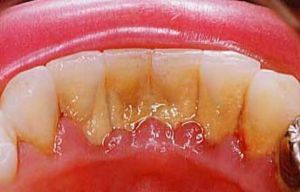
 Surface formations and deposits on the teeth affect the condition of the oral cavity and become one of the reasons provoking caries and periodontal disease.
Surface formations and deposits on the teeth affect the condition of the oral cavity and become one of the reasons provoking caries and periodontal disease.
Tooth deposits take various forms - from thin and soft films to hard formations. Depending on their consistency and appearance, they to a greater or lesser degree threaten the health of the oral cavity.
Contents
- Nature of formations
- Physiological and pathological formations
- Physiological entities
- Tooth deposits of pathological nature
Nature of
formations All surface formations on teeth are subdivided into physiological, due to their structure, and pathological. The latter are formed due to bacteria accumulating in the oral cavity, as well as food residues.
This is the result of improper care of the oral cavity and neglect of preventive measures to improve the dentition.
Of particular interest are pathological deposits, since physiological, in most cases, do not provoke dental diseases.
Such deposits develop gradually: first they take the form of a soft coating, and then, as crystals grow, they turn into hardened masses and stones.
Physiological and pathological formations
The cuticle and pellicle are referred to surface films of physiological nature.
Pathological deposits are dental plaque, tartar, plaque of various kinds.
The pathological nature of the formation is due to: 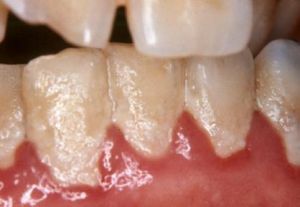
- of unsatisfactory oral care;
- prevalence in the diet is too soft food;
- incorrect bite;
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- damages the structure of the enamel.
Such deposits provoke the destruction of enamel, gum disease, caries, bad breath. In addition, because of them, teeth do not look aesthetically pleasing.
Physiological formations
The purpose of physiological films on the teeth is natural protection of the oral cavity from the development of pathogenic microflora.
Cuticle( Nasmite sheath) is an organic coating covering the surface of the enamel. It consists of two layers - internal and external. The inner layer is also called the primary cuticle, the outer layer is called the secondary cuticle. They are very thin, they are erased almost immediately after teething and if left, only partially, on approximal surfaces. That is why the cuticle does not take part in the physiology of the teeth.
Pellicle, unlike the previous deposit, is formed on the surface of the tooth enamel for life. This formation is also called the acquired cuticle. It is present in every person, covers the entire surface of the crown, appearing after the eruption of the tooth. It is a transparent, thin layer.
Organic film is formed from gel-like components of saliva, does not contain active microflora, is characterized by high concentration of proteins.
This formation is formed on the enamel, has three layers - subsurface, surface and supersurface. This structure makes the pellicle a semipermeable membrane.
To some extent, the shell protects the integrity of the enamel structure, protects hard tooth tissues from the effects of acids. At the same time, the pellicle promotes the attachment of bacterial microorganisms to the surface of the teeth, which leads to the formation of plaque.
This film can create aesthetic problems when it is dyed with food colors( tobacco, coffee, tea).In this case, the film is erased with hard materials - abrasives.

Dental deposits of pathological nature
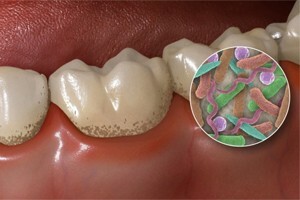 Dental plaque is a soft deposit with a multilayer structure formed on the surface of the pellicle. In this formation are almost all representatives of microflora, characteristic of the oral cavity.
Dental plaque is a soft deposit with a multilayer structure formed on the surface of the pellicle. In this formation are almost all representatives of microflora, characteristic of the oral cavity.
Plaques are localized in the interdental spaces, the cervical region, the natural depressions of the tooth. It is a cluster of bacterial microorganisms and products of their vital activity. The basis of the deposits are substances that fall on the surface of the teeth along with saliva. Here the bacteria get the conditions for active reproduction. Further, they are joined by external microorganisms that cause caries and inflammation of the gums.
As the mass of the plaque increases, more and more bacteria do not accumulate in it, which do not require oxygen to provide vital activity. These microorganisms affect the tooth enamel, destroying it.
Plaque is another type of superficial formation. It is present in all people and is a film consisting of food particles, bacteria, epithelial cells and some inorganic substances. The plaque can be soft or dense.
It fits snugly to the surface of the teeth. In most cases, it does not have a color, but under the influence of certain factors it can be colored.
Most often, dental plaque is observed in the cervical areas, above the gums.
Depending on the color, these types of plaque are distinguished:
- White plaque has a soft structure. It becomes the source of such problems as destruction of enamel, smell from the mouth, caries.
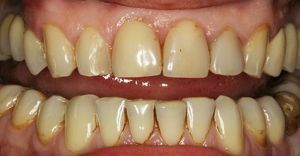
- Brownish with a yellow shade of .It occurs as a result of the coloring of the primary deposit with pigments. Colorants are contained in coffee and tea. Such a coating creates conditions for the formation of tartar, causes increased sensitivity, provokes bleeding and inflammatory processes of the gums.
- Greenish .Plaque of this color indicates a dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity. It is often observed in childhood and adolescence. The deposition spoils the appearance of the teeth, causes irritation of the gums and their inflammation.
- The brown is formed for several reasons. First of all, it is observed in smokers, as the resin penetrates deep into the enamel layers, giving it a specific color. Also, brown coating can indicate a high content of iron in saliva. Promotes the formation of calculus, increases the sensitivity of teeth.
- Black .It is usually formed in children due to dysbiosis and the activity of fungal flora. He can also point to diseases of the liver and bile ducts. It leads to inflammation of the gums, represents an aesthetic defect.
Dental stone is a crystallized deposit formed from a soft mass of plaque. It contains such organic components as proteins, epithelial cells, polysaccharides.
The stones are characterized by considerable density. It is localized on the inside of the teeth, in periodontal pockets, as well as on the surface of dentures. Defeating the enamel, it gradually sprouts into the gingival canal.
This formation is manifested in the appearance of dark spots on the teeth, itching sensation in the gum area, bleeding, loosening of the teeth.
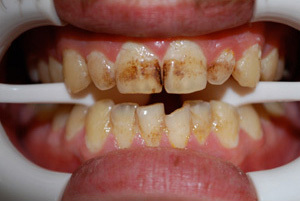 Such deposits not only destroy the enamel, but also provoke the development of caries, inflammatory processes of the gums.
Such deposits not only destroy the enamel, but also provoke the development of caries, inflammatory processes of the gums.
Superficial formations on the teeth, which have a pathological nature, provoke the development of diseases of the oral cavity. They are formed from bacterial organisms, the products of their vital activity, the remains of food.
With improper care, as well as in the presence of concomitant dental diseases not cured in time, dental deposits develop and can eventually cause damage to the integrity of the enamel, dentin and root.
