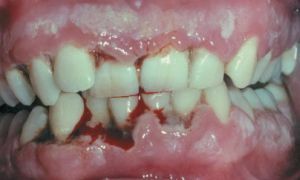
 Ulcerative necrotic gingivitis Vincent( YANGV) is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the gums. The disease develops by itself or simultaneously with other pathologies, worsening their course. The medical name of the disease is Vincent's gingivitis.
Ulcerative necrotic gingivitis Vincent( YANGV) is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the gums. The disease develops by itself or simultaneously with other pathologies, worsening their course. The medical name of the disease is Vincent's gingivitis.
Most often the disease is preceded by untreated catarrhal gingivitis, which has passed into a more serious recurrent form.
A particular feature of this form of pathology is acute inflammation, which is accompanied by ulcers and changes in the necrotic form of the gingival mucosa.
A person with time develops pain in the mouth. Yangw can quickly move into the stage of subacute or chronic development.
Most often, ulcerative necrotic gingivitis develops in the anterior teeth region, the disease manifests less frequently in the region of the lateral teeth. In the absence of treatment, there is a high likelihood that the disease will be transformed into peptic ulcer.
Contents
- Causes of pathology
- Forms and stages of development
- Clinical manifestations and symptoms
- Diagnosis methods
- Treatment regimen
- Consequences - what's the danger?
- Preventive measures
Causes of pathology
Most often ulcerative gingivitis occurs in people who have decreased local immunity. Under the influence of negative factors there is a pathological expansion of the colony spirochetes Vincent and Fusobacteria( under normal conditions are not dangerous).As a result, the inflammatory process develops.

Pathological development is promoted by factors of local and general action. To a number of local reasons carry:
- poor-quality carrying out of daily procedures on care of an oral cavity;
- frequent damage to the oral mucosa by damaged teeth;
- inaccurately fitted dentures;
- incorrectly installed braces;
- prolonged diseases, weakening the immune system;
- chronic oral infections;
- teething wisdom;
- congenital or acquired anomalies of the location of the teeth.
Common causes that provoke the development of Vincent's gingivitis are:
- state of chronic fatigue and lack of sleep;
- hypovitaminosis;
- general body hypothermia;
- permanent stay in stress;
- exposure to radiation;
- pathology of chronic form( heart disease, blood vessels, HIV and others);
- transfer of acute infections;
- intoxication;
- improper diet;
- is a bad habit.
Forms and stages of development of
Gingivitis Vincent may occur in acute or chronic form, the differences of which are the causes, symptoms and progression of the disease.
Acute ulcerative gingivitis occurs because of untreated catarrhal disease and with reduced immunity. For this form of Yangwi is characterized by a sharp onset and rapid development of the disease. The paramount sign is the painful condition of periodontium, which makes it difficult to clean teeth and eat food. The remaining symptoms occur between a few hours and 3 days.
The maximum number of cases occurs in the winter due to a weakened state of the body due to seasonal diseases.
Chronic ulcerative gingivitis develops for several years against a backdrop of poor oral care and teeth. During this time, periodically there is bleeding and swelling of the gums.
The mouth has an unpleasant odor, and ulcers are formed. Gradually, there is a violation of the stability of certain teeth. The chronic form of the disease is most common among adolescents who are poorly monitored for oral hygiene.
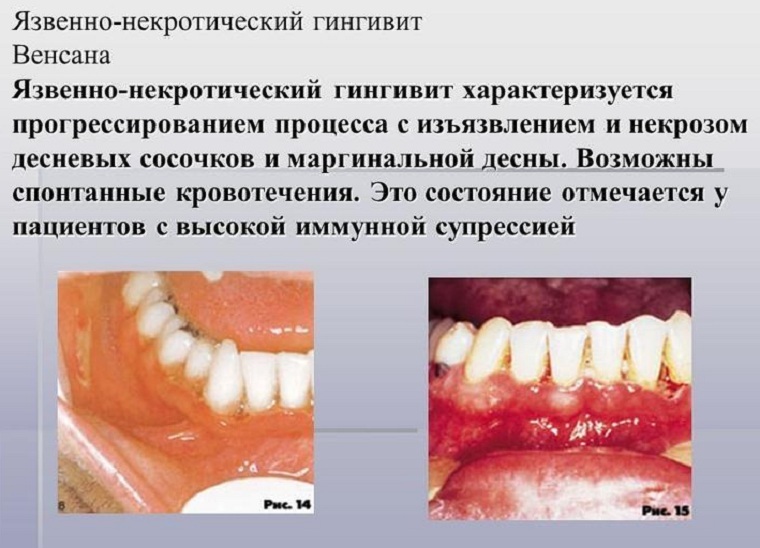
The disease is characterized by 3 stages of percolation: 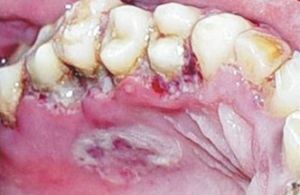
- is an easy - a calm course of the disease, in which the interdental papilla are affected mainly;
- mean - inflammation covers both the interdental papillae and the free gingiva;
- severe - an inflammatory process that seizes the entire gum with its alveolar part.
Depending on the location, necrotic gingivitis can be localized and generalized. With a localized type, the inflammatory condition extends to one or more unconnected gingival sites. The generalized type is characterized by the spread of inflammation to the gum area of all the teeth of one or both jaws.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
The initial stage of Vincent's gingivitis is clearly pronounced and active, the symptoms are acute. Throughout the body, toxins spread rapidly. This is characterized by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, severe headaches and discomfort in the muscles. Local toxic reaction on the gums is manifested:
- by tissue swelling;
- by the processes of infiltration of the gums with leukocytes;
- is the primary formation of necrotic changes.
The main symptoms of YANG are:
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- pain at the site of inflammation;
- pale fibrous plaque on the expressed surface of the mucous gum;
- tissue necrosis of the gingival margin;
- unpleasant taste and smell from the mouth;
- crater-like ulcers between teeth and gums;
- bleeding even with light pressure;
- expression of the gums adjacent to the teeth;
- uncomfortable sensations in the oral cavity;
- an increase in regional lymph nodes and the appearance of pain during their palpation;
- feeling unwell.
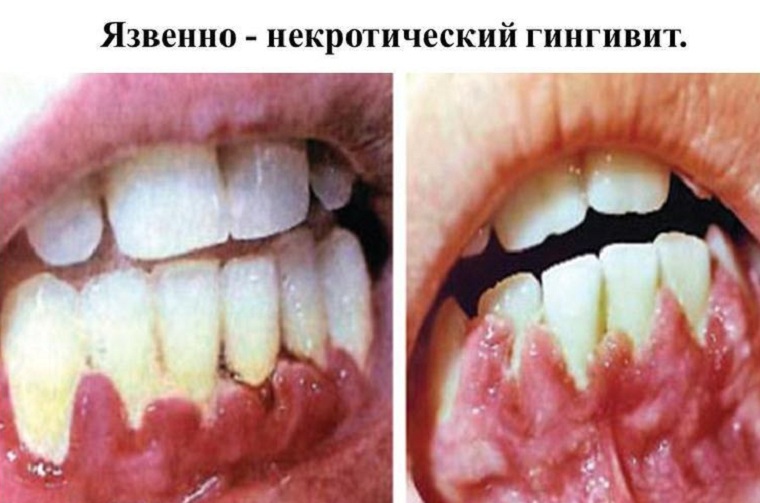
How does peptic gingivitis look like in life, you can see on the photo
Methods of diagnosing
Treatment of ulcerative necrotic gingivitis of Vincent begins after an accurate diagnosis. To do this, the dentist conducts a patient interview, listens to his complaints and performs an examination of the entire body. In addition, a number of diagnostic studies are assigned, which include:
- carrying out functional studies of ( Schiller-Pisarev test);
- laboratory tests ( general blood and urine test, determination of immunoglobulin A level in saliva, detection of pathogen);
- instrumental research ( reoparadontography, orthopantomography).
When diagnosing it is important to exclude secondary gingivitis, formed on the background of tuberculosis or pathologies of the circulatory system.
Consultations of specialists of other specialization( immunologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist and others) are often required. Based on the results of all the examinations, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment Scheme
 The main goal of treating necrotic gingivitis is to remove unpleasant symptoms and gradually restore periodontal disease. Therapy is carried out in a complex manner. Treatment measures include actions of local and general localization. Necessarily recommended dietary food with a full content of useful ingredients and abundant drink.
The main goal of treating necrotic gingivitis is to remove unpleasant symptoms and gradually restore periodontal disease. Therapy is carried out in a complex manner. Treatment measures include actions of local and general localization. Necessarily recommended dietary food with a full content of useful ingredients and abundant drink.
With local treatment, the inflammatory process on the oral mucosa is eliminated, pain relief is removed, tissues are exposed to necrosis, reduces intoxication, regenerates the gums.
Local treatment includes the following steps:
- Analgesia .The procedure is performed using injections of analgesic effect( infiltration and conductive anesthesia), which requires 5% anesthesin suspension, 2% Lidocaine solution, 2% Trimekaine solution, 20% application anesthesia or benzocaine gel.

- Treatment of the gums with antiseptics .The procedure is carried out with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, 0.02% Furacilin solution, 0.06% Chlorhexidine solution or 0.25% chlorophylliptine solution. It is prescribed rinsing with antiseptic means three times a day after eating.
- Disinfection of the gingival margin of in the focal region( 3% tincture of iodine).
- Elimination of the plaque of the necrotic nature of and deposits on the teeth in the affected area.
- Reprocessing with antiseptics .
- Removal of necrotic formations from the gums by the chemical method .To do this, use applications of the solution of Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Himopsin, Terrylitin for 15-20 minutes.
- Treatment with antibacterial drugs .For 15-20 minutes apply applications with Iruksol, Dermazin, 1% Dioxydin, 10% Dimexide. Then the procedures are carried out independently at home for 15-20 minutes three times a day.
- After 3, 5, 7 days after rejection of necrotic formations keratoplastic preparation in the form of applications is used. Use Metiluratsil, Actovegin, rosehip oil, sea buckthorn oil, vitamin A in the form of an oily solution. Treatment is done independently at home 2 to 3 times a day for 15 to 20 minutes.
For general therapeutic effect, take sulfonamides, antibacterial drugs, antihistamines, vitamins C and P, stimulants of the immune system. In addition to therapy, physiotherapy is prescribed( laser treatment, UV, ultraphoonophoresis).
Patients with serious complications are assigned an additional examination by a therapist, hematologist, endocrinologist, venereologist.
Consequences - what is the danger?
The mild degree of Vincent's gingivitis equals catarrhal appearance. With timely treatment, the patient has a high chance of recovery. But the deformed edge of the gum remains so forever.
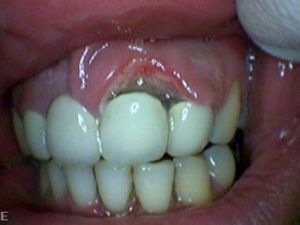 Disease of the middle and severe degree is complicated by necrotic epithelial decomposition. The consequence can be the destruction of the contour, both the gums and papillae, and the exposure of the necks of the teeth. Even after the treatment, there are scars on the gum and not passing through deformed tissues.
Disease of the middle and severe degree is complicated by necrotic epithelial decomposition. The consequence can be the destruction of the contour, both the gums and papillae, and the exposure of the necks of the teeth. Even after the treatment, there are scars on the gum and not passing through deformed tissues.
The lack of correct and timely treatment often causes the transition of the disease from the acute form to the intermediate chronic stage, and even into the periodontitis of the chronic type. In such a situation, the probability of tooth loss is high.
In nursing mothers, this disease causes periodontitis, which provokes the destruction of the tissues of the gums and jaw bones, an abscess, and tooth loss.
Preventive measures
To minimize the risks of formation and development of YangGu it is recommended:
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- adhere to a balanced diet, with a full content of important vitamins and trace elements;
- to properly care for the oral cavity;
- to avoid stressful situations;
- regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist;
- conduct timely treatment of infections, especially in the oral cavity;
- to abandon bad habits.
It is impossible to leave primary signs of ulcerative necrotic gingivitis, as the absence of treatment of the disease can cause serious problems in the future.
