It is important for a woman to know how normally critical days should be: how many days they can last, how much blood loses the body in one cycle. And if suddenly there are clots of blood with menstruation, similar to the liver, is it normal? Many causes lead to increased bleeding during menstruation. It can be both an innocuous pathology that does not threaten life, and serious oncological diseases, as well as incipient miscarriage or systemic diseases. Blood clots can appear in women of any age, but where is the line between norm and pathology?
Causes of
If monthly out clots like the liver, the women this results in a state of panic. They really believe that parts of an organ come out from the vagina in this way. But this is fundamentally not true. Dark-bard, in consistence resembling jellies, of different sizes( from a few mm to 7-10 cm), clots are curled venous blood, possibly with areas of the rejected endometrium or fetal egg( in case of miscarriage).
In adolescence
For the normalization of menstrual function, adolescent girls are given about two years. During this period, critical days may occur with a different, sometimes rather long interval, and this is not considered a pathology. Still an immature organism reacts sensitively to a microclimate in a family, school. Stress, any psycho-emotional tension, whether it's a deuce for a lesson or a failure in the exam, is perceived by many girls to be too close. Negatively affected by excessive obsession with school. As a result, the sexual system reacts, and this is often manifested by juvenile uterine bleeding. Sometimes you can replace not only the increase in the duration of critical days to 14 or more, but also clots during menstruation, similar to the liver. Rarely, such symptoms may indicate an organic pathology in the adolescent organism, or anomalies in the development of the genital organs.
In the pathology of pregnancy
Often, the monthly lumps, like a liver, can accompany a woman during pregnancy. And that the lady is in an "interesting position", she may not even know. The threat of interruption sometimes passes in the early stages similar to menstrual discharge on the days of the expected menstrual periods. In this case, as a rule, together with the clots the woman feels pulling, even cramping pains in the lower abdomen. If there are many such extractions, the threat may have developed into a miscarriage.

Endometrial Pathology
In most cases, large clots with monthly, similar to the liver, are typical for women after 30 and even premenopausal age. It is caused by the pathology of the endometrium, which often occurs against the background of concomitant diseases. Women who have risk factors for developing these conditions:
- With polycystic ovary.
- With irregular monthly for other reasons. This is due to the fact that with non-systemic "cleansing" of the uterine cavity from the upper layer of the endometrium, there is an unregulated growth of the uterus with the formation of polyps and a change in the structure( hyperplasia).
- Overweight. Adipose tissue is hormone-active. Its excess leads to an increase in the level of estrogens in the blood, and they directly affect the intensity of the growth of the endometrium.
- With cystic changes on the ovaries.
- Having diabetes mellitus and thyroid pathology. The increase in the volume of menstrual blood will be due to changes in metabolic processes in the body.
The endometrial pathology can be expressed in the formation of polyps within the uterine cavity or in various types of hyperplasia. Clinically, both of them proceed in the same way - secretions with monthly clots, like the liver, or just very abundant, the number of critical days increases, and there may appear spotting in the middle of the cycle.
Anomaly of development of genitals
In abnormalities in embryogenesis during pregnancy, the formation of the structure of the genital organs is irregular. As a result, the body of the uterus can have a saddle shape, consist of two parts - a bicorne, etc. As a result, during menstruation, the contractility of the organ may be impaired, which leads to increased bleeding and clot formation.
Uterine fibroids
Nodules in the uterus can disrupt the process of normal rejection of the endometrium, deform the body cavity. Especially often this occurs with large-sized formations, and also located inside - submucous myomas. In such cases, women suffer from heavy bleeding during critical days, mark pieces with menstruation, similar to the liver. They can reach large sizes( up to 10 cm in length), appear day and night.
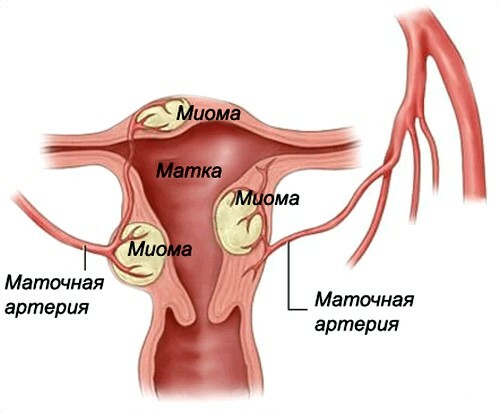
Myoma of the uterus - the cause of abundant secretions in the form of clots
Endometriosis
Adenomyosis - the defeat of the muscular wall of the uterus, almost always accompanied by pain and heavy menstruation, during which clots can also go out. The cause of endometriosis is not reliably established. It is believed that the "culling" of the endometrium is formed on the affected tissues. In the case of adenomyosis, the uterine muscle becomes similar to honeycombs, filled throughout the thickness with similar foci. As a result of this disease, the blood coagulation system, the contractile capacity of the organ, is disrupted. Together, this leads to a corresponding clinical picture.
Functional ovarian cysts
Often even during preventive examinations, enlarged ovaries are identified, on which ultrasound is defined as cystic formations. Sometimes they can bring pain and discomfort, including during sexual intercourse. Such functional cysts affect the hormonal background of the woman, contributing to the lengthening of the second phase of the cycle. Clinically, it looks like a delay or irregular monthly, and then very abundant discharge in critical days, with clots.
After the birth of
After natural birth and cesarean section, especially in the first 7 to 10 days, bloody discharge can normally be with clots. But more often this can be observed in the first three days. Bunches can be of different sizes - from minor to 10 - 12 cm in length. But a very large number of such secretions should always alert the woman, to serve as an excuse to call a doctor.
After cramping of the uterine cavity
Any interventions inside the uterine cavity, accompanied by scraping of its contents, may be accompanied by the appearance of clots immediately after the procedure. Such manipulations are carried out with abortion, miscarriage, as a measure of stopping bleeding. The formed clots in most cases are due to the accumulation of blood in the vagina, where it folds. As soon as the woman rises, the contents come out.
The presence of the intrauterine device
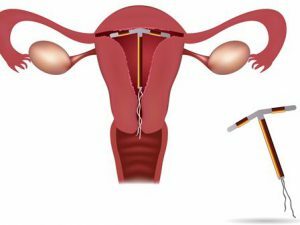
The intrauterine device as a cause of copious monthly clots
The intrauterine device, from which it would not have been made - from gold, silver or ordinary polymeric material, in 70% of cases causes an increase in the volume of menstrual blood. And women note in almost every cycle the presence of clots. The theory that miscarriages occur on a monthly basis, and this is the essence of its contraceptive effect, is absolutely groundless and has no proof. The contraceptive effect is due to the obstruction of the spermatozoa on the way to the egg, the inability of the fertilized egg to attach to the uterine cavity( but at this time the bleeding, especially with clots, can not be), aseptic inflammation, etc.
The plentiful monthly ones are caused by the individual reaction of the organism to a spiral,an increase in the endometrium, a violation of contraction of the uterus when finding a foreign body in the cavity. The exception is the hormonal spiral, the therapeutic effect of which is aimed at reducing the volume of lost blood and normalizing the growth processes of the endometrium.
Oncological diseases of the uterus and cervix
The number of malignant diseases of the organs of the female reproductive system is steadily growing. Ignoring many years of gynecological examinations, a woman condemns herself to identifying ailments in neglected forms. As a rule, it is cancer of the endometrium and cervix. The main manifestations are bleeding, often abundant and with clots.

Blood clotting disorder
For various thrombophilia, which are hereditary or acquired character, there may be a change in the intensity of blood loss during menstruation. Also, these pathologies can be hidden.
Other causes of
Some provocative moments that occasionally appear in the life of every woman cause an increase in bleeding during menstruation even with the formation of clots:
- First, it is physical labor on the eve or during critical days.
- Secondly, transferred before menstruation or during them infectious diseases. Even banal ARVI can cause lengthening of menstruation and the appearance of clots similar to the liver. Such influence is caused by the action of toxins of viruses and microbes on the coagulating properties of blood. As a rule, this only applies to one cycle, and the next month everything will be normalized.
Which allocation requires special attention
In any case, the presence of clots, especially large sizes, in menstrual discharge should alert the woman and cause an unscheduled examination at the gynecologist. Especially in the following situations:
- with regular menstruation with clots;
- if the pieces of coagulated blood are large;
- yield of clots is accompanied by pain;
- bleeding for all critical days of more than 150 - 200 ml;
- has an unusual unpleasant odor of secretions with clots;
- The woman began to notice shortness of breath, palpitation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, pallor of the skin. This indicates a monthly high blood loss, which requires treatment.
 We recommend that you read an article on profuse menstruation. From it you will learn about the symptoms of pathology, the most common causes of its occurrence, types of menorrhagia, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
We recommend that you read an article on profuse menstruation. From it you will learn about the symptoms of pathology, the most common causes of its occurrence, types of menorrhagia, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Treatment options for pathology
Treatment depends on the cause that caused an increase in the volume of blood loss during menstruation, including through the formation of clots.
Conservative therapy
It is aimed at eliminating bleeding factors and replenishing iron stores in the body. Includes:
- Treatment and protection mode. Particularly important with juvenile uterine bleeding.
- Cyclic vitamin therapy, especially group B, A, E and C, folic acid.
- The use of iron preparations with a decrease in hemoglobin.
- Hormone therapy.
Operative treatment
It is aimed at removal of pathological endometrium, uterine fibroids, septum inside, etc.in various ways - from scraping to hysteroresectoscopy. In difficult situations and with recurrent pathology, as well as in case of malignant diseases - removal of the uterus.
Menstruation in a woman should not bring excessive discomfort and lead to disruption of life. In most cases, blood clots, like liver lumps during critical days, are a pathological condition that requires adequate and competent treatment. Otherwise, you can skip serious diseases, including cancer.
