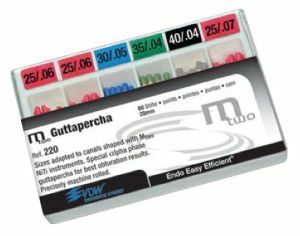 Gutta-percha pin( filler, filler) - rod, which serves as a reliable support for the restored tooth crown and is fixed in the channel.
Gutta-percha pin( filler, filler) - rod, which serves as a reliable support for the restored tooth crown and is fixed in the channel.
It is made of beta material.
Pin composition as a percentage:
- 59-76 zinc oxide;
- 18-22 beta-gutta-percha;
- 1-4% plasticizer candles;
- 1-1.5% radiocontrast substances;
- antioxidants;
- biological dyes.
Due to the presence of zinc oxide in the composition, the pin perfectly fits with the silters, the basis of which is the Eveneng. Both substances bind together, forming a homogeneous mass.
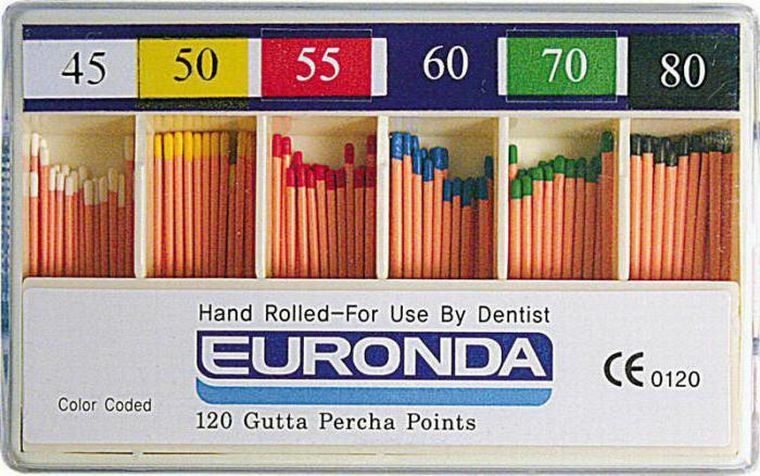
Gutta-percha fillers are of two types:
- standard( ISO standards);
- non-standard( they are thicker and shorter than standard ones, they have a sharp cone shape).
The size of the rods can vary from large to small. Each of them is denoted by a number that determines its thickness. During the treatment, the doctor decides what thickness the stem should be, based on the condition of the tooth and the size of its roots.
Features:
- usability in treatment;
- easy removal of the fixative if necessary aftercare;
- does not cause an allergic reaction;
- is an elastic and flexible structure;
- excellent radiopacity;
- does not absorb liquid;
- low cost.

The cause of tooth decay can be poor oral hygiene and dental care, mechanical injuries, chips and cracks in the enamel, poor nutrition. The tooth, which is in the stage of destruction, does not need to be removed.
If the root is preserved, the crown can be reconstructed with a gutta-percha filler. In some cases, this procedure may be the only solution to the problem.
When such sealing rods are used:
- 50% fracture of the tooth crown;
- complete tooth decay with preservation of the root;
- if you need support for installed prostheses.
Treatment stages
Sealing is performed according to the following algorithm:
- is determined and the tissue affected by caries is removed;
- the pulp is removed from the root and the crown;
- expansion of the channel diameter by machining;
- treatment of the formed cavity with special medicines;
- introduction to the channel opening of the sealer and pin;
- with a red-hot tool cuts the tip of the gutta percha rod;
- installation of temporary seal;
- after a few days a permanent seal is established.
Sealing of the root canals of gutta-percha is a rather complicated process. The main difficulty lies in the flexibility of the latches and their thin shape, which complicates the process of filling the channel. Here you need a high qualification of a dentist and a great work experience.
Various methods can be used for filling with endo-hermetic:
- Hot substance .Hot gutta percha is injected directly into the root. Thus, the material completely fills the channel without the formation of voids. This technique was called "bulk filling".
- Cold finished material .There is a danger that the pins will not completely cover all the root ramifications and there will be an empty space. This carries the risk of infection of the root and the development of periodontitis.
The lateral condensation method
This technique is very effective, despite the ease of action, and is very popular in dentistry. With its 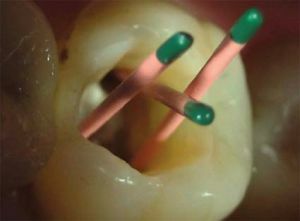 , the pins are used together with the filling paste and tightly fill the channel cavity. As a result, the apical opening closes securely, completely filling the entire root lumen.
, the pins are used together with the filling paste and tightly fill the channel cavity. As a result, the apical opening closes securely, completely filling the entire root lumen.
The lateral condensation of gutta percha is used to seal the broad root cavities of the oval shape. In the course of the procedure, several rods are taken in combination with a small amount of a sealer.
Thanks to this it is possible to achieve a high hermeticity of the root with a continued preservation of the result. But this method has some drawbacks:
- lateral condensation creates a strong pressure on the root walls, which can lead to root damage;
- only one filler is used to close the most important part of the tooth( lower third);
- the apical part of the stem is not amenable to changes, which can not guarantee a reliable apical seal;
- channels are sealed exclusively in combination with a sealer.
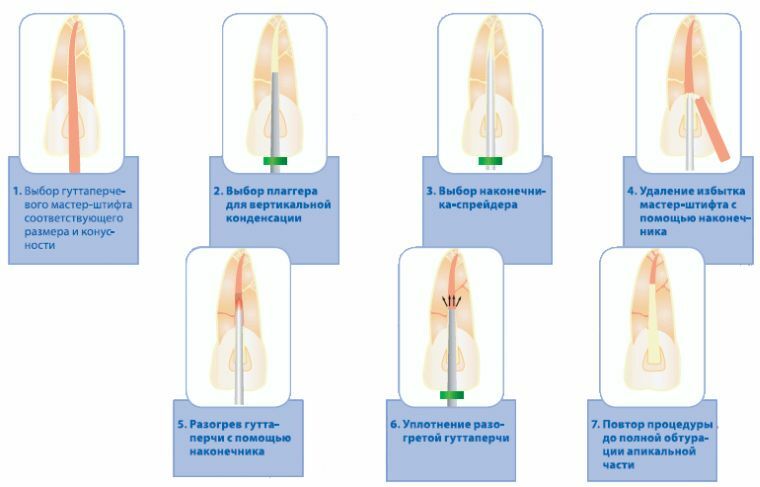
Method of vertical condensation
This method is labor intensive. For sealing in this case, the heated gutta percha is used. First, channels of roots are filled with hot material. The substance in this case can be practically in a liquid state.
The vertical condensation of the gutta-percha is then carried out with a special apparatus. In this case, the minimum quantity of the sealer is used. The use of a hot component contributes to the maximum filling of voids. The filling takes place in several stages.
First fill the bottom third of the root, then the middle and crown. The heated pin acquires sufficient plasticity, which when inserted into the root helps to fully correspond to the shape of the channel with all its branches.
To use this method it is necessary to use special tools - plaggers. At different stages of sealing sealant, plasters with different sizes are selected.
Possible complications of
Some difficulties may arise during the installation of the seal or after the treatment. The main complication is the appearance of the inflammatory process.
This can occur due to poor filling of the cavity, when there is empty space. In this case, a re-sanitation of the channel with subsequent sealing will be required.
Another serious complication is the perforation of the tooth. The doctor will understand this by the fact that the instrument will begin to fall through. The damaged area will also have to be covered with a composite for sealing.
Sealing gutta-percha is accompanied by a number of difficulties, but despite this, this material does not lose its popularity.
Probably, it will be an indispensable tool in the work of dentists for many more years. Have not yet invented a similar substance that would also efficiently and qualitatively cope with the task.
