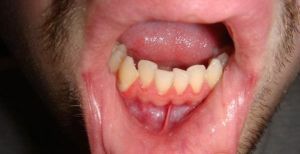
 Atrophic gingivitis is a chronic disease of the mouth, characterized by a decrease in the volume of gum tissue. The peculiarity of this pathology is that it is not accompanied by obvious signs of the inflammatory process.
Atrophic gingivitis is a chronic disease of the mouth, characterized by a decrease in the volume of gum tissue. The peculiarity of this pathology is that it is not accompanied by obvious signs of the inflammatory process.
In most cases, this form of gingivitis develops against other diseases. Treatment of the disease involves the elimination of provoking factors and the use of drugs that suppress inflammatory foci.
Contents
- Unpleasant acquaintance of
- What causes the development of the disease?
- Clinical picture
- Diagnostic measures
- Medical care
- Conservative therapy
- Surgical intervention
- Traditional medicine
- Consequences and prevention
Unpleasant acquaintance
Atrophic gingivitis is a chronic form of the disease. With such a violation, there is a sharp decrease in the volume of the gum( atrophy), caused by dystrophic changes in the epithelium of the tissues that surround the teeth.
As the disease develops, the following occurs:
- , the interdental papillae disappear;
- the tooth roots are exposed.
The disease leads to an increase in the sensitivity of teeth when exposed to external stimuli( cold, heat, etc.).Pathology is more common in men aged 60 years and older. In women, gingivitis is diagnosed less often.
The destructive process affects either the gums along their entire length, or is localized in the region of symmetrical teeth.
What triggers the development of the disease?
Atrophic gingivitis in most cases develops against a background of poor oral hygiene, resulting in plaque and caries forming on the teeth, and a stone accumulates. In addition, in medical practice, it is considered that the pathology under consideration arises for the following reasons.
Internal factors:
- diabetes;
- is an inflammatory process that affects internal organs;
- disruption of hormonal balance caused by treatment of malignant tumors;
- metabolic malfunction;
- cardiac pathologies, including circulatory system dysfunction;
- decreased immune defense of the body;
- frequent allergic reactions;
- tuberculosis;
- stresses, psychological diseases;
- vitamin deficiency.
External causes:
- trauma to the gingival tissues;
- exposure to chemicals;
- poor-quality oral cavity treatment.
Providing atrophic gingivitis may cause bad habits. In particular, smoking plays an important role in this. In addition, the disease sometimes occurs as a complication of congenital anomalies in the form, for example, of powerful gingival ligaments.
It is important to understand that the atrophic form of the disease is, in fact, the last stage of the development of the inflammatory process, which can still be reversed. In the future, the lesion area only increases and other tissues are affected.
Atrophic gingivitis occurs in one of two forms:
- Restricted .It is characterized by a local lesion of the gum tissue followed by its exposure to 1-2 teeth. The structure around the incisors, canines and premolars is mainly broken.
- Generalized( Diffuse) .The disease affects the entire gum tissue. The latter gradually loses its volume, the papillae atrophy, and the distance between the teeth increases.
Any of the above reasons can provoke the appearance of both a limited and generalized form of the atrophic process.
Clinical picture of
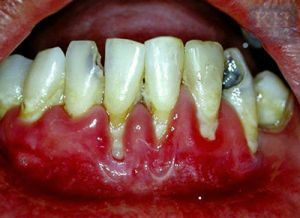
 With the development of atrophic gingivitis, the gingivitis acquires a pale pink shade, bleeding is also observed, which is intensified when cleaning the teeth, and an inflammatory process, but the last two symptoms may be absent.
With the development of atrophic gingivitis, the gingivitis acquires a pale pink shade, bleeding is also observed, which is intensified when cleaning the teeth, and an inflammatory process, but the last two symptoms may be absent.
Due to the reduced volume of tissue in the oral cavity, V-shaped areas are formed. Later, the gums become denser, due to which it becomes visually thick. However, in fact, the tissue continues to atrophy.
Chewing food is becoming more difficult because of the itching inside the gums. Some patients experience an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees.
Among the signs that indicate the course of the pathology, include the following phenomena:
- overflow of blood vessels lying in the gum;
- appearance of edema in the oral cavity;
- presence of soft plaque;
- solid deposits appear on the surface of the teeth.
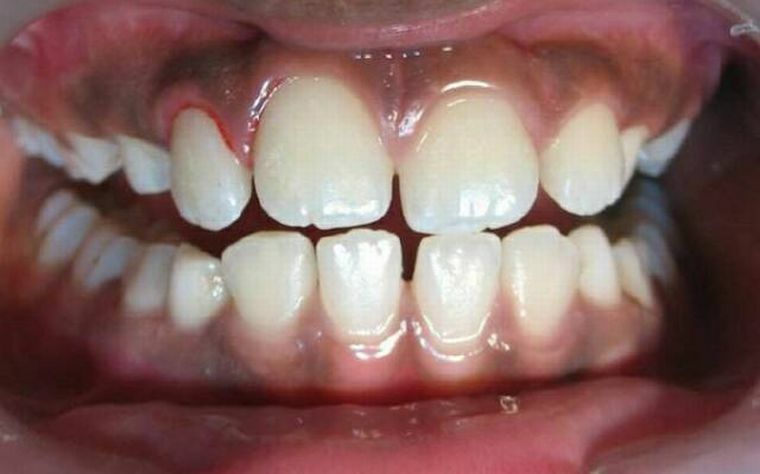
The photo is an impartial picture of what atrophic gingivitis looks like in the life of
Because of the fact that the disease leads to a decrease in the gingival volume and exposure of the roots of the teeth, the latter increases sensitivity to various stimuli. Progression of pathology contributes to the increase of the interdental space, in which pieces of food get stuck. Those, in turn, are a nutrient microflora for the propagation of pathogenic microorganisms, which further worsens the course of gingivitis.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostics involves collecting information during a patient's survey and examining the oral cavity by the dentist( orthodontist).First of all, the specialist draws attention to the condition of the gums around all the teeth, noting the presence / absence of a characteristic plaque.
In the course of diagnosis, a sensing method is used to determine the degree of bleeding gums. Through it, you can also assess the state of the joint teeth. In addition, the dentist analyzes the mobility of the latter and finds out the presence of gingival pockets.
At the end of these procedures, a periodontist is made up. In addition, X-rays are prescribed, through which the condition of bone tissue is checked, and microbiological examination. It is carried out with the goal of excluding other pathologies that have similar symptoms: periodontitis, periodontitis and others.
Other diagnostic measures are possible and examination by an endocrinologist with a gastroenterologist.
Medical care
Atrophic gingivitis often occurs on the background of other diseases, so its treatment is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of patients.
An individual treatment regimen is developed for each patient. It includes activities aimed at strengthening the immune system and eliminating the factors that provoke the disease.
In the treatment of gum atrophy three directions are used.
Conservative therapy
It includes a number of procedures:
- removal from the teeth of soft plaque and solid deposits;
- treatment of caries;
- installation of new implants if necessary;
- fluoridation of bare teeth;
- treatment of damaged teeth with products containing minerals and special oils;
- light therapy, electrophoresis, phytotherapy;
- gum massage.
Conservative therapy necessarily includes the use of medicinal ointments and gels:
- Holisal .Has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Helps eliminate pain syndrome.
- Solcoseryl .Promotes rapid wound healing and locally improves blood flow.
- Asepta- gel .Has anti-inflammatory effect.
- Asset asset .Also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Surgical intervention
It is used only in neglected cases or in the absence of a positive effect of conservative therapy. Treatment is carried out by means of gingivoplasty. It involves a full sanation of the oral cavity, after which the affected tissue of the cavity is superimposed with its own tissue.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine methods can only supplement the basic therapy, but can not replace it. For the treatment of gum atrophy, the following remedies are suitable:
- The first recipe for .2 tablespoonsPine needles are poured into a glass of boiling water, after which they are put on fire for several minutes. The solution is infused for 40 minutes, and then taken 2-3 times a day in an amount of 50 ml. This remedy helps to destroy germs.
- The second recipe is .Mix 4 portions of oregano and St. John's wort with 7 portions of peppermint.3 tablespoonsof the resulting composition is poured into 300 ml of boiling water. Next, the preparation is cooked over low heat for 30 minutes and infused for 4 hours. The broth is used to rinse the mouth.
Consequences and prevention
 Modern medicine can not completely cure atrophic gingivitis. A positive outcome is observed if treatment begins with the appearance of the first symptoms of pathology.
Modern medicine can not completely cure atrophic gingivitis. A positive outcome is observed if treatment begins with the appearance of the first symptoms of pathology.
Prevention of the disease requires regular hygiene of the oral cavity, during which special toothpaste is used, which prevents bleeding.
It is also necessary to choose the right brush: it should not injure the gum. In addition, regular measures should be taken to strengthen the immune system and stop smoking.
