 Phlebology is a special section of vascular surgery that deals with varicose veins and other diseases of the veins.
Phlebology is a special section of vascular surgery that deals with varicose veins and other diseases of the veins.
According to the World Health Organization, the problems of venous disorders occur so often that they are included in the list of "diseases of civilization".Therefore, the importance of this direction in medicine is undeniable.
Contents
- Functional tests in phlebological practice
- Functional tests in phlebological practice
- Assessment of deep vein condition
- Evaluation of insufficiency of superficial veins
- Evaluation of valve insufficiency of communicative veins
- Diagnosis for trophic ulcers
- Used for thrombophlebitis
- Assays for the diagnosis of venous insufficiency
- Assessment of the state of veins in case of suspected varicosity
- Samples for the diagnosis of varicocele
Functional tests in the phlebological practice
To determinethe cause of the disease associated with veins, modern medicine uses functional tests and instrumental methods. The first type of research is widely used at present and provides guaranteed results, based on which further treatment of the patient occurs.
Samples and specific symptoms make it possible to investigate changes in the performance of various body systems and, based on data on these changes, assess the severity of the disease, the load, the body's response to a certain effect, its compensatory capabilities.
Functional test is designed to study the reaction of a particular system to the influence of some factor, most often it is physical activity. Any functional tests begin with the determination of the initial data of the investigated parameters of the venous system.
Then compare them with the same indicators immediately or after exposure to a certain factor and to a state of rest. These data determine the nature and duration of treatment.
If the clinical trial is performed in accordance with the rules and a qualified specialist, then it is possible to accurately determine the diagnosis in the majority of patients with pathology of veins. Qualification of the doctor is of great importance, becausefor taking functional tests requires a special skill.
All functional tests known to modern medicine can be divided into three categories:
- for determining the permeability of deep veins;
- assessment of valvular insufficiency of superficial veins;
- study of valvular insufficiency of communicative veins.

The purpose of each clinical trial is to analyze the venous state of any of the above categories.
Deep vein assessment
Clinical trials for deep venous penetration:
- The Delbe-Perthes probe or as it is also called the marching. In the process of its study, the reaction of veins below the
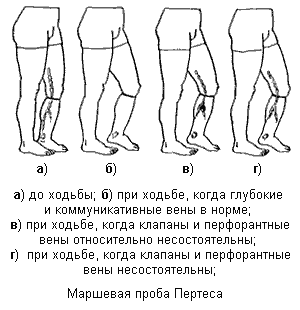 harness is studied after an active five-minute walk. They can fall off or fill, the result depends on it. The patient should lie on his back so that the subcutaneous veins are sufficiently filled. The doctor puts a tight bandage on the thigh so that the pressure is solely on the subcutaneous veins. The patient rises and starts walking or marching for five minutes. After the time set, the result is evaluated. The fall of the subcutaneous veins means that the deep ones are okay. If swelling of the subcutaneous veins is observed, a conclusion is made about the impassability of the deep veins. However, swelling may indicate not only a disease, but also an incorrect sample. When the tourniquet is too tightened or there are pathologies of the vein walls.
harness is studied after an active five-minute walk. They can fall off or fill, the result depends on it. The patient should lie on his back so that the subcutaneous veins are sufficiently filled. The doctor puts a tight bandage on the thigh so that the pressure is solely on the subcutaneous veins. The patient rises and starts walking or marching for five minutes. After the time set, the result is evaluated. The fall of the subcutaneous veins means that the deep ones are okay. If swelling of the subcutaneous veins is observed, a conclusion is made about the impassability of the deep veins. However, swelling may indicate not only a disease, but also an incorrect sample. When the tourniquet is too tightened or there are pathologies of the vein walls. - The Mayo-Pratt test is considered complete only if there is sufficient arterial supply to the limb, characterized by pulsation on the foot. The patient is lying on the couch lying on his back and lifting his leg to empty the superficial veins. Next on the thigh, near the groin fold, have a fixative bandage, designed to squeeze the superficial veins. Then completely bandage the foot, leaving only the fingers free. The patient should walk in such a bandage for 30-40 minutes. If after this time there is a pain, especially in the calf area, then this is an indicator of obstruction.
Samples that determine the inconsistency of superficial veins
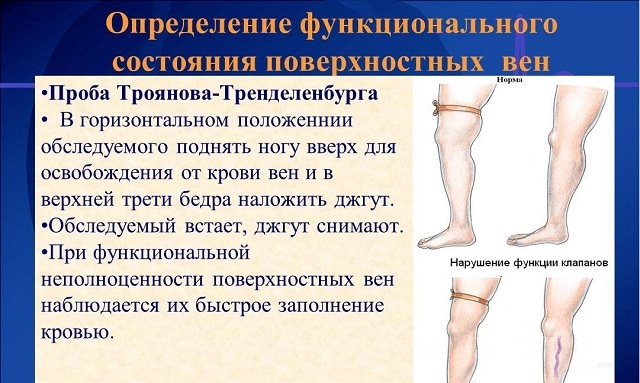
The Brody-Troyan-Trendelenburg test is considered the most common.
The patient lies on his back, draining the veins with his legs. The limb is stroked by the hand from the foot to the groin area, thereby freeing the veins from blood. After this procedure, the vein is occupied by a tourniquet or by pressing the finger in the uppermost region. Next, a fifteen-second observation of the affected veins, after the patient was on his feet.
The result can be interpreted according to four characteristics:
- Negative result of .The large saphenous vein quickly fills with blood for 5-10 seconds and after the removal of the tourniquet its degree of filling does not increase. The result indicates that the valves of the perforating veins are untenable.
- Zero result .If, regardless of the removal of the tourniquet, the blood fills the vein gradually and slowly, then it can be said that the consistency of the superficial and perforating veins is beyond doubt.
- Positive result .If, after the patient has gotten on his feet and the tourniquet has been removed, the large saphenous vein quickly fills, this indicates a general failure of the valves of this vein.
- Double positive result of .Vienna at the same time is filled quickly and after removing the tow, the degree of filling is increased. This indicates that the large subcutaneous and valvular vein is not in order.
Other samples of this plan:
- Testing the symptom of Gackenbruch-Sikar is to feel the tremors with the help of palpation during the time when the patient fictitiously coughs. The brush is placed on the joint of the femoral and subcutaneous veins. As a result, intracavalous and intra-abdominal pressure rises sharply and a push can be felt under the fingers. If such a cough push occurred, this indicates a deficiency of the ostial valve, the sample is considered positive.
- Test of Schwartz-McKeling-Heyerdahl , also called percussion-palpation test. In fact, the Schwartz and McKeling-Heyerdahl test are two different samples. They are similar, therefore united in one. According to Schwartz, the patient needs to take an upright position to contribute to sufficient stretching of varicose veins. The specialist feels a place in the upper part of the thigh where the large saphenous vein ends and puts the palm in this place, and with the fingers of the second hand it makes light pushes down the nodes. If the shocks are transmitted - this is the failure of the valves. McKeling and Heyerdahl suggest acting according to the Schwartz scheme, but jerky movements should be made in the oval fossa region, and the second hand should be above the tibia or knees on the affected veins.
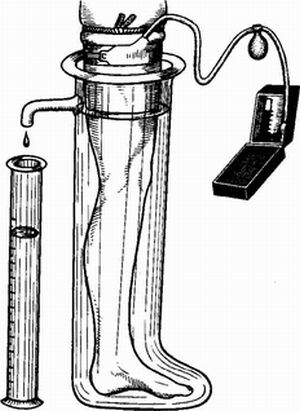
- The test of Alekseev-Bogdasaryan is carried out with the help of a special vessel resembling a boot. At the top, it has a drain cock. The vessel is filled with water that does not exceed 34 degrees. The veins of the leg are emptied, a fixing bandage is applied on the groin fold. The leg is placed in a vessel with water. The liquid expelled under the weight of the leg, with the help of a tap, flows into the measuring vessel. Its volume is measured. Then the tourniquet is removed, the blood rushes down the veins, correspondingly, the leg volume increases. The additional liquid is again forced out through the tap. The measurement time is 15 seconds. This determines the arterial-venous influx. The volume of arterial inflow is determined after 20 minutes. Carry out the same procedure, only under the tourniquet have a blood pressure monitor with a pressure of 70 mm Hg.
Evaluation of valvular insufficiency of communicative veins
For this purpose, samples are taken:
- Pratt-2 test requires the patient to lie on his back. The veins must be emptied( by lifting the leg).Further,
 is applied to the bandage, starting the procedure from the foot. Slightly below the inguinal fold on the leg is a tourniquet. The patient rises to his feet. The specialist has a second bandage right under the harness, during the time when the lower bandage is gradually removed. Such manipulation is carried out to the very bottom. The lumen between the two bandages should be 5-6 cm. If the varicose nodules in the free area quickly fill, this indicates the failure of the valves of the communicative veins.
is applied to the bandage, starting the procedure from the foot. Slightly below the inguinal fold on the leg is a tourniquet. The patient rises to his feet. The specialist has a second bandage right under the harness, during the time when the lower bandage is gradually removed. Such manipulation is carried out to the very bottom. The lumen between the two bandages should be 5-6 cm. If the varicose nodules in the free area quickly fill, this indicates the failure of the valves of the communicative veins. - The Valsalva test consists of inhaling air through a tube connected to a manometer for 15 seconds. The patient is in the position lying on the back. In carrying out this study, the diameter of the vessels increases by almost 50%.
If the retrograde flow of blood occurs and the pressure in the vessels of the lower extremities increases, then we can talk about the failure of the valves of the veins.
Diagnosis with trophic ulcers
Trophic ulcers can occur due to any problems with deep or superficial veins and are accompanied by venous insufficiency. To make a diagnosis, you need to establish a disease, through the fault of which and there was an ulcer. This is very important, because the treatment and prognosis are largely dependent on venous pathology.
In case of this disease, specialists can use Brody-Troyanov-Trendelenburg and Schwartz samples. In addition, ultrasound of lower extremities and duplex ultrasound are used.
Used for thrombophlebitis
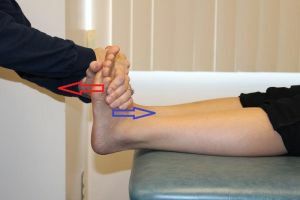 A blood clot may appear in the blood vessel due to problems with blood outflow or if the vein wall is inflamed. The disease can affect both superficial and deep veins.
A blood clot may appear in the blood vessel due to problems with blood outflow or if the vein wall is inflamed. The disease can affect both superficial and deep veins.
Therefore, for the diagnosis apply march test, Mayo-Pratt, Schwartz, Alekseev-Bogdasaryan, the symptoms of Homans and Moses are revealed.
The cough symptom of Gakkenbruch clearly characterizes thrombophlebitis,when coughing, there is pain in the legs.
Assays for the diagnosis of venous insufficiency
Venous insufficiency characterizes the first stage of varicose veins. The disease can be localized in the superficial, deep veins or both.
The examination includes 3 tasks: to find out how the saphenous veins are enlarged, to analyze the deep state( functional and anatomical), to determine where the communicative veins with insolvency are located. Based on these tasks, any of the above is performed, which the doctor considers necessary to conduct.
Assessment of the state of veins with suspected varicose veins
In varicose veins, many functional tests are used, but the most effective ones are used. Most commonly used are: Trianov-Trendelenburg, Mayo-Pretta, Delbe-Perthes, Pratt-2.
Samples for the diagnosis of varicocele
Varicocele is characterized by the pathological condition of the vein of the spermatic cord as a result of malfunctioning of the testicle. Initially, the disease is asymptomatic and it can be recognized only with the help of the Valsalva trial. Sometimes a cough test is performed( Heckenbruch-SikaSikara test).
Functional tests can tolerate inaccuracies, therefore specialists use along with them other methods of research, called "instrumental"( ultrasound angioscanning, Doppler, radionuclide and radiopaque phlebography, clearance method, etc.).
After clinical trials showing the degree of valvular insufficiency of superficial, deep, communicative veins and other necessary studies, a final anamnesis develops. And only after this, individual treatment can be prescribed.
