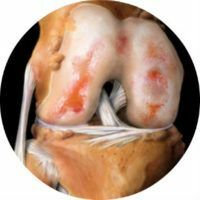
Osteoarthritis( gonarthrosis, osteoarthrosis) of the knee is a disease that is accompanied by dystrophic changes in the tissues of the hyaline cartilage, a decrease in functions and deformation of the bone articulation. The most common disease among all joint injuries and appears mainly in older people, but can also occur among young people. The pathology without timely treatment leads to irreversible and unpleasant consequences, therefore at the first symptoms of the disease it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo a recommended course of therapy.
- reasons
- Symptoms
- Types
- Rheumatoid
- deforming
- Posttraumatic( traumatic)
- patellofemoral
- Degrees
- How dangerous
- Disability
- Disability Groups
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Drug
- Operation
- LFK
- Physiotherapy
- Power
- Massage
- Knee
- Folkfunds
- Treatment for Bubnovsky
- In children
- Prevention
Causes
Primary form of the disease according tois due to congenital defects in the knee joint, is accompanied by an incorrect formation of its surface, which subsequently leads to degenerative changes. To develop such an arthrosis begins with childhood, sometimes in adolescence.
Also the cause of the development of the primary form is natural aging - the older a person is, the higher his risk of developing osteoarthritis. This is due to the fact that with age, the cartilage's ability to restore and regenerate decreases, and the local metabolism deteriorates. So in the interval from 45 to 65 years, pathology appears in 30% of the population, and from 65 to 85 years - in 80%.
Secondary form of the disease may occur for the following reasons:
- Injuries to ( bruises, fractures and dislocations of the knee).Quite often, leg fractures and dislocations of the knee joint lead to the fact that the knee begins to lose its original shape, a little deformed and stops fully bending. Such changes are accompanied by worsening of the blood circulation of articulations of the joint and development of stagnant phenomena, as a result of which the mechanism of the development of the disease is triggered.
- Damage to the meniscus - their tearing, jamming or tearing, which is accompanied by "wedging" of the knee, also contributes to the arthrosis of the joint, especially if the "jamming" was not quickly eliminated and dragged on for a long time.
- The operation to remove the meniscus disrupts the structural integrity of the knee joint, and it begins to wear out quickly.
- Large load on the legs .Basically, this applies to athletes and people whose profession makes them constantly on their feet.
- Arthritis ( inflammation of the joint).A long-lasting inflammatory process leads to the formation of a fluid in the joint cavity and this is complicated by arthrosis.
- Large body weight .With excess weight, a greater burden falls on the knee joints, provoking or intensifying zabolevanie.
- Metabolic disorders leads to accumulation of salts in knee joints.
- Hormonal changes in significantly affect the degenerative processes of cartilage and connective tissue.
- Spasm of the muscles of the anterior surface of the thigh is a combined spasm of the rectus and ilio-lumbar muscles.
- Psychological trauma ( negative experiences, stresses).There are cases when patients begin to complain about the appearance of pain in the knee joints after some experiences, for example, a divorce, death of a loved one, dismissal and so on. Also, the disease often accompanies people who are constantly depressed and unhappy with their life, consider it bleak, gray and meaningless.
Symptoms of
For arthrosis of the knee joint:
- stiffness in the joint;
- difficulty walking;
- irritation and burning when climbing the stairs;
- pain after prolonged walking or prolonged standing;
- crunching in the knees;
- uncomfortable sensations in the joint, mostly after waking up and trying to get up after a long sitting;
- limitation of mobility during flexion and extension;
- weakness in the legs.
The main symptom of gonarthrosis is pain in the knee area. At the same time the disease does not appear abruptly, painful sensations increase for many months and even years. At first the pains are disturbed only with strong loads on the legs, and then at rest.
Species
to contents ^Rheumatoid
Autoimmune lesion of articulations of joints, as it progresses, their destruction and deformation occur. Degenerative changes can affect bones, cartilage and even soft tissue, which leads to irreversible processes. With severe tissue destruction, osteoarthritis is formed, which is accompanied by impaired motor functions.
Inflammation occurs due to the fact that the tissues of the joints are perceived by the body as foreign, which leads to their destruction by killer cells. Rheumatoid arthrosis is accompanied by lack of mobility of the joints, especially after sleep, swelling and redness of the affected area, constant soreness, which increases with loads and movements.
to contents ^Deforming
The disease is chronic and is accompanied in most cases by irreversible changes. In pathology, the connection of the joint state with the deficiency of chondroitin particles is noted. With reduction of chondrocytes to a minimum, the cartilage is thinned, broken and cracked. The process becomes worse with time, which affects the condition of the adjacent bones.
Post traumatic( traumatic)
Develops due to frequent knee injury or severe mechanical damage. It can be a dislocation, fracture of the knee, pinching, tearing, tearing of the meniscus with jamming of the knee joint, damage to the ligamentous apparatus and cartilage.
Minor and minor injuries rarely cause serious problems, but they can lead to the development of avascular( aseptic) necrosis of the condyle of the tibia and thigh. Changes in the joint appear after a lapse of 5-6 years after the injury, in rare cases before - in 2-3 months.
Patellofemoral
In most cases, arthrosis begins with the patellofemoral syndrome. It develops because of excessive loads or traumas. Symptoms of this form are the following: pain on the front side of the knee joint, increasing with additional load( running, descending or climbing stairs, jumping, squats, etc.), pain in sitting position and bent legs. As a rule, the patellofemoral form of arthrosis proceeds without inflammatory processes, and with timely diagnosis it is quickly cured and does not lead to negative consequences.
to contents ^Degrees
There are 3 degrees of arthrosis:
- 1 degree - deformity of the knee joint is absent, but the connective tissue can be slightly swollen due to the accumulation of pathological fluid in the knee. It is characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the joint, minor changes in the tissue of the articular cartilage, moderate restrictions of movements, fatigue of the limb, a slight crunch is possible. Pain sensations appear in the morning after waking up;at the beginning of walking or after a long load. At rest and with minor loads, pain is absent. The treatment is mainly aimed at reducing the load on the joint( body mass correction), as well as the massage of the diseased knee and exercise therapy.
- 2 degree - degenerative changes in articular cartilage are observed. X-ray image shows bony marginal proliferation and narrowed articular fissure. This stage is characterized by pain almost every time it moves, more after prolonged exertion( walking, wearing of small weights), muscle hypotrophy, deformation of the joint, crunching in the knee during movement, lameness also appears.
- 3 degree - the heaviest, having a pronounced symptomatology. Almost on the entire affected area of the knee there is no cartilage. There is also severe bone sclerosis, a lot of osteophytes and a sharp narrowing of the joint gap. Perhaps the formation of a joint cavity chondromes( loose bodies).The stage is characterized by severe pain not only during movement, but also at rest, there is a reaction to changes in weather conditions, the mobility of the joint is reduced to a minimum. It becomes difficult for a patient to find a comfortable position in bed, put his feet so that his knees do not ache. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated, sometimes the knee joint needs replacement.
Than
is dangerous. Uncontrolled progressive arthrosis eventually leads to:
- limitation of the motor ability of the leg in the knee joint;
- aesthetic deformation of the legs at the site of inflammation;
- full loss of health, further disability.
Disability
With the diagnosis of arthrosis, disability is formalized after a medical and social examination in the health facility at the place of residence.
Reasons for disability:
- Progressive arthrosis of both knee joints is at least 2 stages.
- Deforming arthrosis of one or two knee joints in 3 stages, with shortening and ankylosis of the limb.
- One-sided or bilateral endoprosthetics, which provoked the development of severe disorders.
Disability groups
- The first group is given to those who have completely impaired motor activity. Persons with disabilities in Group I can not walk, sit, stand, and so on. Usually this is observed in patients on stage 3 of the disease.
- The second group is given to patients whose motor function is partially lost, that is, a person is able to move, but in most cases he needs help from the outside.
- The third group is assigned to patients with moderately severe or minor limitations of joint function. This means that a person can move independently, but with a lower speed and stops for rest.
Diagnosis
The doctor may suspect arthrosis of the knee joint during examination and conversation with the patient. However, additional studies are needed to confirm the diagnosis:
- X-ray - allows to assess the degree of destruction of cartilage and determine the stage of the disease.
- Ultrasound is a method of studying soft tissues, in which it is possible to detect the accumulation of fluid in the joint bag, which is not available to the X-ray machine.
- Arthroscopy is the diagnostic method used only in severe cases. During the procedure, above the knee joint, a cut is made, into which a mini-camera is inserted with a lighting device. The tool allows you to see cartilage, bones and determine from within the changes of surrounding tissues.
- MRI is a method that allows you to notice the slightest deformations in the knee joint, when still external signs of the disease are not pronounced.
Treatment of
Knee therapy affected by arthrosis is performed by a complex of medical measures, which consists of medical treatment, massage, physiotherapy and so on.
to table of contents ^Medicated
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroid drugs are used to reduce pain and inflammation in the joint. Appointed drugs Avertal, Diclofenac, Nimulide, Naise, Nimesil, Butadion, Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen, Orcerin and others. However, long-term use is not recommended, as they have many side effects.
- Hormonal medications are prescribed in short courses when NSAIDs are ineffective. They refer to the preparations of "heavy artillery" and help to quickly eliminate pain, remove swelling and inflammation of surrounding tissues. Frequently used medicines include: Diprospan, Hydrocortisone, Kenalog, Flosteron, Celeston. The funds are injected into the articular cleft no more than once in 10 days.
- Ointments and creams - contribute to reducing pain. In most cases, warming ointments are prescribed to increase blood circulation in the affected joint. Effective are Gevkamen, Menovazin, Nikofleks, Espol and others. If arthrosis is accompanied by a synovitis( inflammation of the inner shell of the joint with the formation of a liquid in it), then appoint Dolgit, Voltaren-gel, Fastum-gel.
- Chondroprotectors - restore the damaged structure of articular cartilage and are considered the most effective in the treatment of 1-2 degrees of arthrosis. Glucosamine triggers a natural mechanism of cartilage regeneration, thereby preventing its destruction. Chondroitin sulfate - neutralizes enzymes that corrode cartilaginous tissue and stimulates the growth of the protein collagen. To achieve therapeutic results, it is necessary to use glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate in the complex and courses( 2-3 times per year).In the pharmacy network, chondroitin sulfate is presented: in ampoules for injections( Artradol, Mukosat, Hondrolon, Hondrogard, etc.), in tablets( Structum, Chondroxide, Chondroitin), ointments and gels( chondroitin, chondroxite).Glucosamine can be purchased in ampoules( Don, Elbon), capsules and powders( Ellastanga, Stopartrose and others), gel( Ellastang and so on).There are also combined preparations containing glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate - tablets and capsules( Teraflex, Solgar, Arthra, Alflutop and others), cream( Honda).
- Vasodilators - eliminate vascular pain, relieve spasm in small vessels, improve the delivery of nutrients and blood supply to the joint. These include: Agapurin, Theonikol, Trental, Pentoxifylline, Xanthinolnikotinate, Vasonide Retard. The drugs are used in conjunction with chondroprotectors.
- Muscle relaxants are medicines that are used to eliminate muscle spasm. Most often appointed: Sirdalud, Midokalm.
- Selective anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate inflammation and pain. Preparations are much less likely to produce negative side effects, practically do not cause side effects and do not adversely affect the structure of the articular cartilage. They can be taken for a long time. Assign: Movalis, Meloksikam, Movasin, Amelotex and others.
- Hyaluronic acid is effective at the initial stage of the disease, reduces the abrasion of cartilage surfaces. The medication is administered intra-articularly, most importantly, the acid does not penetrate into the bloodstream, since there is a risk of embolic complications. Often the prescribed drugs are: Fermatron, Ostenil and others.
- Vitamins reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease and bring about a recovery after the inflammation in the joints subsides. With arthrosis prescribe vitamins C, B3( nicotinic acid), B5, E. They include Milgamma and others.
- Compresses - relieve the inflammatory process in the joint. For the procedure it is recommended to use Dimexide, Medical bile, Bishofit.
Operation
Operative treatment is resorted to if neither physical nor medication therapy brings relief.
- Endoprosthetics - replacement of the knee joint. Carried out at the last stage of the disease, and this operation is the only measure that will help improve the patient's condition. There are no age limitations to endoprosthetics, but mostly it is carried out by patients from 50 to 70 years. During the operation, the affected joint is replaced by an artificial joint, which consists of polymers and metal. The prosthesis can be partial or complete, it serves for 15-20 years. Operative treatment is under general anesthesia. After 24 hours the patient can move with crutches, after 5-7 days they are discharged from the hospital. The whole period of rehabilitation takes 2-3 months.
- Artrodes. During the operation, remove all joint components and connect the bones to each other. The joined bones subsequently fuse due to the bone callus, as a result of which the joint ceases to exist. The rehabilitation period lasts several months, during which the operated area is immobilized with plaster casts.
- Synovectomy ( removal of the synovial membrane) is an operative treatment in which the doctor performs all manipulations through microprojections. During the operation, the synovial membrane is removed from the joint cavity, which provokes the inflammatory process. Upon completion, the joint is washed with saline solution. Indications for synovectomy are: damage to ligaments, articular membranes, cartilage, meniscus rupture. At the 3 stages of the disease, when almost the entire joint is destroyed, this procedure is ineffective.
- Arthroplasty .It is shown for incomplete destruction of articular cartilage and bone surfaces. During arthroplasty remove all damaged and dead tissue, after which the defects are covered or filled with biological material - the cartilage tissue or skin of the patient( donor).Thanks to the operation, joints in the joint can be stopped and its function restored.
LFK
Therapeutic gymnastics means a measured, slow exercise, excluding squats, bouncing, twisting of the joint. It is recommended to exercise LFK, lying or sitting, for 20 minutes, repeating each exercise 10 times.
The main tasks of gymnastics are: relaxation of muscle spasm, causing pain, slowing the progression of the disease, increasing blood supply to the joint and preventing further destruction of the cartilage. During exacerbation of the disease, exercise is contraindicated.
In addition to exercise therapy, the best kinds of sporting exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint are aqua aerobics and swimming.
to the table of contents ^Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures help accelerate recovery, but they are not allowed to be used during the acute period of the disease.
- Magnetotherapy .The effect of electromagnetic radiation removes edema and inflammation of tissues, promotes the acceleration of metabolic processes in cells, stimulates blood circulation and promotes the rapid restoration of the damaged joint. The duration of the course is 10-15 procedures. The physiotherapy is carried out daily or every other day for 15 minutes each.
- Ultraviolet irradiation - has a pronounced bactericidal action( eliminates pathogenic microorganisms) and stimulates local protective properties of tissues. It is carried out with the help of special lamps on the site of the inflamed joint. Duration of the course is 5-10 procedures for 3-10 minutes.
- Laser therapy. Radiation improves microcirculation in the area of the inflamed joint, stimulates local immunity and accelerates regenerative processes in the affected tissues. The course of therapy - 5-7 procedures lasting for 5-20 minutes.
- Phonophoresis with hydrocortisone. On the skin in the region of the affected knee joint, apply an oily ointment Hydrocartisone and rub it for 3-5 minutes, then this section is exposed to the ultrasound wave emitter. The procedure promotes the improvement of microcirculation, the acceleration of metabolic processes in tissues and the deep penetration of the drug, which has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Ultrahigh-frequency therapy( UHF). Exposure by high-frequency electromagnetic field promotes the expansion of blood vessels, which improves the flow of immune cells to the focus of the inflammatory process. In addition, UHF treatment stimulates the regeneration of cartilaginous tissue, which is necessary during the rehabilitation period. Course - 10-15 procedures lasting for 5-10 minutes.
- Diameter. Use of high-frequency current for heating fabrics. Under the influence of heat, the vessels expand, the blood flow improves, and the inflammatory process is removed. The course of 10 procedures.
Nutrition
The right diet is an important part of successful therapy for arthrosis.
Recommendations on nutrition:
- diet should be low-calorie;
- microelements, vitamins and other useful substances should be included in the diet in the required volume;
- is not allowed fasting and diets with large product restrictions;
- food should be fractional and frequent, up to 6 times a day;
- light snacks are allowed;
- food should be cooked, steamed or baked( frying is excluded);
- dinner must be no later than 18:00 hours or at least 3 hours before bedtime.
Prohibited products that adversely affect cartilaginous tissue:
- smoked meat and fatty meat contribute to weight gain, disrupt the activity of the stomach and intestines;
- Bulgarian peppers and tomatoes have the ability to bind chondroitin and collagen;
- Citrus fruits and cherries bind the mineral salts that are needed for bone tissue;
- coffee is flushed out of the body by calcium;
- sweets and flour products lead to an increase in weight, which means an extra burden on the knee joints;
- cigarettes and alcoholic beverages negatively affect the state of blood vessels and metabolic processes.
It is also necessary to exclude fast food, chips, crackers, mayonnaise, ketchup, ready-to-eat breakfasts, convenience foods and other harmful foods with flavor enhancers and preservatives.
Recommended products:
- lean poultry meat;
- black bread;
- fish( trout, mackerel, herring);
- butter;
- whey, natural yoghurt without sugar, kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese;
- greens( salad, parsley, dill);
- nuts( walnuts, cedar, hazelnuts);
- vegetables( zucchini, carrots, pumpkin, broccoli);
- pasta and bread from wholemeal flour;
- pomegranate juice;
- fruits( pineapples, apples, pears and so on);
- beans( beans, peas);
- cereals prepared on water;
- quail eggs and chicken eggs( no more than 2 per day).
Massage
It is recommended to use manual techniques during the period of convalescence, when acute inflammatory phenomena in the affected joint subsided. Also, massage can be used in the postoperative period to accelerate healing.
Massage has the following useful effects:
- improves nutrition( trophism) and microcirculation of tissues in the area of exposure;
- stimulates the removal of fluid from the joint cavity due to the acceleration of metabolic processes in tissues;
- warms up by filling blood with tissues;
- prevents the development of complications( ankylosis, contracture), which often cause mobility disorders in the joint.
Knee pads
In the treatment of arthrosis, knee pads and bandages are also used. They are of different types:
- Closed - are used when the diagnosis is not established and the origin of the pain sensations is unclear. They help to overcome the pain syndrome thanks to a large area of support for the knee.
- Open - prescribed for mild or episodic pain, for example, when descending or climbing the stairs.
- Joint - universal, are prescribed for post-traumatic arthrosis.
- Warm ( with halogen lamp, magnetic, mineral, woolen) - warm up the joint, relieve muscle strain, and anesthetize.
Folk remedies
Successfully used as an additional treatment. However, with knee arthrosis, folk medicine can be used only on the advice of a doctor, so as not to provoke the development of adverse reactions and complications.
- Infusion of calendula. Provides antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory action, promotes rapid healing of wounds and restoration of damaged tissues.1 tablespoon of flowers pour 250 milliliters of boiling water, leave to infuse in a dark place at room temperature for 2-3 hours. A means to filter and take inside 1 tablespoon( for adults) and 1 tea( for children) three times a day for 30 minutes before meals.
- Herbal infusion of St. John's wort. The composition of St. John's wort includes tannic substances( have anti-inflammatory effect), vitamins E and C( have an antioxidant effect), routine( increases the strength of the walls of blood vessels) and other useful substances.30-40 grams of crushed raw materials, put in a glass container and brew in 300 milliliters of boiling water. Let it brew in a dark place for 3-4 hours, then strain and take 1 tablespoon three times a day 20 minutes before meals.
- Compress of fresh leaves of cabbage. 2 fresh cabbage leaf to pass through a meat grinder, apply a lot of weight to the folded in several layers of gauze and attach to the sick joint for 2.5-3 hours, tying it with a handkerchief or a towel.
- Compress from the grass of mother-and-stepmother. 1 tablespoon of crushed raw material pour 250 milliliters of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. After cooling, moisten the gauze in the broth and apply it to the affected joint for 3-5 hours.
- Compress of nettle leaves. 1 tablespoon of the ground leaves of the plant, pour 300 ml of boiling water and insist 2-4 hours. Then impregnate the product with gauze and attach to the affected joint for 2-3 hours before going to bed.
Used for the treatment of the knee joint and warming compresses, for example, ozocerite, paraffin, sand, salt. However, the joints can be warmed up under the supervision of the doctor, since with incorrect use this method can lead to unpleasant consequences.
to the table of contents ^Treatment for Bubnovsky
For each patient, after an X-ray examination of the musculoskeletal system, an individual complex and schedule of physical therapy and kinesitherapy exercises are compiled. The patient may not use anesthetics at the same time and do not apply great physical effort, since the main load on himself takes the MTB simulator.
When performing exercises, special attention is paid to proper breathing, it is believed that without it it is impossible to achieve the desired result.
In parallel with gymnastics, the doctor recommends the following procedures:
- massage;
- steam room, sauna;
- swimming in the pool;
- cryosauna.
In children
In children, arthrosis in children may appear for the following reasons:
- joint dysplasia;
- injury;
- excess weight;
- disturbances in metabolic processes.
The most common cause of pediatric arthrosis is fractures, subluxations, distension. Post-traumatic period in most cases is accompanied by inflammation, which negatively affects the structure of the cartilaginous tissue, soft tissues and the quality of the joint fluid. Injuries can inflict great harm to children, since the damaged joint is deformed and can move relative to its natural position.
For the treatment of arthrosis in children, as in adults, according to the doctor's recommendations, they use:
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- medication;
- means of traditional medicine;
- surgery( in severe cases).
Prophylaxis of
To prevent the development of arthrosis, it is recommended that the following rules be observed:
- Move more, walk regularly, do warm-up after prolonged sitting. Motor activity and physical activity promote joint mobility, strengthen muscles and prevent injuries.
- Keep track of body weight. Excess weight is unacceptable for knee joints. Normalization of body weight will reduce the additional burden on the joints and prevent the development of arthrosis.
- Wear shoes with elastic soles on low heels.
- Avoid lifting weights. Do not wear a heavy load in one hand.
- Do not sit with your feet crossed. This position contributes to the curvature of knee joints.
- Timely pass preventive examinations.
