 Fracture of the lower jaw is a violation of the integrity of the bone for some reason. Often this is due to mechanical effects, is somewhat less likely to result from the development of common diseases.
Fracture of the lower jaw is a violation of the integrity of the bone for some reason. Often this is due to mechanical effects, is somewhat less likely to result from the development of common diseases.
This problem occurs more often in males.
Contents
- Classification and types of injuries
- Trauma of the angular part of the mandible - angular fracture
- Common causes and mechanisms
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnostic criteria
- How is the first aid performed?
- Treatment methods
- Probable consequences
Classification and types of injuries
Fractures can be industrial and non-industrial, which occur in 90% of patients. And, as for the last form of injury, it in turn is divided into:
- street;

- household( most common);
- sportswear;
- transport and others.
In addition, specialists use the most convenient classification system Malyshev and Kabkov. Proceeding from it, all the mandibular injuries differ:
- on the consequences of : lack of a tooth or finding a tool in the moon;
- for areas of lesions of : fracture of branch, base of condylar process or process of lower jaw;
- in form : latent or open fracture;
- by type : linear, comminuted fracture, damage with or without fragments displacement;
- fractures in place of pressure - direct and at a distance - indirect;
- in direction : transverse, longitudinal, zigzag and oblique;
- small- and coarse-fragmented fractures;
- by the number of injuries : multiple, double or single;
- at the location of : two-sided and one-sided.
A fracture can occur under the force of an excess of the tooth's power - traumatic and the one that was obtained by the force, which is weaker than the characteristics of the incisors - caused by a pathological disease.
Also worth noting, the following groups of injuries:
- fracture of the front teeth( from the canine to the canine);
- teeth injuries from the fangs and in the side;
- angular fracture.
When the fragments move, the mucosa of the alveolar tissue break, in fact, like the periosteum. And in the event that trauma and crowns and roots occur, the connective tissue is completely or partially torn.
Injury of the angular part of the mandible - an angular fracture
This type of fracture can be in reflected form or in a straight line. If the fracture occurs at the site of the force, a straight form is diagnosed, and in the symmetrical one it is reflected.
Also, the angular fracture can be one-sided and two-sided:
- Two fragments in the corner of the jaw are formed with the unilateral form .They have completely different sizes. In this case, the smaller
 fragment is shifted to the top and closer to the front, and having a larger size - down to the rear. The situation is different when the wisdom tooth is in a smaller fragment, then it moves upwards and can come into contact with the oppositely placed tooth. In the absence of the second and third molars at the top, the lower wisdom tooth will rest against the mucosa of the alveolar process, which is located above it. This can cause traumatic erosion and ulcers.
fragment is shifted to the top and closer to the front, and having a larger size - down to the rear. The situation is different when the wisdom tooth is in a smaller fragment, then it moves upwards and can come into contact with the oppositely placed tooth. In the absence of the second and third molars at the top, the lower wisdom tooth will rest against the mucosa of the alveolar process, which is located above it. This can cause traumatic erosion and ulcers. - As a result of two-way damage to fragments is formed a little more, actually their implementation can be realized in other parts.
With an angular fracture, attempts to move the jaw are accompanied by painful sensations. In addition, soft cheek tissues become swollen in the parotid-chewing part of the lower jaw.
In this case, specialists will not be able to palpate the affected area, since this will interfere with the chewing muscle. To determine the location of the fracture, you should look for the most painful point. In addition, in order to diagnose this form of injury, an X-ray will be required.
Common causes and mechanisms
The most common jaw fractures in the area of angles, cheeks, incisors and canines. Often this happens as a result of an accident, impact, fall, professional and sports factors. In the future, the degree of trauma will determine what consequences await the patient, as well as the structural and physiological state of the bone prior to fracture.
There are the following mechanisms that can provoke a fracture:
- In places where bone tissue is less thick or curved, bends ( fang, angle of jaw and others) occur. Subsequently, because of an inflection, a fracture occurs.
- pressure comes from below, where there is no support, and subsequently the shift occurs.
- Compression is characterized by simultaneous impact and resistance. In this case, the blow comes from the bottom up into the corner area.
- The gap is the result of the pressure from the top when the jaw is closed. Attached to a thin coronoid process powerful temporal muscle in the process of injury can come off the branch of the jaw.
Features of the clinical picture
Symptoms indicating a fracture of the mandible:
- asymmetry of the face;

- pain even with light touches;
- mobility of fragments;
- violation of the usual position of the incisors;
- bite violation occurs;
- increases the excitability of the incisors;
- painful sensations;
- marked respiratory and speech impairment;
- appears dysfunction of the masticatory and swallowing reflex;
- also shows the hyperactivity of the salivary glands;
- gaps appear between the teeth in the affected area;
- marked loss of sensation and numbness in the chin and lips;
- the patient experiences weakness.
Also more serious signs are possible: nausea with all the ensuing sequelae, concussion, hemorrhage from the ears and fainting. Depending on the severity of injury, the clinical picture may change. In addition, the time that passed after the injury and other factors also plays a role.
Diagnostic criteria
In order to establish the shape and severity of injury diagnosis should be carried out comprehensively. Specialists are currently conducting the following activities:
- non-vascular examination of - examination of the jaw from the outside;
- intraoral inspection ;
- is performed by the X-ray study of to exclude multiple and bilateral fractures.
How is first aid provided?
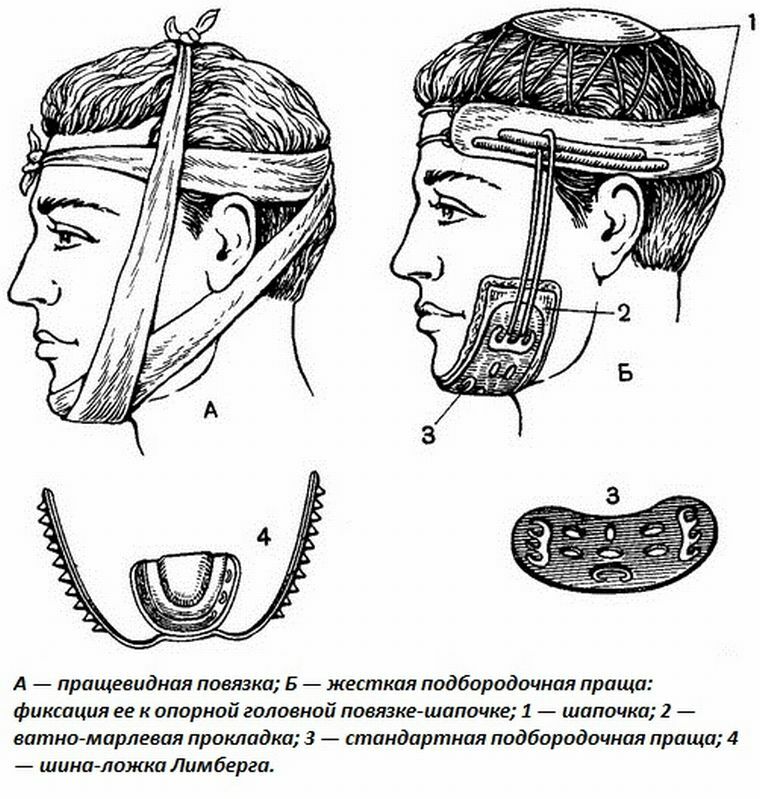
In respect of the victim, it is necessary to carry out anti-shock therapy and prevent asphyxiation( the person is lying on his side or settles down).In addition, transport immobilization is necessary - a rigid bandage bandage is applied to the chin, and hemorrhage is stopped by using bandages and other materials.
If as a result of a fracture bleeding from the artery is observed, then pressing the vessel will be necessary to stop it. The injured person should remain in a conscious state, in case of a fainting, the tongue must be fixed to prevent its sinking. All further activities are already carried out by specialists in the hospital.
Methods of treatment
Specialists treat wounds and bind large blood vessels and trachea if necessary. A special tube is also introduced to facilitate breathing. There are also anti-shock procedures.
Depending on the nature of the damage, therapeutic measures are carried out, which involve the following manipulations:
- specialists under local anesthesia combine fragments;
- for the period of recovery by means of tires, fragments are fixed;
- in the fracture region creates comfortable conditions, so that the healing process takes place much faster;
- also uses physiotherapy, prescribes vitamins and antibiotics to strengthen and prevent infectious-inflammatory complications.
If there is a need in the future, the doctors resort to surgical procedures:
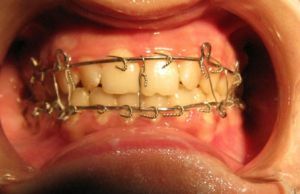
Shinning - a method of treatment that is often used for fracture of the lower jaw
- uses medical wire or a nylon vein to sew the bone;
- may also require bone consolidation( medical knitting needles are used);
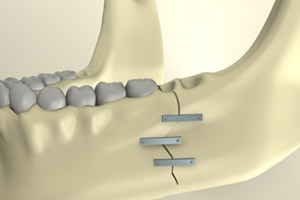
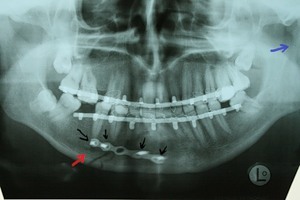
- also uses bone metal plates, thus the fragments are fastened;
- requires the installation of additional structures for bonding the bone from the outside.
If severe damage is observed and the appearance is severely damaged, the plastic surgeon may need to be medicated. When all the activities are over, the tires have already been removed, medical gymnastics and mechanotherapy are being carried out in order to restore the jaws of the former mobile abilities and chewing functions.
Probable consequences
It can be observed:
- change of the location of the incisors from the whole row;
- as a result of damage shifting fragments;
- atrophy bite;
- pain in the lesion;
- can have problems with habitual possibilities, chewing, speech, swallowing and respiratory function is broken;
- in the lower part of the skull may feel numb;
- as a result of a double fracture marked by a tongue sinking;
- headaches, pre-syncope, dizziness and nausea;
- general weakness.
In addition to the above-mentioned consequences, the work of some other organs may be disrupted as a result of a fracture, and the development of serious diseases( osteomyelitis, meningitis and others) occurs.
