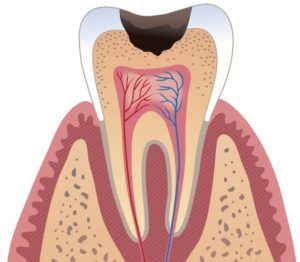
 Caries is one of the most well-known diseases affecting hard tooth tissues. The development of the disease is accompanied by thinning of the enamel, softening of the dentin and the formation of a carious cavity.
Caries is one of the most well-known diseases affecting hard tooth tissues. The development of the disease is accompanied by thinning of the enamel, softening of the dentin and the formation of a carious cavity.
Speaking of tooth decay, it is impossible to confine ourselves to only one classification, which would fully meet the requirements of specialists.
Therefore, the existence of several classifications of the disease is fully justified.
Contents
- Classification according to Black
- Classification of disease according to ICD-10
- Classification of caries process according to the depth of lesion
- Classification by the presence of complications
- Types of disease by activity
- How quickly the carious process develops
- Classification of the disease by process intensity
- Classification by process localization
- Classificationon the priority of development
- Selection of therapy methods
- Treatment for spot stage
- Treatment of superficial caries
- Leix average caries
- Treatment of deep lesions of the tooth
Classification by Black
greatest recognition dentists today received caries classification by Black, which reflects the process of the depth and location of caries:
-
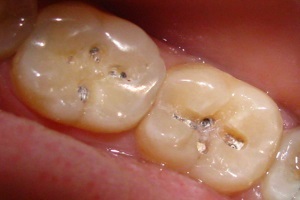
Pictured surface caries
First class( surface ).The cavities are located in the zone of natural depressions and fissures. The defeat is superficial.
- Second class( weak ).The process develops on the contact surface of the lateral teeth.
- The third class( caries of medium degree ).The carious lesion affects the contact surface of the canines and incisors.
- Fourth class( heavy form ).Launched the stage of moderate caries. Carious lesions move to the dentin at the angle of the cutting edge.
- Fifth class( very heavy ).The gingival margin of the lateral or anterior teeth suffers. Basal caries develops.
- Sixth grade( atypical ).There is a destruction of the cutting edge.
Classification of the disease according to the ICD-10
The ICD-10 suggests dividing the caries into the following classes:
-
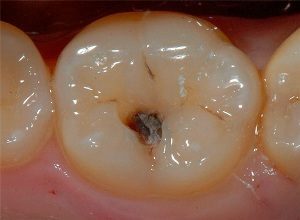
In the photo, the lesion of the dentin
K02.0 is a caries affecting the enamel;
- K021 - caries of dentin;
- K02.2 - caries of cement;
- K02.3 - caries, the development of which has stopped;
- K.02.3 - odontoclasis( resorption of the root of milk teeth);
- K02.8 - other types of dental caries;
- K02.9 - unspecified caries.
The classification proposed by ICD-10 is quite popular and differs in its merit - the allocation of a class of suspended caries and caries of cement.
Classification of the carious process according to the depth of the lesion
This classification of caries is considered by dentists to be the most convenient. Therefore, it has become widespread in the domestic space. Specialists identify the forms of the disease related to the uncomplicated and complicated course of the disease:
-
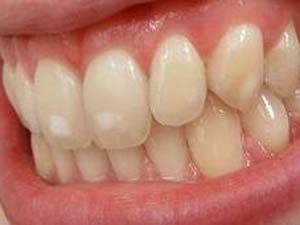 Spot stage is the initial stage when white strips or dark spots appear on the enamel, but it is smooth to the touch, not yet subject to destruction. Toothache at this stage of the patient's stain does not bother.
Spot stage is the initial stage when white strips or dark spots appear on the enamel, but it is smooth to the touch, not yet subject to destruction. Toothache at this stage of the patient's stain does not bother. - Surface caries is the second stage of the carious process. Tooth enamel continues to break down, but tooth decay does not go beyond the limits of the enamel layer. Dentin is not damaged, however, a periodic toothache can already manifest itself. The reaction of the tooth to cold and hot, to sour or sweet is noticeable. The carious stain on the tooth surface is rough to the touch.
- Medium caries , when carious lesion passed the enamel layer and affected the upper layers of the dentin. The pain intensifies, has a permanent character.
- Deep caries , in which only a thin layer of dentin is to be preserved. At this stage, the tooth tissue is severely damaged. Lack of proper treatment of the tooth at this stage causes damage to the pulp and periodontitis.
Classification by the presence of complications
This classification assumes the isolation of two types of caries:
-
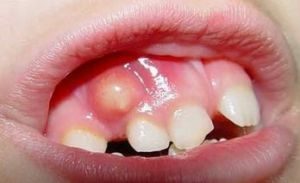 complicated , accompanied by concomitant inflammatory processes( in the photo to the right the flux in the child), this form of the disease occurs if the doctor does not contact the doctor in due time or if there is no proper treatment;
complicated , accompanied by concomitant inflammatory processes( in the photo to the right the flux in the child), this form of the disease occurs if the doctor does not contact the doctor in due time or if there is no proper treatment; - of an uncomplicated - a typical process that involves the presence of its individual stages( surface, middle, etc.).
Types of the disease by the degree of activity of
Distinguish:
- compensated caries, characterized by the lack of obvious progress in the carious process, the teeth are affected slightly, which does not cause the patient discomfort;
- is a subcompensated , characterized by an average speed of development;
- decompensated , which is characterized by intense current, at this stage is diagnosed acute pain in the tooth.
How fast the carious process develops
In this case, the classification is the arrangement of the following four categories of caries:
-
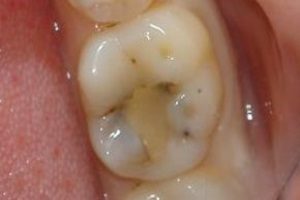 Acute .Symptoms of tooth lesions appear within a matter of weeks.
Acute .Symptoms of tooth lesions appear within a matter of weeks. - Chronic , developing for a longer time. Affected tissues take a yellowish or dark brown color, stained with plaque and food colorings.
- Blooming , which entails multiple lesions of dental tissue. The carious process progresses in a short time.
- Secondary , which develops under a previously established seal( photo on the right) as a result of weakening of the enamel of the tooth, neglect of the rules of oral hygiene, decrease of the body's immunity.
Classification of the disease by the intensity of the process
This classification assumes the existence of:
-
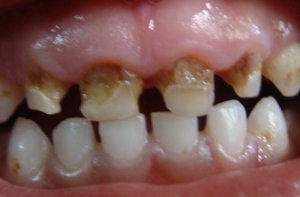
In the photo, multiple ring caries in a child
of a single caries, in this case only one tooth is affected;
- of multiple ( systemic caries), with this form of disease affects five or more teeth in children, six or more in adults.
Among the patients with this diagnosis are those who suffer from acute infectious diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system, respiratory system. Among the children suffering from multiple caries, they have been ill with chronic tonsillitis, scarlet fever.
Classification by process localization
Depending on the location, specialists distinguish the following types of caries:
-
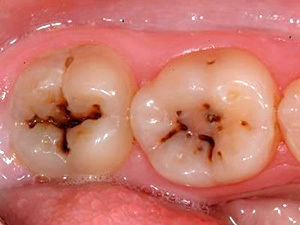
On the photo fissure caries
Fissure , in which the natural depressions of the tooth surface are affected.
- Interdental carious process , developing on the contact surface of the tooth. For a long time the disease can not be diagnosed due to the specific form of the development of the disease: caries, in the process of affecting the tooth surface develops towards the center of the tooth, and the cavity itself is covered with healthy enamel layers.
- Cervical , which is located between the root and the crown of the tooth, in the area adjacent to the gum. The reason for the development of the process is insufficient hygiene of the oral cavity.
- Ring , affecting the circumference of the tooth. Externally it looks like a yellowish or brown belt on the neck.
- A hidden carious process , evolving in a difficult area for viewing - a tooth gap.
Classification according to the primacy of development of
It is not difficult to guess that this classification subdivides tooth decay into:
- primary , which affects either a healthy tooth or an area previously untreated;
- secondary , which is recurrent, since it develops on previously healed sites, sometimes this kind of carious process is called internal: the disease is often localized in the area under the seal or crown.
The choice of methods of therapy
The choice of the method of caries treatment depends on its type and degree of development.
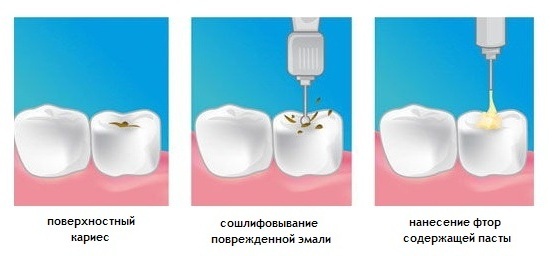
Spot treatment at site

Gel for remineralization of enamel
Implies a conservative method that excludes the need to drill a tooth. At the initial stage, a remineralization procedure is carried out.
The need for it is quite understandable: the carious process is accompanied by the washing away of calcium from the tooth enamel, and the therapy used in this case is aimed at filling the formed white strips or spots with the same calcium.
Drugs used today in the process of caries treatment at the initial stage, are much more effective than calcium gluconate tablets used earlier.
Modern products contain calcium and fluoride in ionized form, which easily penetrate into the tooth enamel, which can not be said for calcium gluconate, consisting of an almost insoluble salt.
About the treatment and prevention of tooth decay will tell the doctor dentist:
Treatment of superficial caries
In the process, the dentist performs a number of the following manipulations:
- Removes dental plaque with a brush and a special polishing paste.
- Isolates the tooth from the saliva .This is necessary to prevent the development of secondary caries and the rapid loss of a seal. Isolation is carried out using a cofferdam.
- Etching enamel with acid , after which it washes off the tooth surface.
- Applies adhesive , which acts as a glue for the seal. The agent is applied to the defect area and is illuminated by a light-polymerization lamp.
- Seals .A certain portion of the filling material is applied, after which the doctor models the missing part of the tooth from this composition and then lights it with a lamp.
- Grinds and polishes the seal with special dental equipment.
Treatment of medium caries
With an average form of the disease, a carious cavity is necessary to dissect. In this case, the algorithm of the specialist's actions remains classical:
-
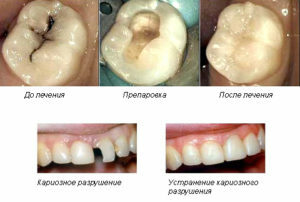 the tooth region affected by the caries is reamed( possibly anesthesia);
the tooth region affected by the caries is reamed( possibly anesthesia); - removes non-reconstructable dental tissues;
- enamel and dentin, which make up the walls of the carious cavity, are subjected to instrumental processing;
- cleared cavity is disinfected with antiseptics;
- an insulating gasket is placed in the cavity;
- the seal is established.
Treatment of deep tooth damage
Treatment can be started only after preliminary anesthesia. After cleansing the cavity, the doctor performs its sealing - this is the most typical option.
However, in the case of a deep form of the carious process, a lesion of the dental nerve is possible. In this case, the dentist resorts to depulpation of the tooth - the removal of soft tissue pulp, nerve, including.
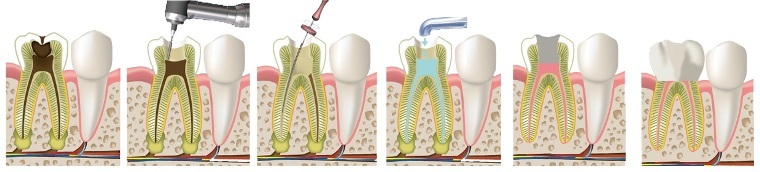
In the photo treatment of pulpitis
In case of timely treatment with deep caries it is possible to keep the tooth alive without removing the pulp. If belated measures are taken, the affected tooth should be removed.
Despite general awareness of the disease, caries carries a huge threat: the process sometimes proceeds very rapidly, damaging the dentin, and then penetrating into the soft tissue of the pulp, leading to the development of pulpitis and periodontitis( flux).Therefore, timely treatment of the disease - the guarantor of a further favorable prognosis for the patient.
After all, modern technology can not only relieve pain, but also restore the functionality and aesthetic appearance of the affected tooth without pain and threat to the health of the patient.